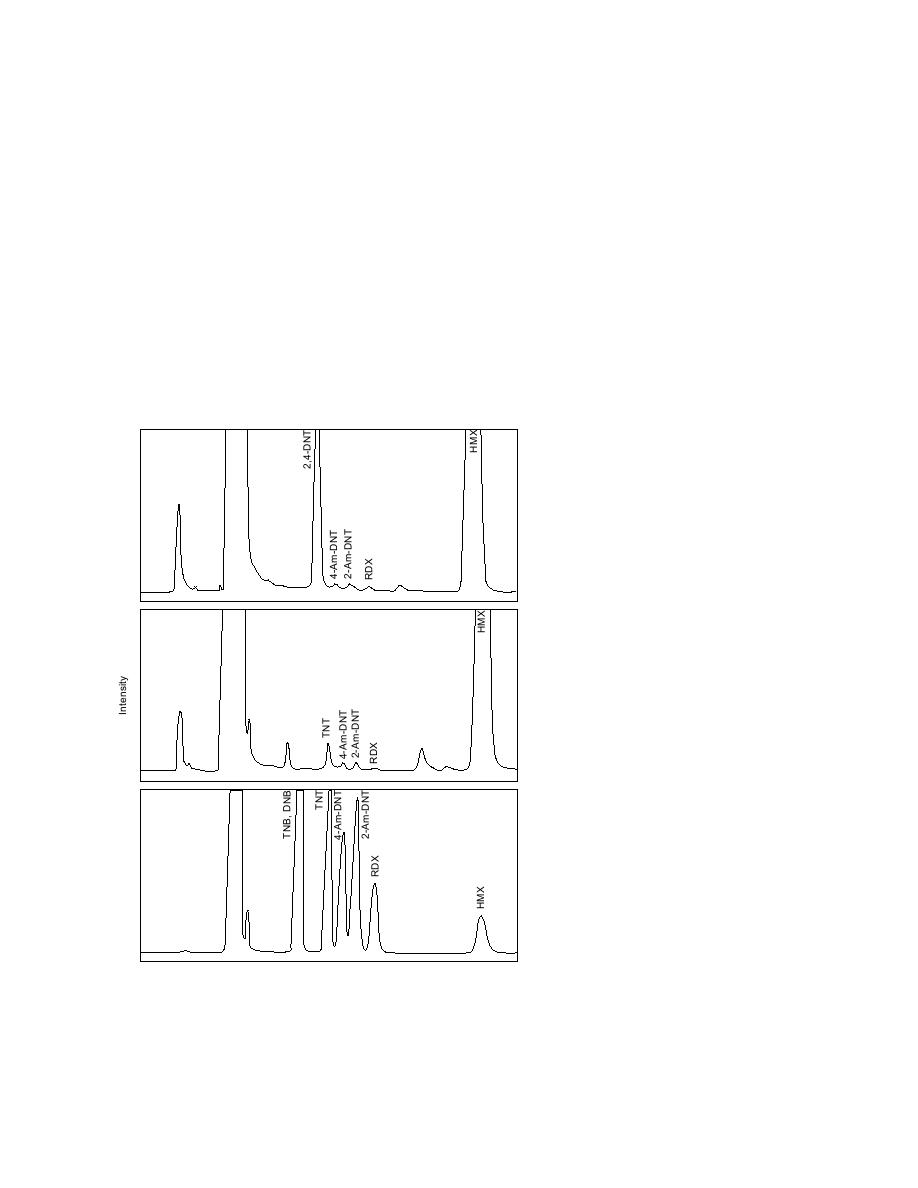
The elution order for LC-CN is opposite that of
Laboratory analysis
LC-18, and hence acetone did not interfere with
of acetone extracts
HMX on LC-CN. Results from the LC-CN analy-
RP-HPLC
sis for some of the acetone extracts showed the
The RP-HPLC conditions were modified from
potential presence of high concentrations of 2,4-
those in EPA Method 8330 (EPA 1995) to accom-
DNT, which, due to the close elution times of 2,4-
modate the change in extraction solvent from
DNT and TNT, prevented TNT determination
acetonitrile to acetone, which absorbs in the UV
(Fig. 8). The compounds present in these extracts
and can interfere with HMX and RDX determina-
and in some others that appeared to contain
tion. For each sample, 1.00 mL of the acetone
HMX, and the amino-DNT transformation prod-
ucts of TNT, were confirmed by GC-ECD (gas
extract was mixed with 5.00 mL of reagent grade
chromatography--electron capture detection) as
water prior to analysis using an LC-CN column
described below.
(Supelco) eluted with 1:1 methanol:water at 1.2
mL/min. Absorbance was recorded at 254 nm on
GC/ECD analysis
a Spectra Physics Model 8490 variable wavelength
A 1.0-L aliquot of the acetone extract was
detector and peaks were recorded on a Hewlett-
directly injected (270C) into an Hewlett-Packard
Packard 3396 Digital Integrator operated in the
peak height mode.
5890 gas chromatograph equipped with an elec-
tron capture detector (300C). The tem-
perature of the dimethylpolysiloxane
fused silica column (J&W DB-1, 0.53 mm
D2B
ID, 6 m, 1.5-m film thickness) was held
at 100C for 2 min, then ramped at 10C/
min to 200C, and 20C/min to 250C and
held for 3 min. The carrier gas was hydro-
gen (LV [linear velocity] = 150 cm/s).
Examples of the GC-ECD chromatograms
obtained for a standard and the same
acetone soil extracts depicted in Figure 8
are presented in Figure 9.
C4CC
Laboratory analysis
using Method 8330
Subsamples of all the soil samples col-
lected for this study were sent to an inde-
pendent commercial laboratory for analy-
sis. Duplicate 2-g portions of soil were
analyzed using acetonitrile extraction and
reversed-phase HPLC as described in
EPA Method 8330 (EPA 1995).
Standard
Water samples
Groundwater was collected from a
monitoring well located between the fir-
ing point and the target tanks. Surface
water was collected from two impact
craters near tanks A and B (located in the
upper reaches of the site). These water
samples were analyzed at DREV within
one day of collection using Method 8330
RententionTime (min)
Retention Time (min)
by the salting-out solvent extraction pro-
Figure 8. HPLC chromatograms (LC-CN) for a standard and two
tocol. Subsamples were refrigerated and
acetone soil extracts showing analytical difficulty in quantifying
analyzed at CRREL three weeks later
TNT when large concentration of 2,4-DNT was present.
using HPLC and GC-ECD methods.
8




 Previous Page
Previous Page
