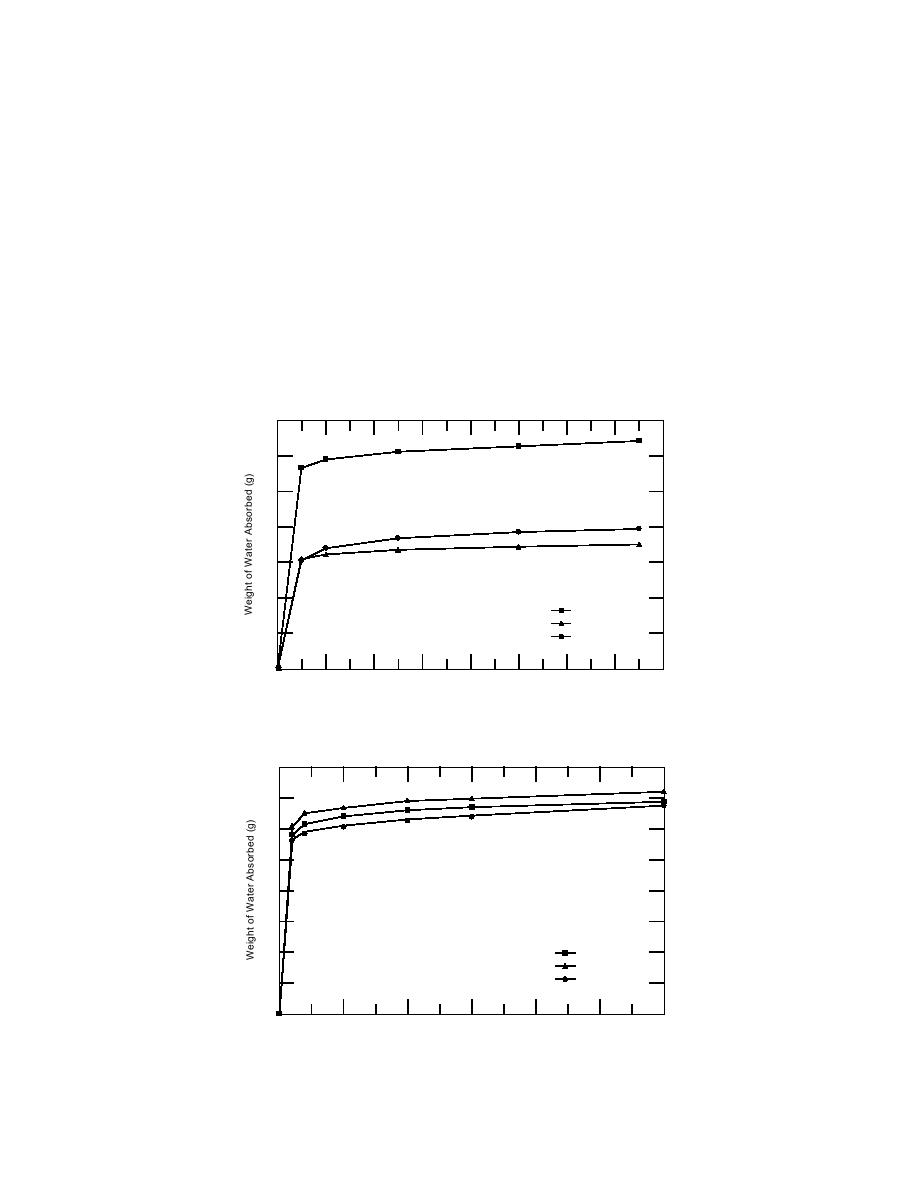
Effect of unit moisture. The dry concrete brick
tent, units were fully immersed in water for 24
absorbed nearly twice the water weight in the
hours and then allowed to dry until they aver-
aged 50% of their total absorption. The units
partial immersion test in comparison with the
referred to as "wet" contained much more mois-
normal and wet units (Fig. 2). The water uptakes
ture than units typically used in winter construc-
were nearly identical for the normal and the wet
tion. This condition was achieved by allowing
units after 1 minute of immersion time, but after
saturated units to air-dry only to the point that
15 minutes the wet units absorbed nearly 15%
there was little to no remaining free surface mois-
more water than did the normal units.
ture present, although a large majority of the sur-
Effect of water temperature. This comparison
face area was still observed to be damp. The re-
used dry brick. Water temperature appeared to
sulting moisture content of these units averaged
have little effect on the ability of cold units to
85% of total absorption.
absorb water in the partial immersion test. As
Appendix A summarizes the water uptake re-
shown in Figure 3, cold units were able to absorb
slightly more 20C (68F) water than 5C (41F)
sults. Figures 2 through 5 provide a discussion of
water and slightly more 5C water than 30C
the most important findings from the partial im-
(86F) water. However, there was never more
mersion tests.
70
60
50
40
30
20
Dry Units
Normal Units
10
Wet Units
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
Time of Partial Immersion (min)
Figure 2. Effect of unit moisture on water uptake. The brick, water, and
air temperatures are 20C.
80
70
60
50
40
30
5C Water
20
20C Water
30C Water
10
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Time of Partial Immersion (min)
Figure 3. Effect of water temperature on water uptake. Brick and air
temperatures are 5C.
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
