where
a weir. However, data indicate that the water in
v = particle settling velocity (cm/s: fresh-
the Flats area is brackish. Tidal invasion of the Flats
water)
regularly introduces seawater, which mixes with
g = gravitational constant (980 cm/s2)
freshwater from the Eagle River and groundwa-
ρ1 = particle density (g/cm3)
ter sources. Salinity measurements in the region
ρ = fluid density (g/cm3)
where the dredging is proposed indicated the sa-
d = particle diameter (cm)
linity of the water was between 5 and 7 ppt (nor-
= fluid viscosity (dyne-s/cm2).
mal seawater has a salinity of about 36 ppt). Be-
cause settlement rates can be much higher in wa-
The Reynolds Number
ter that contains salts in solution (Thackson et al.
1984, Palermo et al. 1978) than in freshwater, settle-
R = vρd/ (dimensionless)
(2)
ments times on the order of hours rather than days
is used to determine if settling is laminar or tur-
were postulated after we recognized the impact
bulent.
of salts in the sedimentwater solution. The elec-
Settling times in Table 1 are given for both white
trolytes in saline sediments reduce the repulsive
phosphorus and silt particles. Times are a func-
forces between soil particles. If the concentration
tion of particle size and depth of ponded water.
of electrolytes is strong enough, particle repulsive
forces will be neutralized. Particle attraction forces
Note that the cycle time does not take into consid-
will then dominate and particle aggregation will
eration the decanting time for removing the su-
become more common. The larger aggregations
pernatant after settling is complete.
of particles will settle more quickly than the
smaller individual particles. Only small salinity
Laboratory sediment tests
levels in the range of 26 ppt are required for the
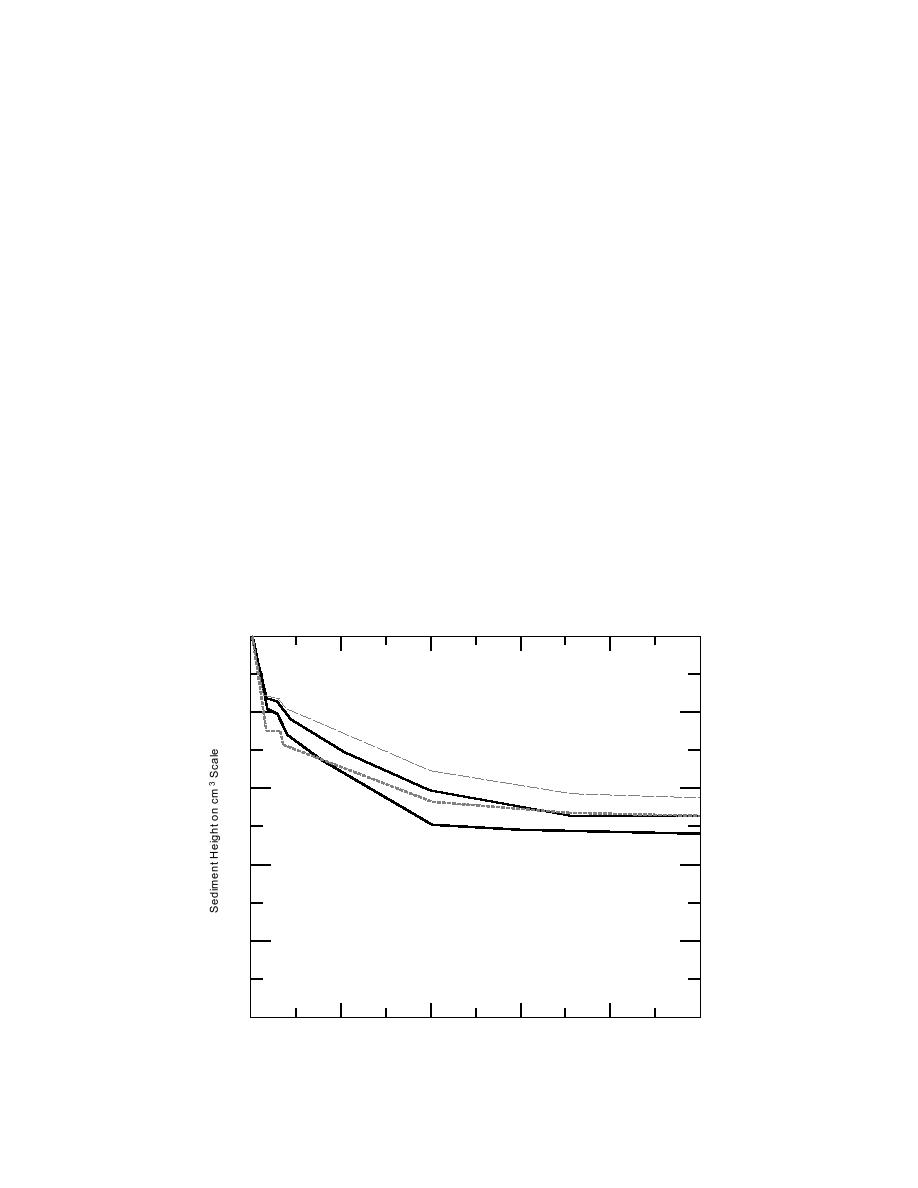
The relatively long settlement times in Table 1
flocculation process to be effective (Praudic 1970).
would adversely affect the dredging and filling
Preliminary laboratory sedimentation tests with
operations. Several days of calm water in the set-
samples from ERF (Fig. 1) showed that settling
tling basin would be required before relatively
times would be less than one hour, not the several
clear supernatant could form and be decanted over
1000
800
Sample No. 3
No. 2
600
No. 4
No. 1
400
200
0
20
40
60
80
100
Elapsed Time (min)
Figure 1. Results of preliminary sedimentation tests.
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
