the freezing plate. Also, the sludge was too thick
be frozen as well as the surface area requirement.
to flow down the freezing plate.
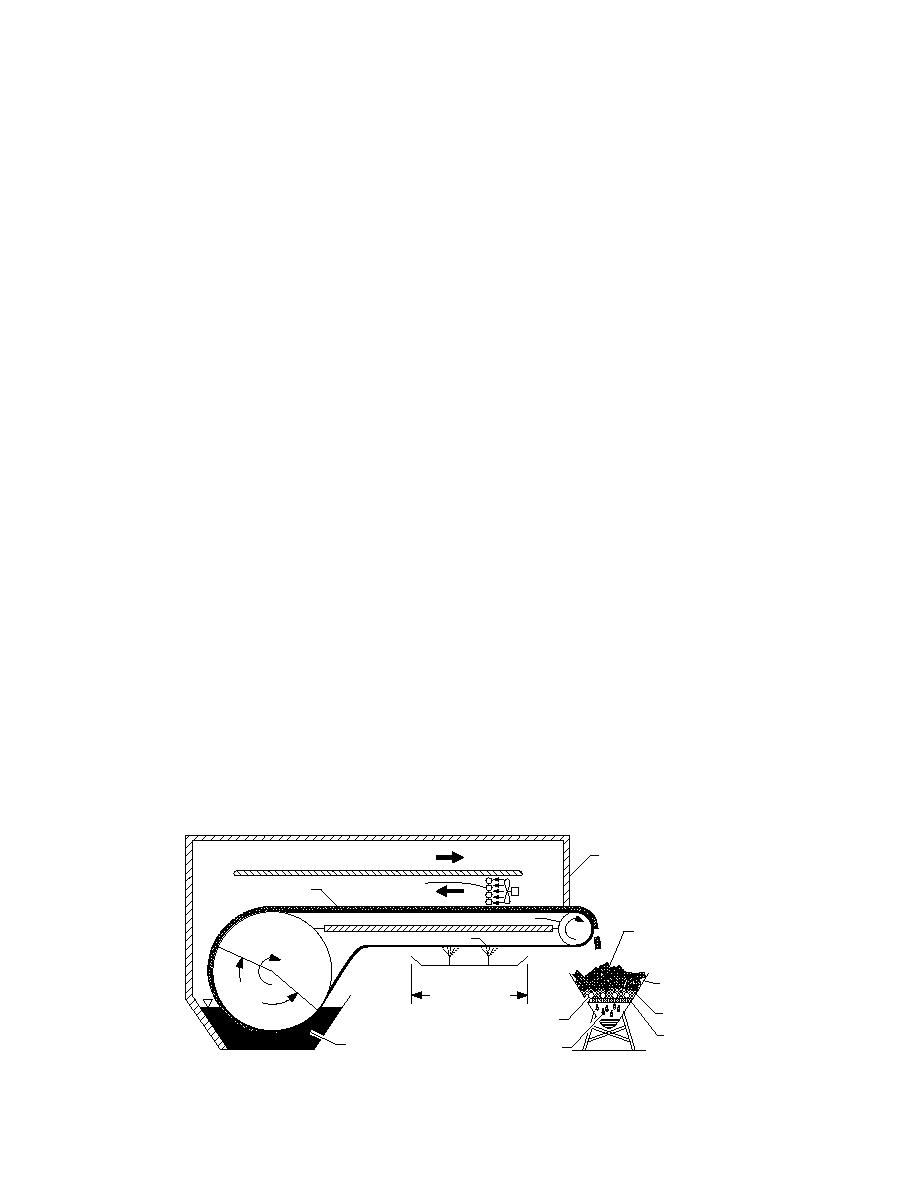
Another important function of the drum filter is
to attach the sludge to a flat surface in a uniform
thin layer. A uniform layer is needed in order to
Conclusions from literature review
The layer freezing method appears to offer the
ensure that the sludge is completely frozen by the
best chance for commercializing the freezethaw
time it exits the freezer.
conditioning process. It avoids the structural fail-
Operation of the device begins at the vacuum
ure problem common to bulk freezers and the ice
drum filter. A rotating drum, immersed in a con-
crystal/solid particle separation problem com-
stantly replenished vat of sludge, filters free
mon to freeze crystallizers. The large surface area
water through an attached cloth or metal belt. As
required by the layer freezing method is the main
the drum rotates, a layer of sludge builds up on
obstacle to overcome.
the belt. The thickness of the sludge layer will
In spite of the high cost of freezing, we believe
depend on the filtration characteristics of the
there is a niche for this process in conditioning
media, and the amount of vacuum applied. The
difficult sludges like alum and other hydroxide
filtrate is either returned to the head of the plant
sludges. Freezethaw conditioning is the only
or used in the washing section. After the belt
process that can transform these sludges from a
emerges from the vat, it enters the freezing cham-
thin pudding-like liquid into a granular material.
ber. The speed of the belt is controlled so that the
Dewatering this granular material is a simple
sludge layer is completely frozen by the time it
matter of decanting or filtering the meltwater. No
exits the chamber. The frozen sludge layer is then
polymers or further mechanical processing are
separated from the belt and discharged into a
needed. The granular nature of the final product
collection hopper. A heated roller may be needed
has an added benefit in that it can greatly facili-
to break the bond between the sludge and the
tate handling for both disposal and beneficial re-
belt. The frozen sludge layer is then thawed using
use. As a result, the overall cost of this method
the heat removed from the freezing chamber.
may be less than that for conventional methods
Meltwater produced during this thawing opera-
when disposal costs are included.
tion is collected and mixed with the filtrate from
the vacuum section. The remaining granular
solids are then transported to a storage area,
PROPOSED FREEZE SEPARATOR
landfill, or land application site. Meanwhile the
CONCEPT
belt continues on through a washing section
The proposed freeze-separator combines a
where any residual sludge particles are removed.
vacuum drum filter with a horizontal belt freezer.
The belt then reenters the vat and the cycle is
A sketch of the proposed freeze-separator device
repeated.
is shown in Figure 3. This device is patented (no.
As mentioned earlier, the main advantage of
5,202,039).
this design over other freezing devices is that
The purpose of the drum filter is to remove
much of the water is removed before freezing. As
most of the free water from the sludge before
a result, the energy required will be significantly
freezing. This will reduce the amount of sludge to
reduced. Another advantage is that it is a contin-
Insulated Freezing Chamber
Cold Air Return
Freezing Coil
Sludge Cake
Fan
Heated Roller
Crozen
F
Filter Cloth
hunks
Sludge Collection
H
Vacuum
F
opper
Washing Station
ilter
Granular Solids
Thawing
C
oils
Coarse Screen
Sludge
Meltwater
Figure 3. Conceptual sketch of freeze separator.
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
