m
h
where cl is the fractional low cloud amount, ceff and ceff are the effective middle and high
cloud cover amounts based on the principle of random overlap, and χ (i,m,h ) is the cloud
m
h
irradiance factor for low, middle, and high clouds, respectively. ceff and ceff are given as
ceff = cm (1 - cl ) and ceff = ch (1 - cm )(1 - cl )
m
h
(3.6)
where cm (ch) are the fractional middle (high) cloud cover amounts. Hodges et al. (1983)
originally defined χ (i,m,h) as
χ (i,m,h ) = 80 - 5Z(l ,m,h )
(3.7)
where Z(l ,m,h ) is either the low, middle, or high cloud base altitude in kilometers. Equation
(3.7) has been modified based on the Geophysics Laboratory model atmospheres (tropics,
mid latitude summer, mid-latitude winter, subarctic summer, and subarctic winter) and is
given as
χ (i,m,h) = 94 - 5.8Z(l ,m,h) .
(3.8)
The cloud base altitude, if not available from observations, has been parameterized in
terms of season and latitude following the approach by Stowe et al. (1980) and London
(1957) and data from the Global Distribution of Total Cloud Cover and Cloud Type
Amounts Over Land (1986) prepared by DOE and NCAR (Table 3.1.0). The basic
equation is given as
Z(l ,m,h) = a(l ,m,h) - b(l ,m,h){1 - abs[cos(c(l ,m,h){λ - d(l ,m,h)})]}
(3.9)
coefficients given in Table 3.1.0.
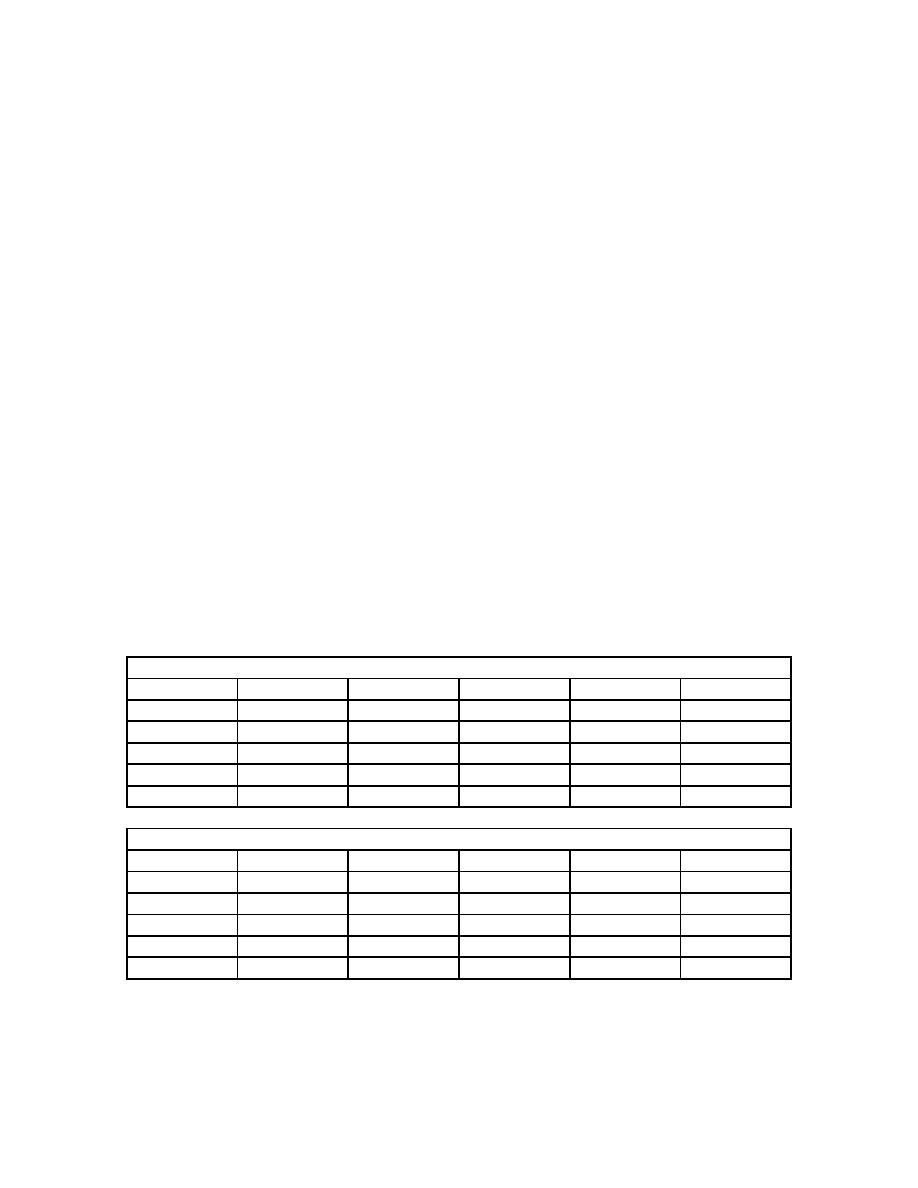
Table 3.1.0 Coefficients for determining cloud base altitude (meters) as a function of season,
latitude, and cloud type.
Winter (Dec, Jan, and Feb)
Cloud Type
Latitude
a
b
c
d
low
>=25
1050
600
1.5
25
low
<25
1050
600
5.0
25
middle
>=25
4100
2000
1.7
25
middle
<25
4100
300
4
25
high
all
7000
1500
3
30
Non-Winter (Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, and Nov)
Cloud Type
Latitude
a
b
c
d
low
>=25
1150
600
1.5
25
low
<25
1150
450
5.0
25
middle
>=25
4400
1200
3.0
25
middle
<25
4400
300
4
25
high
all
7000
1500
3
30
The total downwelling radiation is given as
Iir↓ = Iicrl↓ + Iicrl↓ .
r
d
(3.10)
16




 Previous Page
Previous Page
