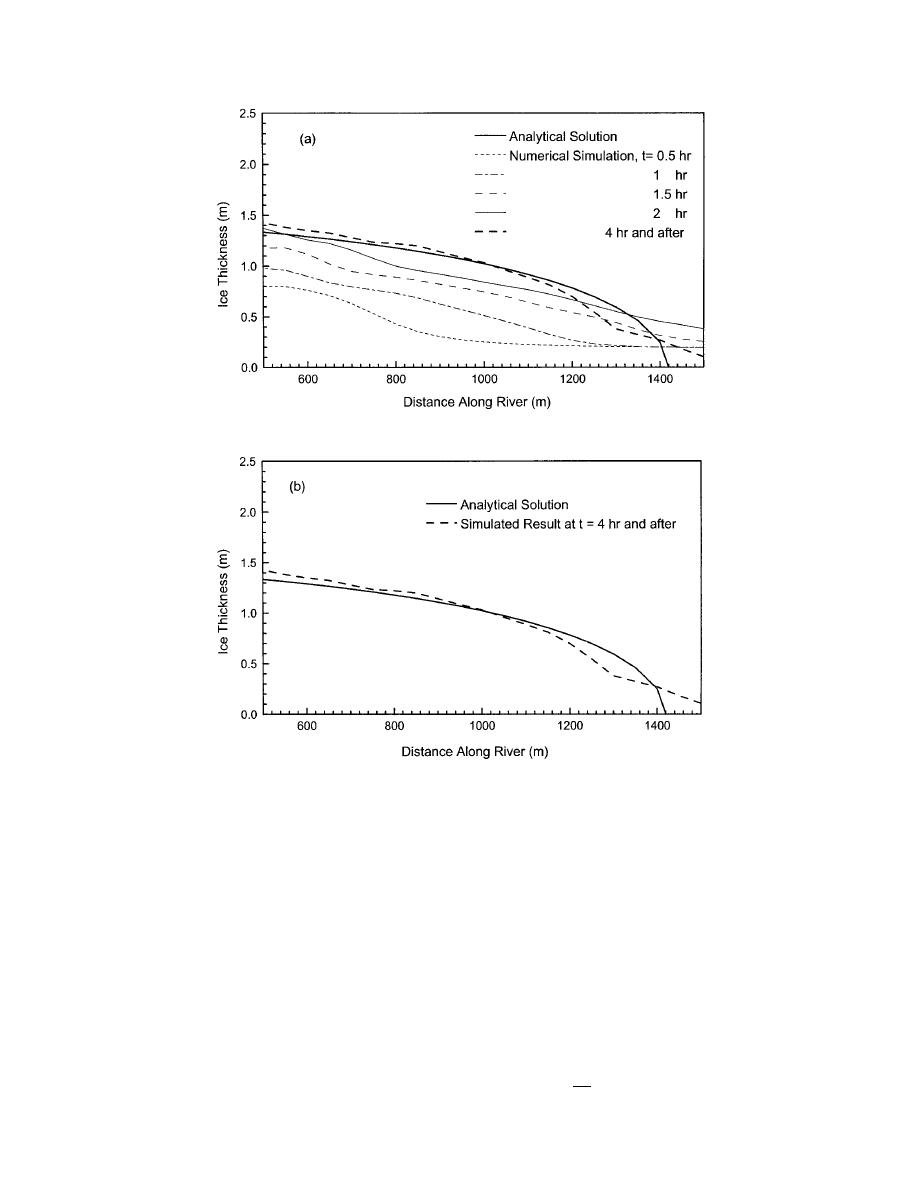
a. Simulated time-dependent evolution of ice jam profile.
b. Comparison of final jam profile with steady-state analytical solution.
Figure 7. Comparison of simulated jam profiles and the analytical solution
for the zero bank friction case.
The simulated result and analytical solution are
In this study, the constitutive law is modified for a small
compared in Figure 8. The simulated profile for t ≥ 4
strain rate condition to avoid these problems.
In the simulation, critical values of σij and P for
hours and the analytical solution are different because
the ice momentum was neglected in the analytical
each ice parcel were determined as the following
solution. Figure 9 presents two-dimensional plots
conditions are all satisfied: 1) ice parcel velocity is
showing the development of the ice thickness
smaller than a small critical value of 0.001 m/s, 2) ice
distribution upstream of the boom.
parcel velocity is smaller than the value in the previous
time step, and 3) δ =| ε1 - ε2 | is smaller than a very
Theoretically, the viscousplastic constitutive law
small value δc = 1 104s1. When these critical
cannot simulate static conditions correctly. For very
small strain rates, the viscosity becomes very large. In
conditions are reached, the following approximation is
numerical computations, a limiting value for is often
introduced to calculate ice stresses for the particular
used. This approximation changes the constitutive
ice parcel:
relationship to a linear viscous law and the shear stress
P
σij = σijc
approaches zero when the strain rate approaches zero.
(53)
Pc
12




 Previous Page
Previous Page
