σw′ = 0.16 u ; this relationship is also developed from measurements at four different heights, as
indicated earlier). Kai further noted that the ratio of σw′ / u at the highest level (i.e., z = 29.5 m) is
slightly lower than those at levels z = 1.6 to 12.3 m.
Figure 5b shows the relation of σ u′ vs. u2m (the value of σ u′ is generated not from the
unidirectional sonic anemometer but from the hot-film anemometer). A linear relationship of
σ u′ = 0.35 u2m
(67)
represents the data rather well, but the increase of σ u′ with u2m is about 60% higher than the one
reported by Kai (i.e., σ u′ = 0.25 u ). This discrepancy might be due to the fact that σ u′ was mea-
sured from a hot-film anemometer (which is not as sensitive as the sonic anemometer) and the test
site is much less homogeneous than the one Kai used. Kai also points out that there seems to be
smaller scatter in σw′ than in the horizontal components σ u′ and σ v′ .
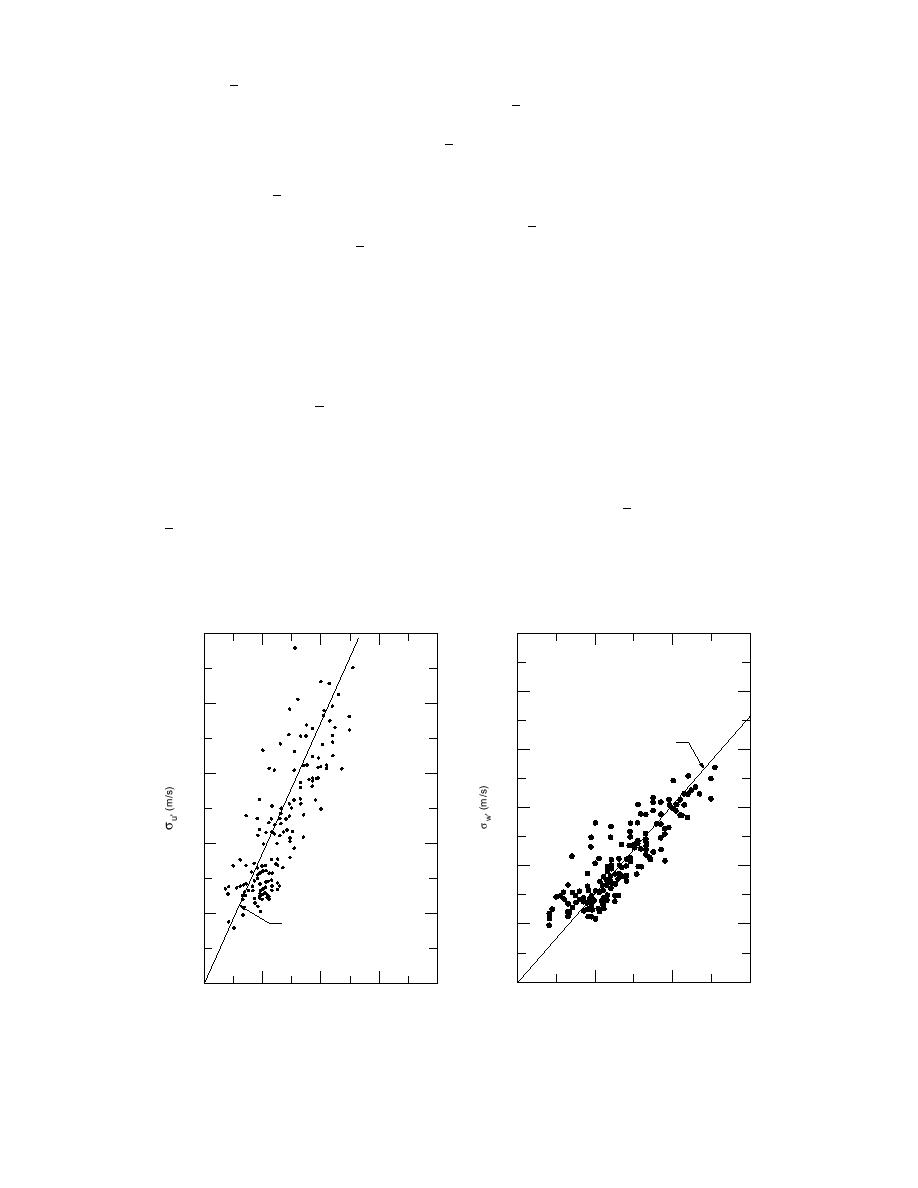
Figure 6a shows the variation of σ u′ (the horizontal component of the turbulent fluctuation)
with u* and can be represented by
σ u′ = 3.7 u* .
(68)
Like the case of σ u′ vs. u2m , this relation has a higher coefficient than the one presented by Kai
(i.e., σ u′ = 2.53 u* ). Figure 6b shows the variation of σw′ with u* and can be represented by
σw′ = 1.6 u* ,
(69)
which is nearly identical to the relation presented by Kai (i.e., σw′ = 1.58 u* ) covering the measure-
ment at four levels. As noted in Kai's paper, in both plots of σw′ vs. u* or u2m and σ u′ vs. u* or
u2m , the horizontal components σ u′ and σ v′ (in Kai's case) have a greater scatter than the vertical
component σw′ . The ratio of σ u′ / σw′ is about 2.33 in this study as compared with Kai's of 1.60.
The higher ratio of σ u′ / σw′ can be attributed to the inhomogeneity of the test site (the upwind
fetch length requirement was never met).
1.2
2.0
1.0
1.6
σ w' = 1.6 u
*
0.8
1.2
0.6
0.8
0.4
0.4
σu' = 3.7 u*
0.2
a.
b.
0
0
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
u (m /s)
u (m /s)
*
*
25




 Previous Page
Previous Page
