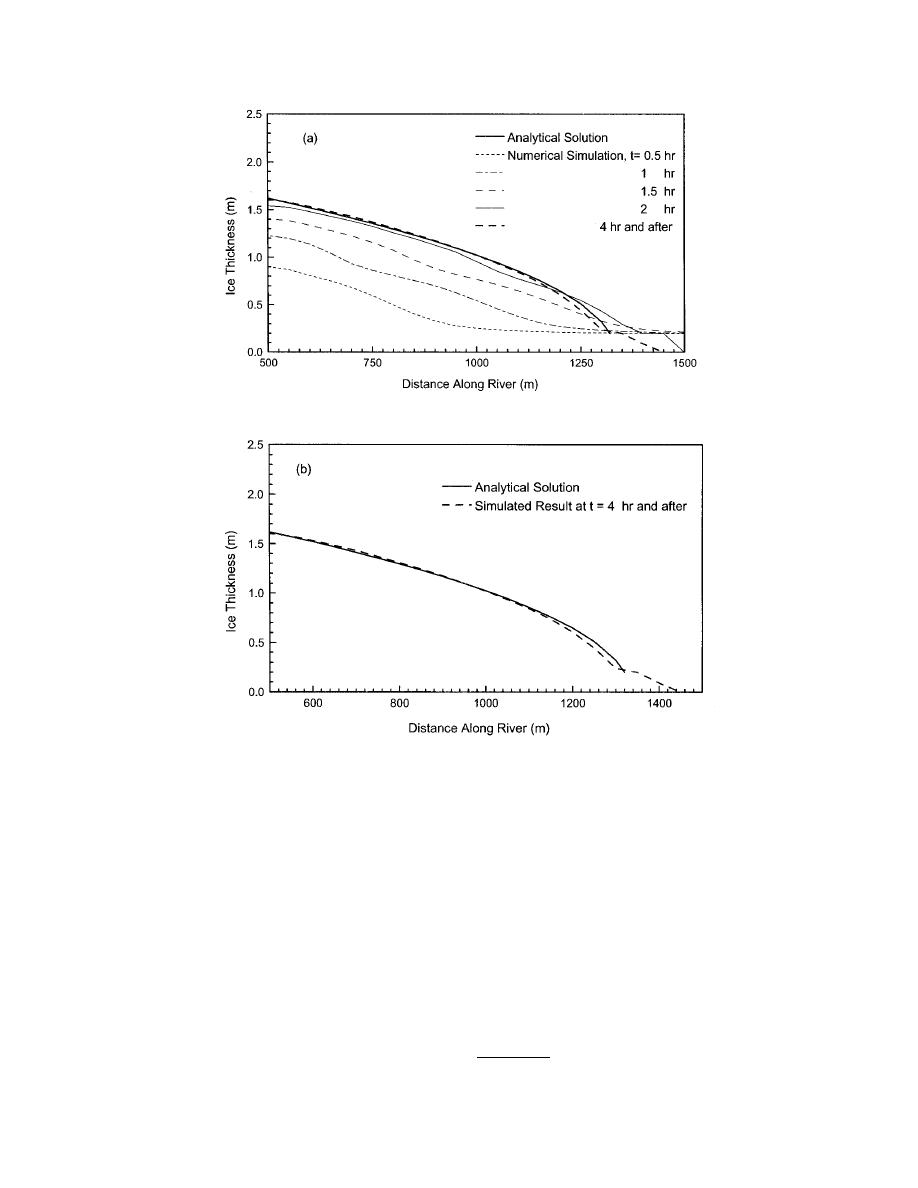
a. Simulated time-dependent evolution of ice jam profile.
b. Comparison of final jam profile with steady-state analytical solution.
Figure 8. Comparison of simulated jam profiles with the analytical solution
for the case with bank friction.
where σijc and Pc are critical values of σij and P,
RM 0 to 24, as well as the Mississippi River from St.
respectively. In addition, when the velocity of an ice
Louis to the mouth of the Missouri (RM 187195), with
parcel is less than 0.5 mm/s, the parcel is stopped. Using
cross sections about 300 m apart. Tuthill* developed
this method, we can simulated the static ice jam
the stagedischarge relationships using HEC-2
condition with the viscousplastic constitutive law.
simulations for the reach from the St. Louis gage up to
about RM 30 on the Missouri River (see Fig. 1 for a
Open water calibration for Missouri River
map of the confluence area). The HEC-2 model was
The model is calibrated for the open water condition
calibrated to flows in September 1994 at Hermann,
to determine the Manning's coefficient of the channel
Missouri, the corresponding observed water surface
bed so that the model can correctly simulate the current
elevations, and average velocity from USGS stream
velocity distribution and water surface slope. The
detailed geometry survey data provided by Kenneth
Balk & Associates, Inc., cover the Missouri River from
*Personal communication with A. Tuthill, CRREL, 1997.
13




 Previous Page
Previous Page
