A
Chord: 6.5 km
400
300
W
200
100
Basin IV
III
II
I
P
kqfj
uw
e
d
c
2.5
3
Lapse
2.0
1.5
2
1.0
0.5
1
0
2.5
4
Inversion
2.0
1.5
3
1.0
0.5
2
0
0
2
4
6
8
Projected Distance (km)
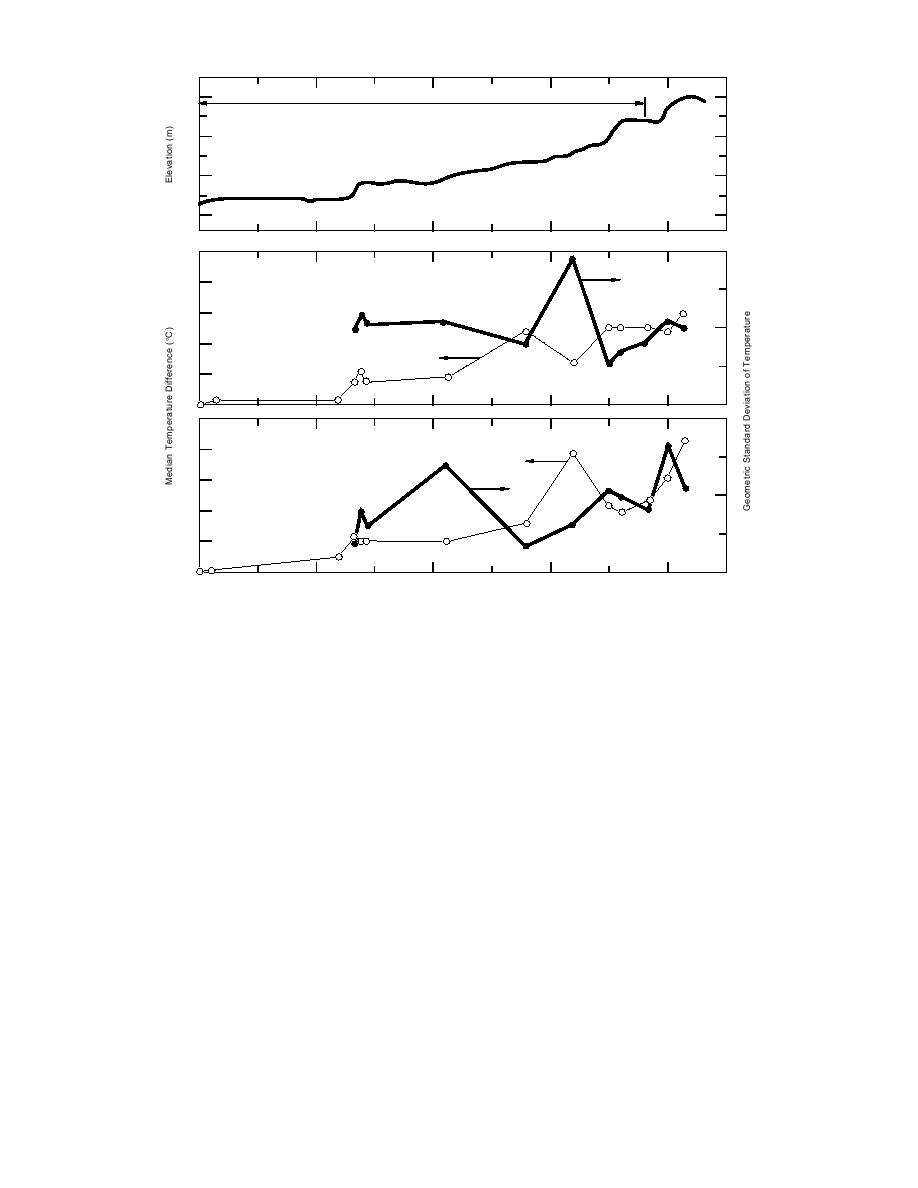
Figure 12. Median temperature difference and geometric standard deviation of temperature
difference along the path PWA. An exaggerated topographic cross section shows the slope in
the vicinity of each measuring point.
ference and GSD occurs at W. The inflections re-
An exaggerated elevation cross section along
verse under inversion. The largest absolute tem-
the observation path PWA of Figure 9 is shown
perature difference occurs at A, the apex of
in Figures 12 and 13. The distance between mea-
observations, under both lapse and inversion.
suring points has been conserved in the elevation
The 84th percentile of temperature difference,
projection of Figures 12 and 13. The coordinated
with respect to P, is shown in Figure 13. The
designators may be used to identify the points on
temperature differences shown are again the ab-
the figures, the maps, or in Parts I and III. Rhumb
solute difference in temperature with respect to
line distances between nonadjacent observation
that at the bridge P, as in the temperature differ-
points are best estimated from Figure 9.
ences along the river shown in Part I. The fre-
The median value of the absolute temperature
quency of lesser temperature at the point, with
difference, with respect to the temperature ob-
served at bridge P, at observation points along P
respect to P (i.e., the fraction of times that it is
colder at the point than at the bottom of the val-
WA, is plotted for lapse and inversion conditions
ley) is also shown for lapse and inversion. The
in Figure 12. The geometric standard deviation
temperature at A is not uniquely lesser than at P
(GSD) of the temperature differences are also plot-
under lapse conditions, as we have stratified our
ted. Note that the scales of GSD differ; systemati-
data on the temperature difference in the layer
cally greater GSD occurs with inversion structure.
WA. Under inversion conditions the air tempera-
The median temperature difference with respect
to P increases with elevation as expected under
ture at elevations near that of W are frequently
lapse, but an inflection in both temperature dif-
less than that at P, and the frequency of lesser
16




 Previous Page
Previous Page
