Navigation
Period
-- 2.0 -- Isoline and Maximum Velocity
(knots)
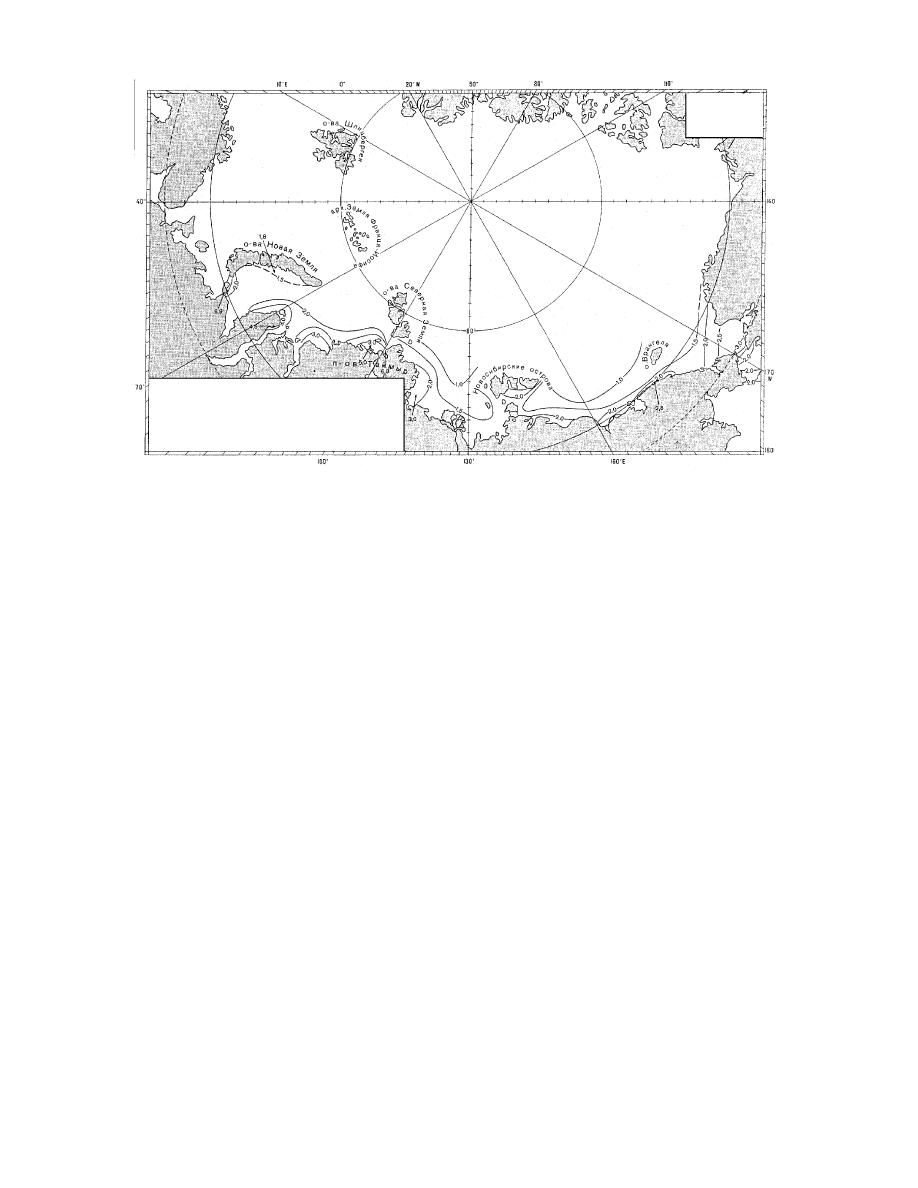
Figure 22. General scheme and maximum velocities of summary currents near the ocean surface (010 m
deep). Summary currents are the resultant combination of all local currents (i.e., tidal current, wind-
driven current, permanent current, etc.). (Translated from RSMOT, in prep.)
any season of the year, but their occurrence reaches
mum currents in the narrowest section of the strait
a maximum during July and August.
due to semidiurnal tides are about 2.5 kn, while
The Matochkin Shar Strait, currently closed to
currents due to northeast winds can reach 4.5 kn,
foreign vessels, is approximately 55 nm long, and
which can interrupt the tidal current. Figure 22
trends west to east from the Barents to the Kara
shows the general scheme of summary current
Sea. The strait cuts between the high mountains
velocities along the northern Russian coastline.
of the northern and southern main islands of
Though highly variable, the mean date for ice
Novaya Zemlya and is only a mile wide on aver-
breakup in the strait is June 28, and for the end of
age. Depths are very irregular throughout, but
the navigation season it is November 23.
the minimum fairway depth of 12 m is found near
Karskiye Varota, commonly referred to as the
the western end. Due to high intervening moun-
Kara Gate, is the most often-used passage from
tains, the weather conditions at the west end of
the Barents to the Kara Sea. It is approximately 18
the strait can be very different from those at its
nm long and also trends in a southwest-to-north-
eastern end. Ice conditions, though usually mild
easterly direction. Due to many islands, islets, and
at the western end, can be severe during east winds
submerged obstacles, its fairway is reduced to less
at the Kara Sea entrance due to the presence of
than 14 nm wide at its narrowest point. Surface
the Novaya Zemlya massif. Tidal currents are
currents trend from the Barents toward the Kara
quite regular, averaging about 2 kn, and revers-
at a rate of 0.5 to 1 kn, but with a southwest wind
ing direction every 6 hours. In the narrowest
they can reach 2 kn. Tidal currents are greatest in
sections of the strait these currents can reach 3.5
the western end of the strait, where they can reach
to 5 kn. Winds can affect the period and direction
2.5 kn; they decrease in the middle section to as
of the currents so that a change in regularity of
little as 0.5 to 0.75 kn. Ice conditions are highly
the currents is an indication of the winds to be
dependent on those in the adjacent waters of the
expected.
Kara Sea; northwest winds can quickly move the
The Vil'kitskogo Strait, a west-to-east trending
Novaya Zemlya ice massif in to block the east
strait from the Kara to the Laptev Sea, is approxi-
entrance. Heavy fogs and poor visibility are fre-
mately 60 nm long and 30 nm wide at its narrow-
quent throughout the archipelago region during
34




 Previous Page
Previous Page
