3.1.1 Modification of the Cloud Irradiance Factor (CIF)
The total downwelling radiation at the ground, assuming a single optically thick overcast
cloud layer, can be written as
Iir↓ = ε aσ Ta + (80 - 5Z )
4
(3.11)
based on the original CIF (Z is the cloud base height). The total downwelling radiation
can also be written as
Iir↓ = ε aσ Ta + (1 - ε a )σ Tc .
4
4
(3.12)
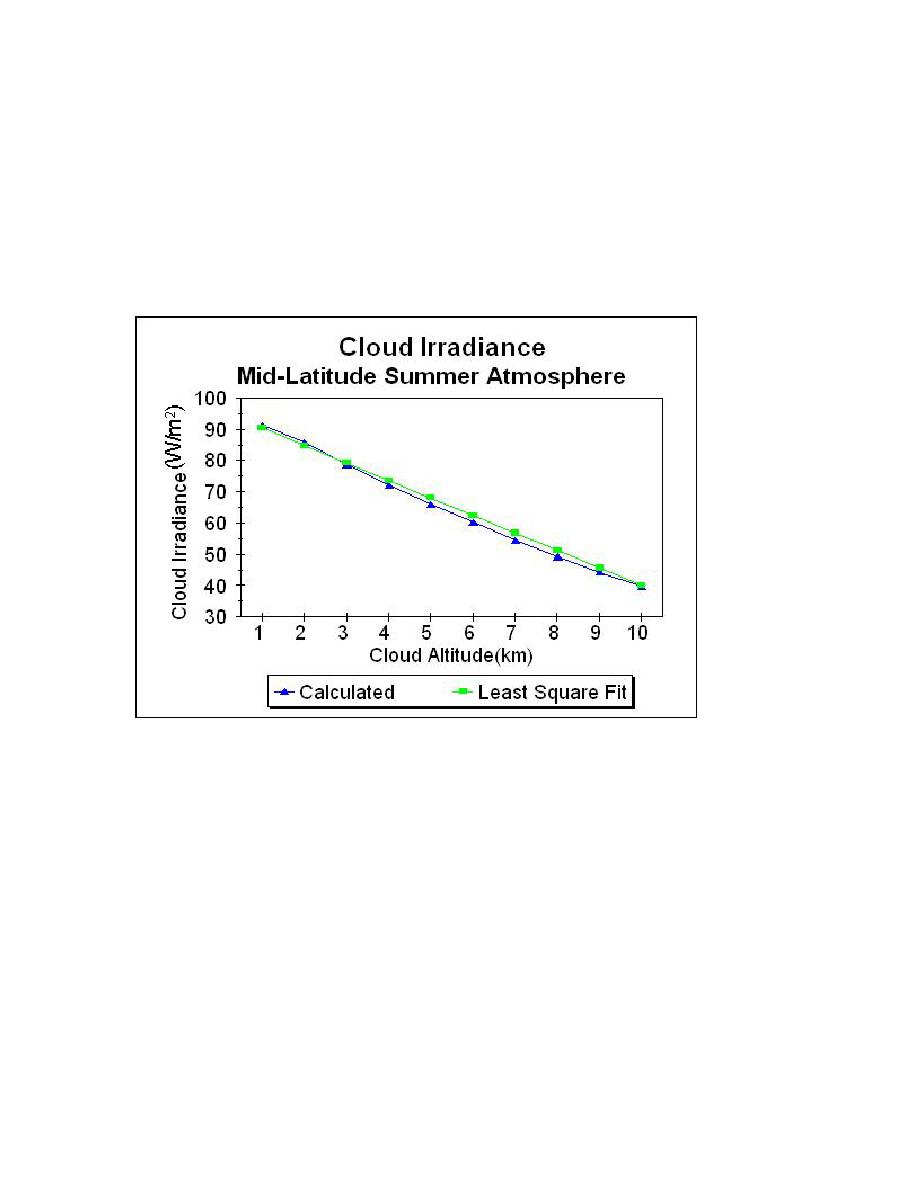
Figure 3.1 Calculated cloud irradiance in accordance with Equation (3.12) and the least
square fit to the data points. Calculations are based on a mid-latitude summer
atmosphere.
The term in parentheses is the atmospheric transmission below the cloud and Tc (K) is
the cloud base temperature. The cloud emissivity is assumed to be one, implying the
cloud reflection and transmission are zero. Using a cloud emissivity of one and the cloud
base temperature (clouds radiate at a temperature slightly colder than the cloud base
temperature) will result in an overestimation of the emitted cloud radiance. This is offset
by the fact that the cloud reflection is assumed to be zero and therefore the cloud does not
reflect downward any of the earth-emitted radiance. Equating Equations (3.11) and
(3.12), we can re-derive the term in parentheses in Equation (3.11) by computing the
cloud contribution to the total downwelling radiation using either measured moisture and
atmospheric temperature profiles or the Geophysics Laboratory model atmospheres. The
atmospheric emissivity was calculated using the Geophysics Laboratory model
atmospheres and Equation (3.2) (and Equation [3.3] etc.). Next, the cloud radiance was
17




 Previous Page
Previous Page
