COLD REGIONS TECHNICAL DIGEST NO. 96-1
26
Lw = the length of the weir, which is 883 ft* for this ex-
ample
H = the flow depth over the weir.
Assuming upstream channel width is roughly equivalent to the
weir length Lw, average velocity upstream of the dam can be
expressed as
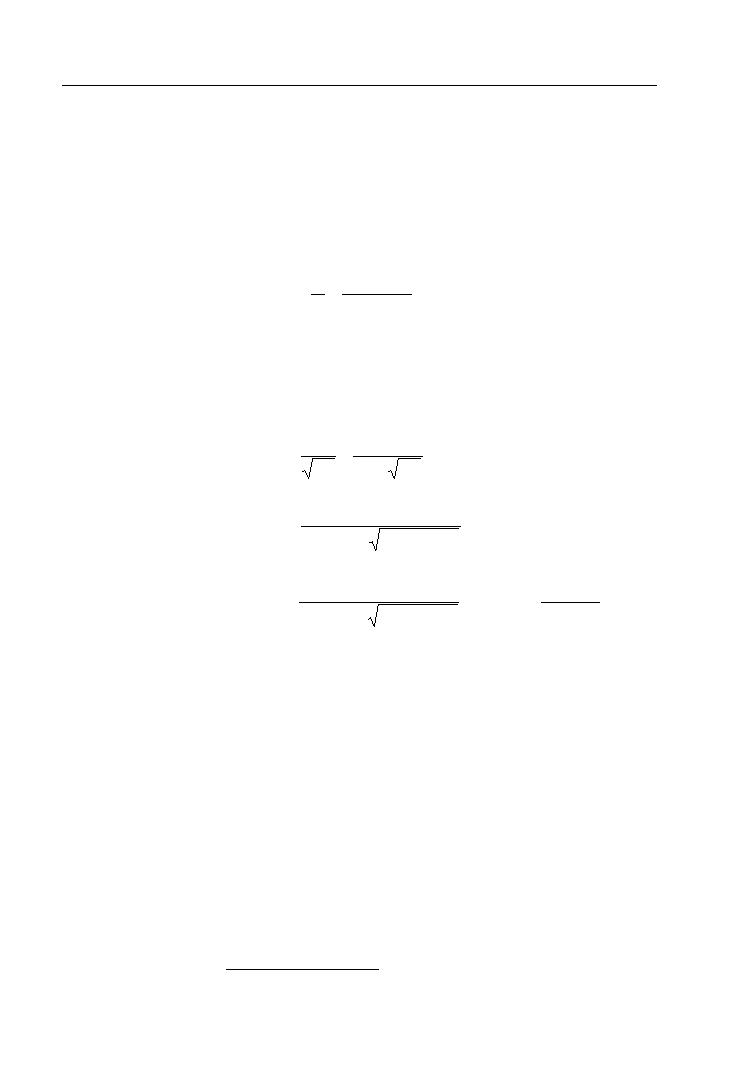
Q CLw H 3 / 2
V= =
A
Lw D
where D is the flow depth of the river upstream of the dam. Using
the elevations presented in Figure 16, the height of the weir =
745.0 726.5 = 18.5 ft. The upstream depth is then D = 18.5 + H.
Combining these gives:
CLw H 3 / 2
V
FR =
=
≤ 0.08
gD Lw D gD
CH 3 / 2
0.08 ≥
(18.5 + H ) g (18.5 + H )
H 3/ 2
3.3H 3 / 2
= (0.5815)
=
18.5 + H
(18.5 + H ) g (18.5 + H )
Solving for H by trial and error gives:
H ≤ 6.7 ft
The average depth (D) upstream of the weir, at a Froude number
of 0.08 is then:
D = 18.5 + 6.7 = 25.2 ft
Discharge and average velocity at the boom location can then be
calculated:
Q = CLH3/2 = (3.3) (883) (6.7)3/2 = 50,500 ft3/s
Average velocity is then:
*Only English units are used in Design Example.




 Previous Page
Previous Page
