1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
CMU A
CMU B
0.2
CMU C
Brick
0.0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
Time of Partial Immersion (min)
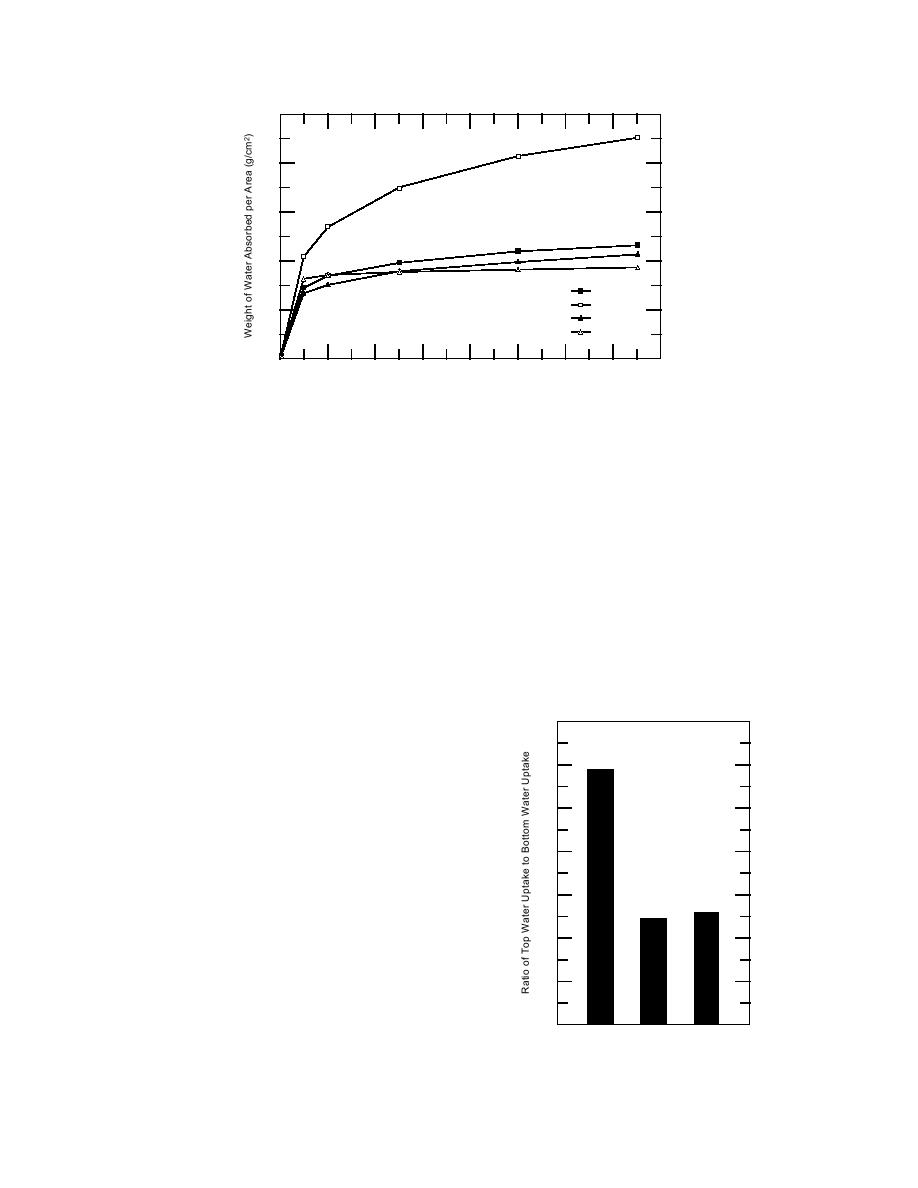
Figure 4. Effect of unit manufacture on water uptake. Unit, water, and
air temperatures are 20C.
ference in water absorptions of approximately
than 7% difference between the absorption rates at
100% between the top and bottom surfaces of the
any time during the test.
same unit, with the bottom manufactured surface
Effect of unit manufacture. The difference in the
having the greater capillary suction. However,
water uptake test results of CMU B in comparison
the results of tests on CMU A prevent drawing
with the other units indicates that physical unit
the conclusion that the bottom surface consist-
characteristics can significantly influence capillary
ently results in increased water uptake. While the
suction (Fig. 4). While the absorption rates (top
water weight absorbed by the two surfaces of
and bottom surfaces averaged) of CMU A and
CMU A were nearly identical, the smaller surface
CMU C were very similar, CMU B had absorbed
area of the top of the unit as manufactured actu-
nearly 50% more water than the other two CMUs
ally gave it a greater water absorption per unit
after 1 minute and nearly 100% more water after
area than the bottom surface.
15 minutes. The water uptake rates of the concrete
brick were more similar to those of CMUs A and C.
However, while the concrete brick absorbed more
water than either of these two CMUs after 1
1.4
minute, it absorbed very little additional water
over the next 14 minutes of immersion in compar-
1.17
1.2
ison with CMUs A and C such that its total absorp-
tion was less than that of the two CMU types.
Effect of absorption surface. The top and bottom
1.0
surfaces of concrete masonry units can differ sig-
nificantly in surface texture and appearance. The
0.8
bottom surface of the unit is molded against the
machine pallet during manufacture, resulting in a
smooth and fine texture. The top of the unit is not
0.6
0.51
molded, however, and therefore is typically
0.49
rougher and more open. In concrete masonry, the
0.4
mortar bed joint is in contact with both of these
unit surfaces from the units above and below it.
Water uptake tests were performed on both sur-
0.2
faces of the concrete masonry units to determine
surface effects.
0.0
CMU A
CMU B
CMU C
As shown in Figure 5, surface characteristics
can have a significant influence on capillary suc-
Figure 5. Effect of absorption surface
tion. In the case of CMUs B and C, there was a dif-
on water uptake.
6




 Previous Page
Previous Page
