Table 8. Coefficients to Speedy's (1987) empirical equations
for calculating the thermophysical properties of supercooled
water.
α 103
κT
Cp
(bar1)
1mol1)
x
(K)
(J
K
Cx
0.80
20.0
14.2
Bx(0)
1.802 180 3
4.120
25.952
Bx(1)
0.941 698 0
1.130
128.281
Bx(2)
0.905 507 0
77.817
14.2
Bx(3)
0.80
78.143
221.405
Bx(4)
54.290
64.812
max resid
1.2 ppm
0.2%
0.03%
ties of supercooled water. His expression for the constant-pressure heat capacity of
supercooled water is
4
∑ BCn)εn + 2CC
(
ε 1/2
Cp =
(42)
p
p
n=0
(0)
(4)
where BCp ,K , BCp and CCp are fitted coefficients. The estimated values of these
coefficients are presented in Table 8. The parameter ε is a reduced temperature
T Ts
= T , Ts being a limiting temperature that is assumed to be exactly 227.15 K
s
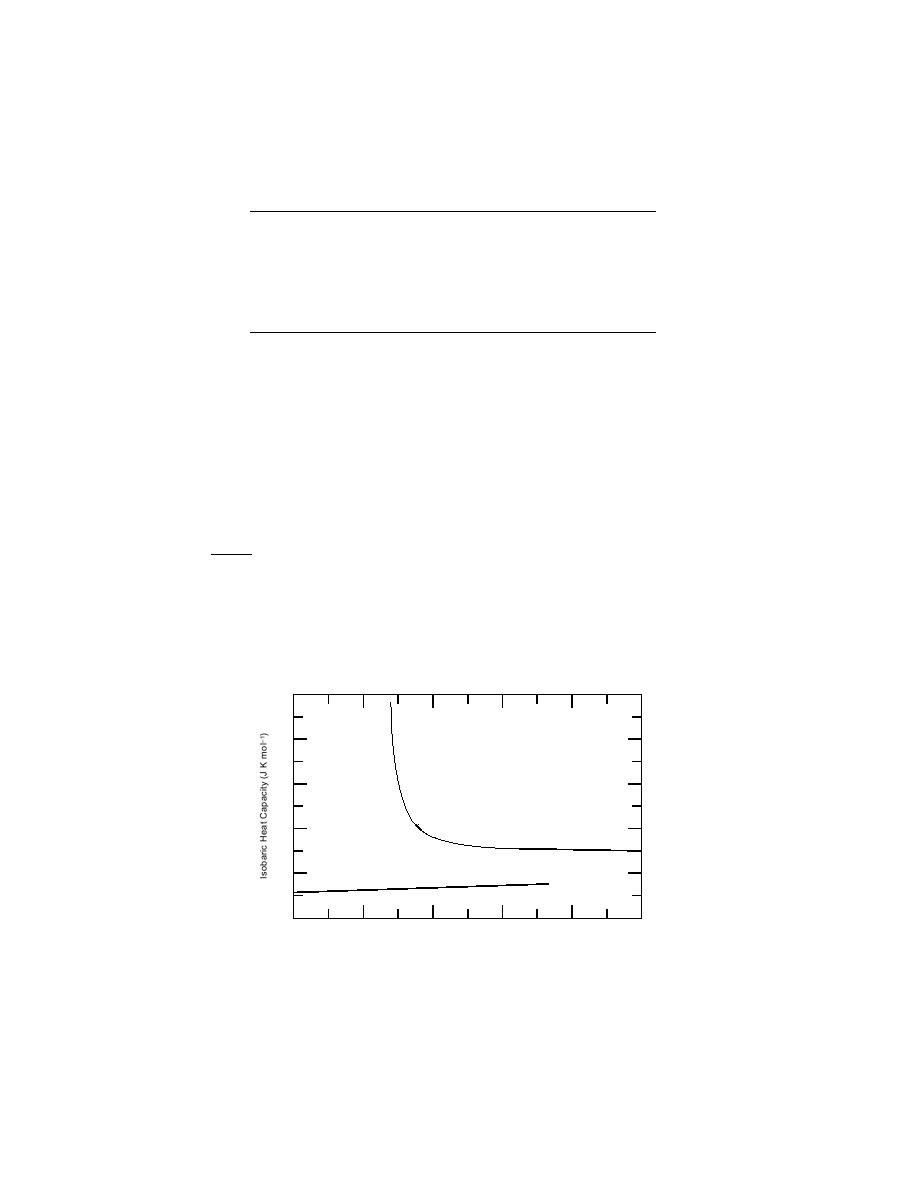
(46C). Figure 8 presents the constant-pressure heat capacity of water as calcu-
lated by the models of Hill (1990) and Speedy (1987).
The entropy changes of supercooled water can be calculated by evaluating the
integral:
250
200
H2O(l)
150
100
50
H2O(cr,I)
0
200
220
240
260
280
300
Temperature (K)
Figure 8. Constant-pressure heat capacity of H2O(l) and H2O(cr,I)
under p = 0.101325 MPa and T = 200 K to 300 K. Cp[H2O(cr,I)]
values were calculated with the MaierKelly model. Cp[H2O(l)]
values between T = 200 K and 273 K were calculated with Speedy's
(1987) model. Cp[H2O(l)] values between T = 274 K and 300 K
were calculated with Hill's (1990) equation-of-state model.
16




 Previous Page
Previous Page
