EM 1110-2-2907
1 October 2003
b. The best projection and datum to use will depend on the projection of accompa-
nying data files, location of the origin of the data set, and limitations on acceptable pro-
jection distortion.
5-14 Rectification.
a. Image data commonly need to be rectified to a standard projection and datum.
Rectification is a procedure that distorts the grid of image pixels onto a known projec-
tion and datum. The goal in rectification is to create a faithful representation of the scene
in terms of position and radiance. Rectification is performed when the data are unpro-
jected, needs to be reprojected, or when geometric corrections are necessary. If the
analysis does not require the data to be compared or overlain onto other data, corrections
and projections may not be necessary. See Figure 5-3 for an example of a rectified im-
age.
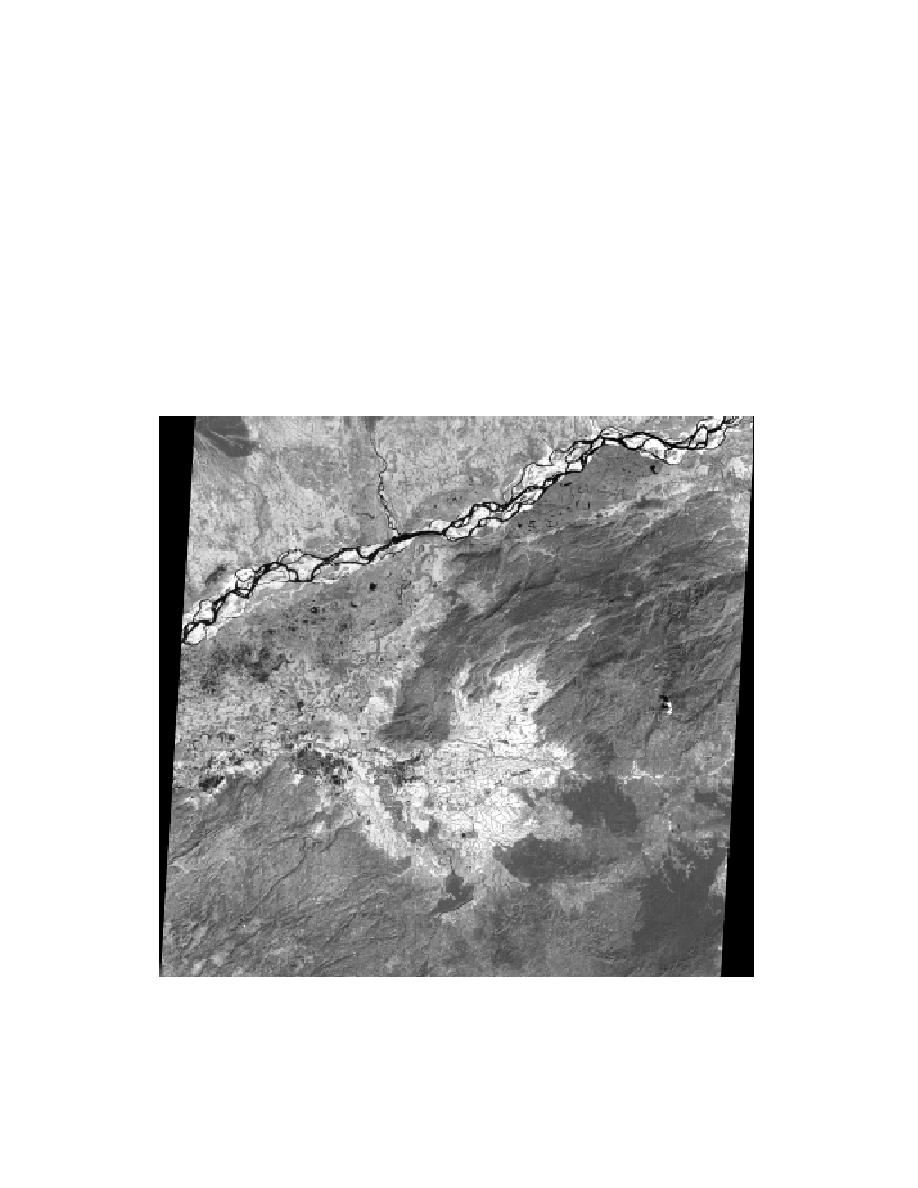
Figure 5-3. A rectified image typically will appear skewed. The rectification cor-
rection has rubber-sheeted the pixels to their geographically correct position.
This geometric correction seemingly tilts the image leaving black margins were
there are no data.
5-6




 Previous Page
Previous Page
