Alaska
M
Coastal Route
GREENLAND
Bering
S
T id Route
ea
Oransit Route
C hS k c h i
u
ver-the Pole Route
ea
Provideniya
TH
P
S Mys
hmidta
Pevek
ARCTIC
OCEAN
st
S
Ea
n
ia
a d yr
NORWAY
er a
b
Si Se
0
60
SWEDEN
12
90
In
Barents
Laptev
e
Riv
Sea
FINLAND
Murmansk
ea
Magadan
Kara Sea
i ver
Tiksi
St. Petersburg
Nordvik
r
Dikson
Arkhangel'sk
Khatanga
O ea of
S
r
ek
Dudinka
khotsk
River
Salekhard
Noril'sk
0
500
E
Yakutsk
Yamburg
CL
Igarka
IR
C
Nautical Miles
R
IC
ARCT
0
1000
R
U
S
S
I
A
Kilometers
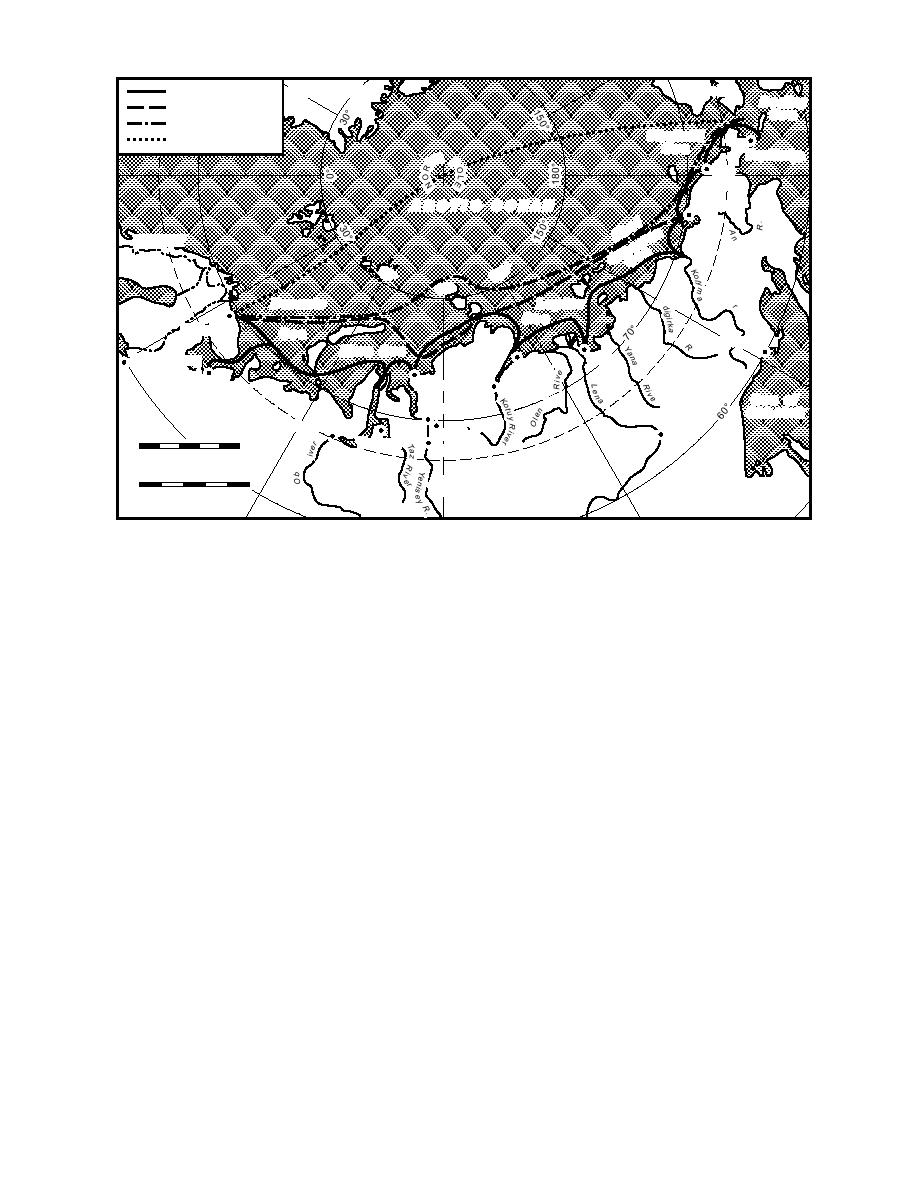
Figure 1. The various Northern Sea Route options.
eliminating all foreign traffic. Before 1991, the last
breakers since 1977. Year-round maintenance of
transit of the NSR by a foreign ship was in 1940.
the entire route is currently being promoted by the
However, in October of 1987, then-General Secre-
Russians as a way of bringing hard currency into
tary Mikhail Gorbachev announced a new spirit
the country. The shorter shipping route might serve
of cooperation in Arctic regions. As one item on
to open the entire northern region to increased
the agenda, he proposed opening the Northern
economic development, foreign trade, and tour-
Sea Route, with certain restrictions, to all foreign
ism.
vessels for peaceful and commercial purposes. This
The shift from socialism to a privatized, mar-
landmark change of policy was the first step in the
ket-driven economy in the Soviet Union that be-
privatization of Russia's Arctic fleet. Important
gan around 1985 resulted in economic and social
assets, the NSR and the northern fleet continue to
disruption. The problems were compounded in
be promoted for bringing foreign currency into
1991 with the transformation of the Soviet Union
the country by "selling" premiere Russian ice navi-
into the Commonwealth of Independent States
gation capabilities to the world. The Russians have
(CIS). One way to address these problems may lie
proposed the following ways of employing their
in the Commonwealth's ability to stimulate do-
Arctic fleet to raise foreign capital:
mestic growth and attract foreign trade. Although
Escorting foreign ships along the route with
it was fortunate that authority over the entire NSR
Russian icebreakers,
transferred intact to the new Russian Federation,
Transporting foreign goods aboard Russian
inexperience with free enterprise and reduced state
ice-strengthened cargo ships,
subsidies have resulted in unemployment and ex-
Encouraging the export and coastal move-
cess capacity in all sectors of the economy, includ-
ment of Russian goods in foreign ships,
ing the Arctic marine transportation system.
Historically, the USSR claimed that crucial sec-
Employing idle Russian icebreakers and
cargo vessels in the U.S. and Canadian Arc-
tions of the Northern Sea Route passed through
tic,
its sovereign waters and they guarded these care-
Promoting Arctic tourism.
fully from incursion by foreign vessels, effectively
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
