800
600
400
ATDD
200
AFDDmax
0
200
400
600
JD AFDDmax
JD start cold
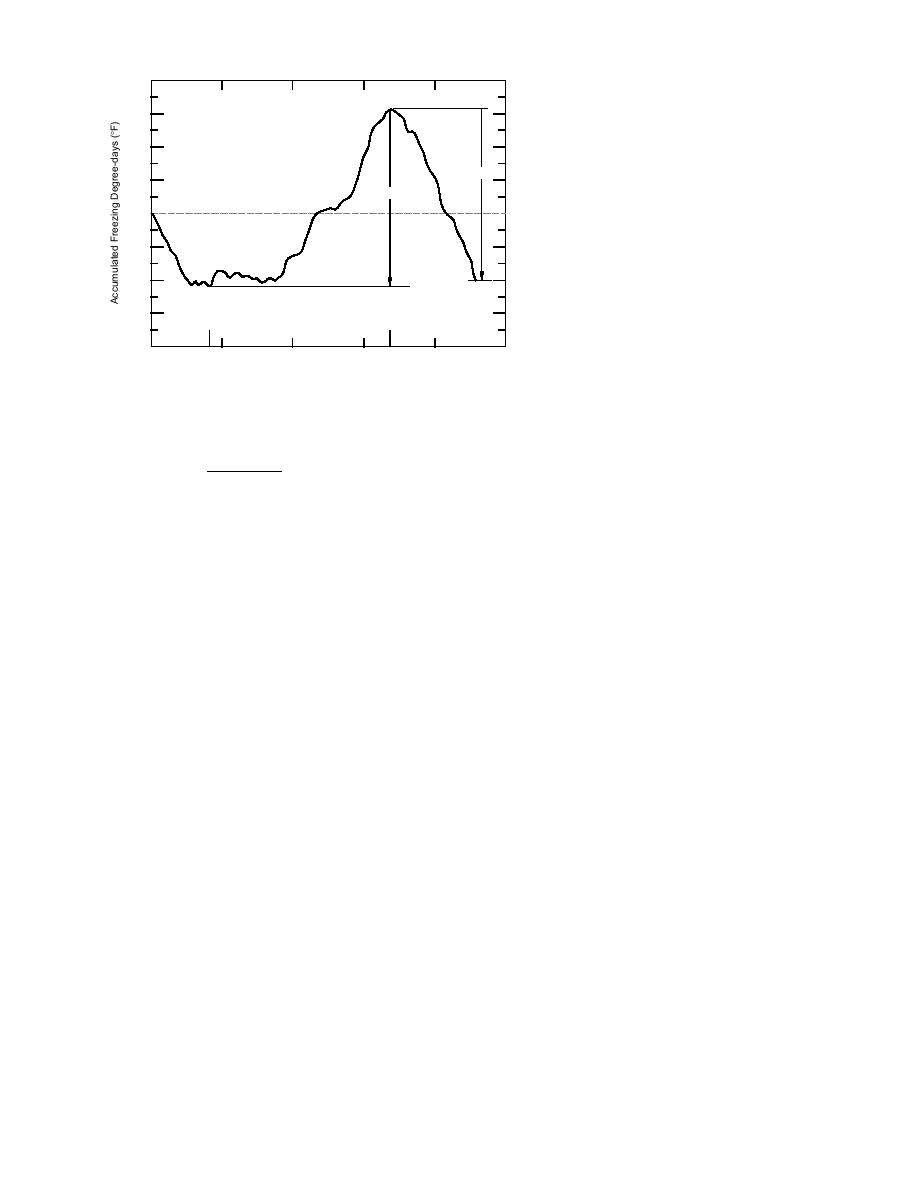
Figure 2. AFDD at the National Weather
800
Service Station at North Platte, Nebraska,
0
50
100
150
200
250
during water year 1960.
Julian Day (1 Oct is day 1)
temperature is simply the average of the mini-
tor of ice thickness and rapidity of snowmelt. They
mum (Tmin) and maximum (Tmax) air temperatures:
are calculated using the equation
Tmax + Tmin
TDD = ADAT Tb
(3)
ADAT =
.
(1)
2
where Tb is the base temperature at which snow-
Freezing degree-days (FDD) are calculated from
melt and ice deterioration are considered to be-
the ADAT using the relation
gin. Because snowmelt and ice deterioration can
occur when the average daily air temperature is
FDD = 32 ADAT.
(2)
less than 32F, the base temperature can range
from about 25 to 32F. Thawing degree-days ac-
A positive value of FDD means that the aver-
age daily air temperature is lower than 32F, while
cumulated after the JD start cold are called ATDD.
a negative value means that the average daily air
If the ATDD drops below zero, accumulation ends
temperature is higher than 32F. Accumulated
and ATDD is considered to be equal to zero until
freezing degree-days (AFDD) are the sum of the
the next positive TDD.
freezing degree-days during the winter, begin-
Snowfall data are important because the pres-
ning 1 October (the start of the water year). Since
ence of snow can affect ice thickness. Snow on top
air temperatures are still relatively high in Octo-
of an ice cover will insulate the ice, slowing its
ber in Nebraska, however, AFDDs are summed
growth during cold weather. Conversely, if there
until some minimum value is reached. The date
is no snow on top of the ice, the ice will thicken
of the minimum AFDD is called the JD start cold.
more quickly during cold periods. Snowfall is also
Upon reaching the JD start cold, AFDD is reset
an indicator of the amount of snowpack available
to zero and begins accumulating again until
during the snowmelt. The combination of deeper
some maximum value is reached (AFDDmax).
snowpacks and rapid snowmelt causes larger in-
creases in stage and discharge than shallower
The date of the AFDDmax is called JD AFDDmax.
snowpacks under the same conditions. Also, the
The AFDDmax marks the change from generally
timing of snowfall can be important since late
colder weather (average daily air temperature
snows are more likely to still be on the ground
below freezing) to weather where the average
when the breakup season arrives. Finally, heavy
daily air temperature is above freezing. After the
snowfall on ice can cause a depression of the ice
AFDDmax is reached, FDDs continue to be ac-
cover that allows water to flood the ice cover. The
cumulated until they drop below zero. Figure 2
saturated snow can freeze into snow ice, increas-
illustrates the parameters derived from the mini-
ing the overall ice thickness. Data on precipita-
mum and maximum temperature data.
tion other than snowfall are also collected because
Negative freezing degree-days are termed
thawing degree-days (TDD). Thawing degree-
precipitation combined with snowmelt can result
days are of interest because they can be an indica-
in rapid runoff and sharp increases in stage that
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
