snow, reflected in the hardening table, has the great-
est influence on resulting tire forces and sinkage.
Changes to the acceleration, velocity, and friction
coefficient have little effect on model results, partly
because of the low velocities and accelerations in-
volved in standard snow rolling resistance tests.
Motion resistance forces and sinkage
The tiresnow model was compared to field
measurement of tire forces made with an instru-
mented vehicle. Model results were also compared to
rolling resistance and sinkage predictions made from
established algorithms for snow (as adopted by the
NATO Reference Mobility Model).
Experimental measurements. Vehicle performance
was measured using the CRREL Instrumented Vehi-
cle (CIV), which is instrumented to measure vertical,
longitudinal, and lateral forces at the tireterrain in-
terface; wheel speed at each wheel; true vehicle
speed; and steering angles. The CIV is designed as a
research tool to perform various mobility tests (trac-
tion, resistance, and maneuverability) using different
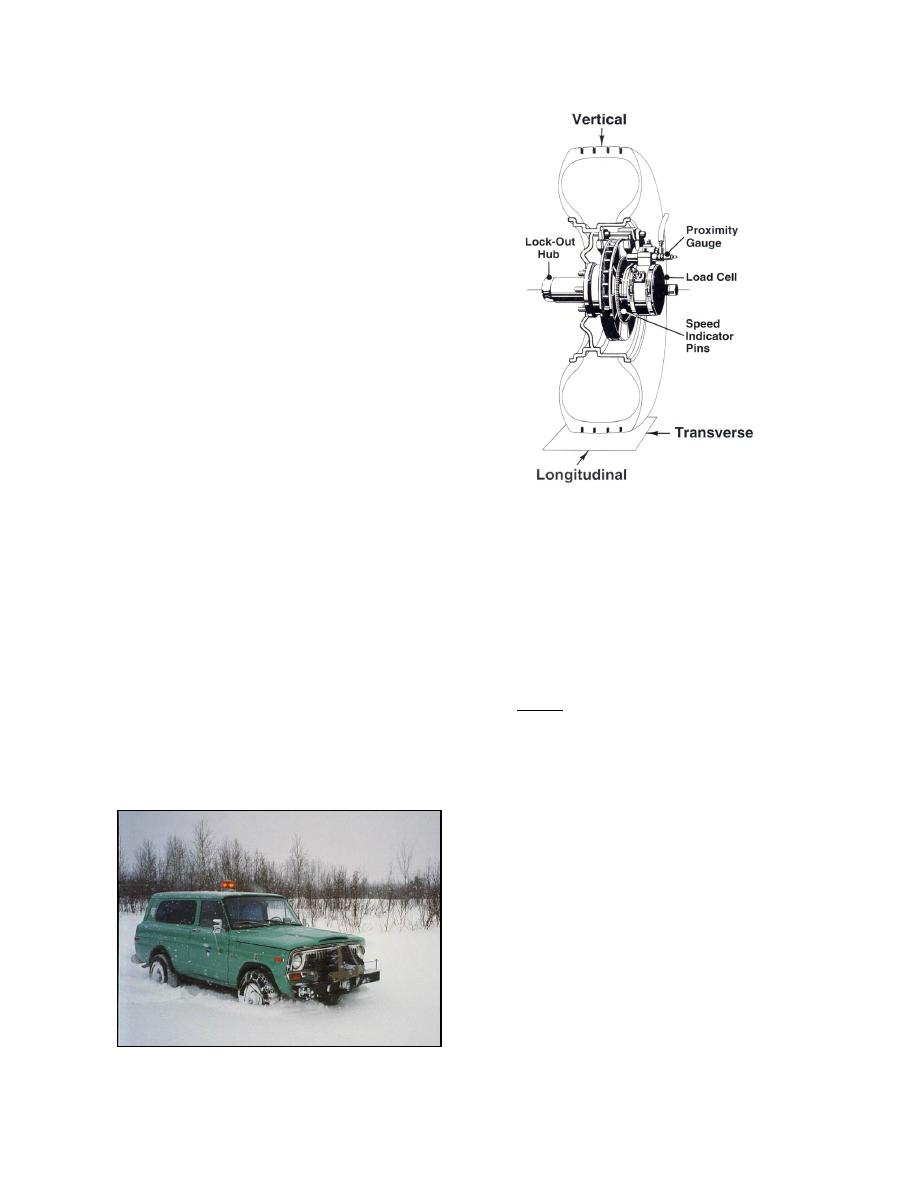
Figure 59. Configuration of speed
tires, traction aids, and vehicle configurations (of
sensors and axle-mounted load
braking and driving wheels) on a range of terrain
cells on the CIV (From Shoop et al.
surfaces including dry, wet, snow, ice, and freezing
1994.)
or thawing ground. The data obtained from these tests
on the vehicle. The difference between the wheel
are used for model validation and for developing al-
speed vw and the vehicle speed vv is termed the dif-
gorithms to predict vehicle performance on cold-
ferential interface velocity (DIV), also called the
weather terrain.
"slip speed" or "longitudinal slip velocity" (SAE
The vehicle, originally a 1977 American Motors
1992). This is often normalized by the speed of the
Corporation Jeep Cherokee, is shown in Figure 58.
vehicle and called slip i (ISTVS 1977):
Each wheel is instrumented with a three-component
load cell (Fig. 59), designed and calibrated to respond
vw - vv
i=
100% .
(28)
to the forces at the terrain interface. The wheel speed
vv
is measured using a proximity sensor with a set of
Using this convention, driving slip is positive and
100 measurement pegs set into the brake rotor. Wheel
braking slip is negative.
speed is compared to the true vehicle speed measured
Rolling resistance or motion resistance is the sum
using a fifth wheel or a sonic speed sensor mounted
of the forces resisting vehicle motion. These are
forces due to the internal friction of the moving parts
of the vehicle, the air drag, the internal resistance of
the tires due to flexing of the belts and plies and vis-
cous properties of the rubber compounds, and the
added resistance due to the deformation of the sur-
face. The CIV measures motion resistance forces
directly at the wheel, eliminating the forces acting on
the vehicle body. Motion resistance is tested with the
CIV by rolling the vehicle through snow at a constant
speed. The vehicle is driven with the rear wheels
only, and the front brakes are released so that the
only forces on the front wheels are due to the tires
and snow. The internal resistance of the tire is meas-
ured by rolling it on a hard surface. This value is sub-
tracted from the snow motion resistance measure-
Figure 58. The CRREL Instrumented Vehicle (CIV).
44




 Previous Page
Previous Page
