The dependent variables p, T, u, and v for the general finite element e are
approximated by
n
∑ Ni (x, y) ui
=
(63)
ue
i =1
n
∑ Ni (x, y) vi
=
(64)
ve
i =1
n
∑ N i (x, y) pi
p
=
(65)
pe
i =1
n
∑ Ni (x, y) Ti .
Te =
(66)
i =1
Applying the Galerkin criterion to element e of an m+1th iterate of the governing
equations, the continuity equation becomes (using eq 63 and 64 and dV = 1 dxdy)
Ni
Ni
p
dxdy ui + ∫ N jp
dxdy vi = 0
∫ Nj
(67)
y
x
Ae
Ae
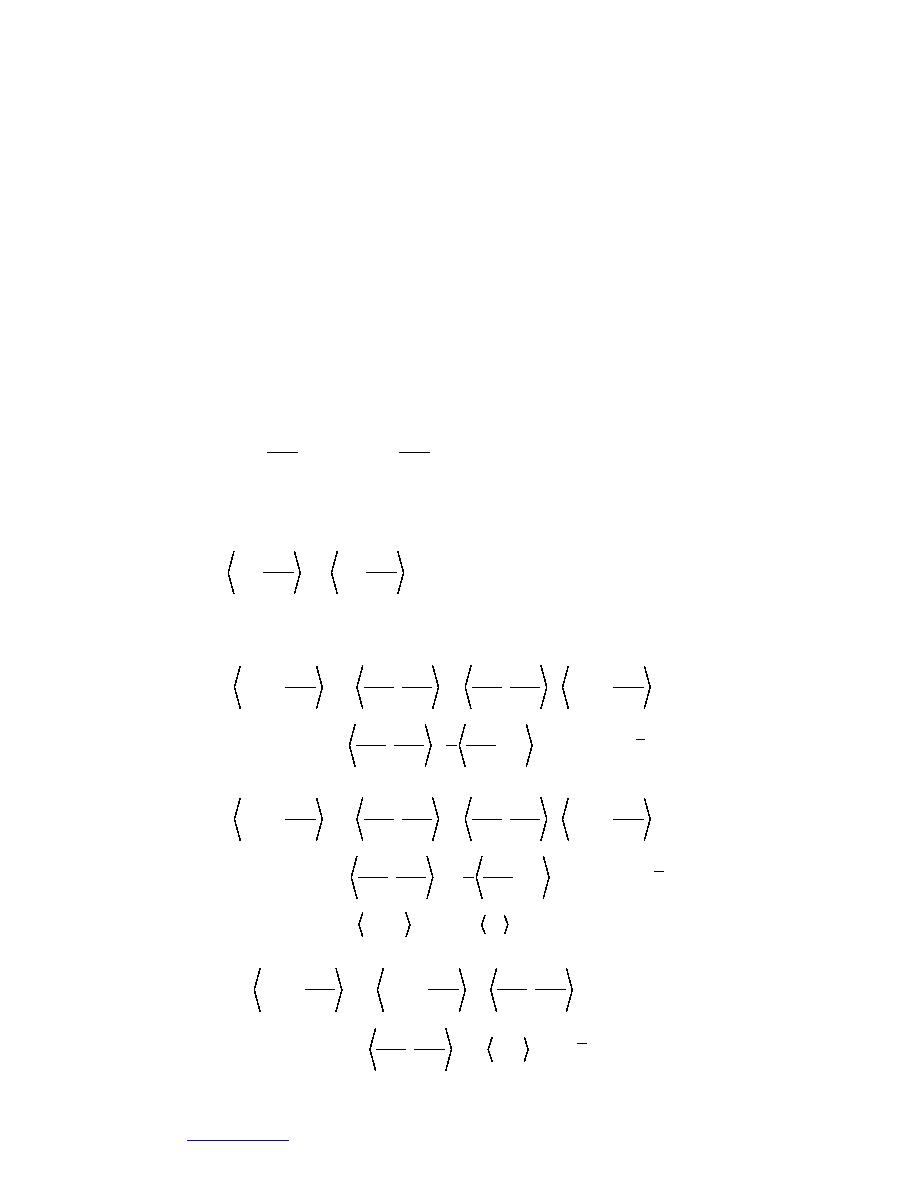
where Nj is the transpose of Ni. By letting the notation 〈a, b〉 represent the area
integral of ab, eq 67 becomes
Ni
Ni
p
p
ui + N j ,
vi = 0 .
(68)
Nj ,
y
x
A simplification is made at this point in that there are no boundaries with pres-
m
Nj
Nj
Ni
Ni
Ni
Ni
+ 2υ
+υ
+ vim , N j
ui , Nj
ui
,
,
y
x
x
x
y
y
(69)
Nj
Ni
Ni
1
p
+υ
+
, N j pi - υ ∫ Ni∇ue n ds = 0
,
ρ
x
y
x
s
m
Nj
Nj
Ni
Ni
Ni
Ni
+ 2υ
+υ
+ v m, Nj
ui , Nj
vi
,
,
i
y
x
x
x
y
y
Nj
Ni
Ni
1
p
+υ
ui +
, N j pi - υ ∫ Ni∇ve n ds
,
(70)
ρ
y
y
x
s
- gβ Ni , N j Ti + gβTref Ni = 0
Nj
Ni
Ni
Ni
+ Cv u m , N j
+k
m
Cv v i , N j
,
i
x
x
x
y
(71)
Ni
Nj
Ti - N j,Q - ∫ Ni k n ∇T e ds = 0.
+k
,
y
y
s
14
Go to Contents




 Previous Page
Previous Page
