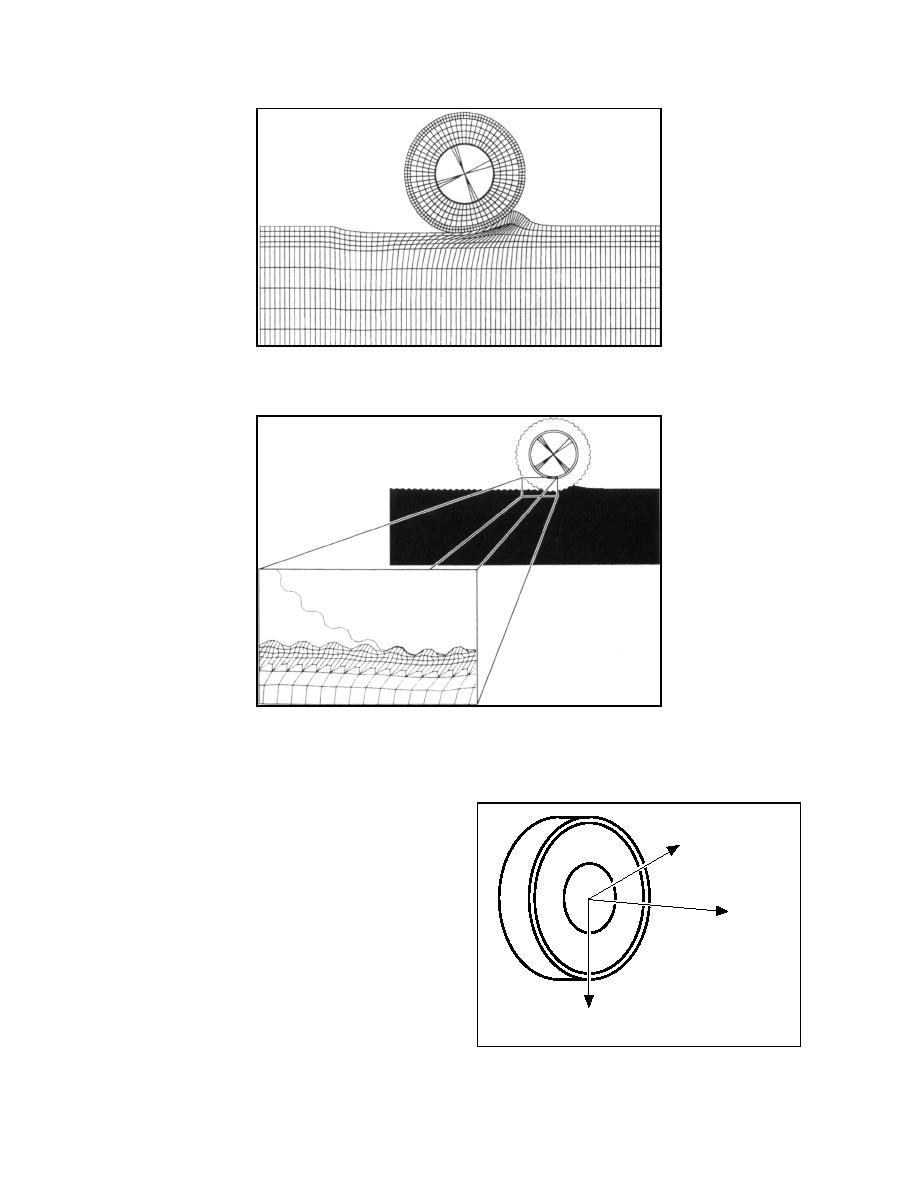
Figure 4. Two-dimensional modeling of tireterrain interaction
by Aubel (1993).
Figure 5. Modeling of the effect of lug design on treadterrain
interaction in two dimensions by Fervers (1994).
Tire terminology
Because of the interdisciplinary nature of this
work, some of the tire terminology and conventions
are presented here, as they are used throughout the
Longitudinal
text. The tire direction convention is based on the
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standard
definitions for vehicle dynamics. Since the tire
terrain models are currently formulated for straight-
Lateral or
ahead rolling (zero slip angle), the tire longitudinal
Transverse
axis is in the direction of travel and the lateral or
transverse direction is perpendicular to travel (in the
horizontal plane), as shown in Figure 6.
The tires modeled are modern radial tires, which are
constructed with numerous components, as shown in Fig-
Vertical
ure 7. Each of these elements contributes to the structural
behavior of the tire and is considered either individually
or en masse when creating deformable tire models.
Figure 6. Tire direction convention.
4




 Previous Page
Previous Page
