2000, 10 minutes after the catalyst was added. Sam-
was being transferred, the VOA vial was positioned
ples can be prepared and analyzed by both methods
on a balance, so that the desired weight could be
within 15 minutes. Like the visual method of analysis,
measured. The binary solvent mixture was used for
the HM 2000 requires the development of calibration
preparing samples for the visual and HM 2000 methods
models for each type of petroleum contamination and
of analysis, and MeOH was used with the gasoline-
sample matrix. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare stan-
contaminated soils for the CRREL reference analysis
dards of the different commercial petroleum products
method. The PE water sample concentrates were diluted
and process them through the steps appropriate for either
in organic free water (Millipore) to a 1- or 2.5-L volume
a soil or water matrix.
(Table 1). After dilution, these aqueous samples were
handled as described below for the fortified laboratory
Detection range
water samples.
The detection limits for TPH associated with both
For the laboratory-fortified samples, stock standards
gasoline and diesel fuel contamination in environmental
were prepared from locally obtained gasoline and diesel
matrices for the HM 2000 have been reported to be 10
fuel by transferring weighed quantities into an appro-
mg/kg for soil and 0.1 mg/L for water samples (Hanby
priate solvent. Gasoline was diluted into MeOH and
diesel fuel into methylene chloride. For soil, 5.0 0.1 g
1998). However, this reference provided no information
on how these detection limits were established. The
of air-dried or moist sample was transferred to a 5-mL
upper end of the working calibration range is 1000 mg
glass ampoule using a spatula, weighing dish, funnel,
TPH/kg and 50 mg TPH/L, for soil and water matrices,
and an analytical balance. Soil samples were spiked by
respectively. When samples exceeded these ranges, a
adding small volumes (less than 0.0125 mL) of stock
dilution of the sample extract is necessary before per-
standard to achieve the desired target concentration
forming the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(Table 2). A syringe (Hamilton) with an extra long
needle (7 cm) was used deliver the spike beneath the
Cost
surface of the soil. In some cases, an aliquot (0.1 to 0.5
The HM 2000 spectrophotometer and data proces-
mL) of organic free water was added right after the
sor (notebook computer and software) cost about 00.
analyte spike to create a known moisture content. Imme-
Each test kit, i.e., one for soils or the one for water,
diately after these solutions were injected into soils, the
costs 00 and comes with enough reagents
to prepare 15 samples (and blanks) for analy-
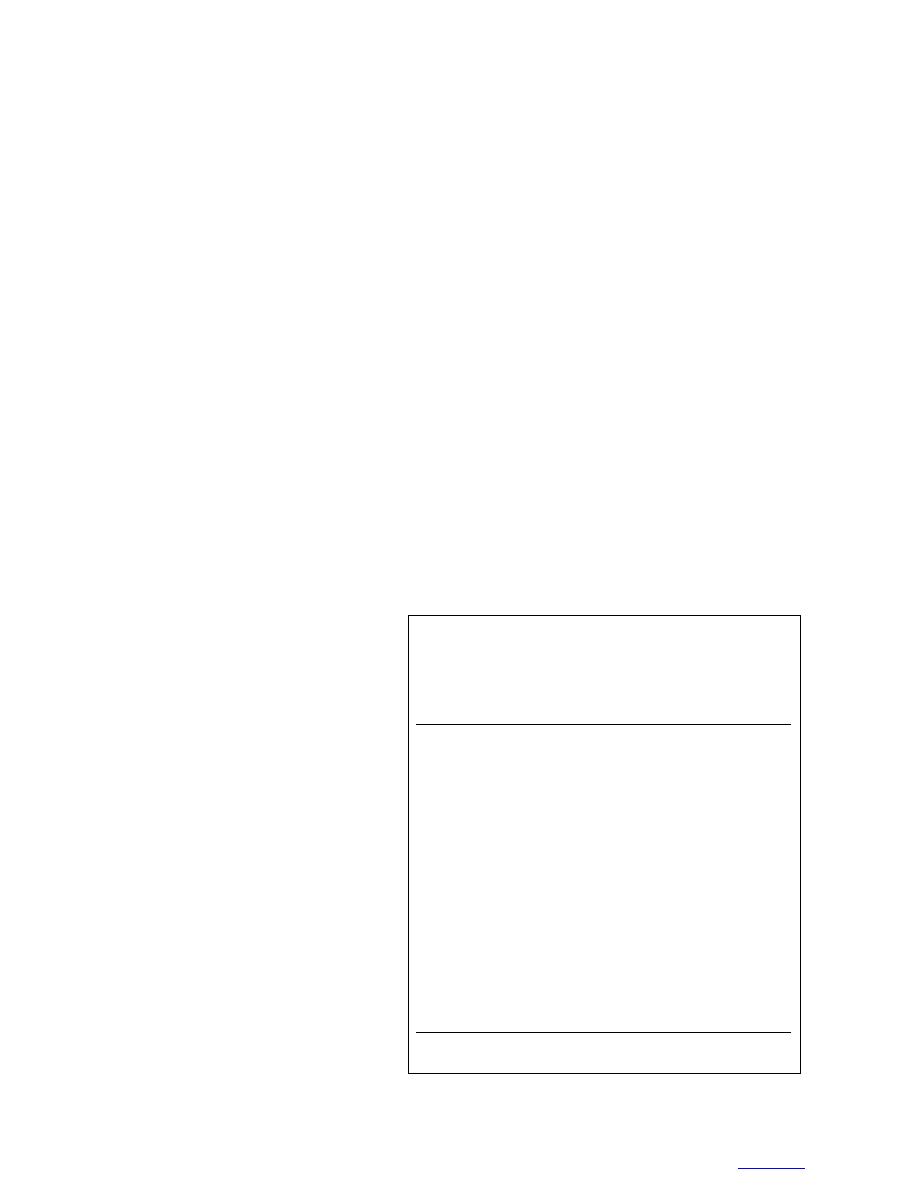
Table 1. Performance evaluation samples used for the labo-
sis. Additional reagents for these kits, allow-
ratory trials. These certified standards were purchased from
ing for the analysis of another 15 samples, can
Environmental Resources Associates, Arvada, Colorado.
be purchased for 0, and cuvettes cost
Sample
Certified
each. To bring the cost per analysis with the
Name
wt. or vol.
concentration
HM 2000 below 0, the approximate cost
Matrix
(ID)
(g or mL)
(perf. acc. limit)*
of a laboratory TPH analysis, about 120 analy-
I. Gasoline
ses would be necessary, which would require
Soil
Cat. No. 763
20 g
510 mg TPH/kg
an initial investment of about ,500 (HM
Lot. No. 40016
(189712)
2000, one Hanby Test Kit, seven reagent sup-
ply kits, 20 cuvettes).
Soil
Cat. No. 763
20 g
1130 mg TPH/kg
Lot. No. 40020
(4031600)
EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
II. No. 2 Diesel
Soil
Cat. No. 765
20 g
401 mg TPH/kg
Laboratory
Lot. No. 40018
(194509)
Commercial performance evaluation (PE)
Soil
Cat. No. 765
20 g
1730 mg TPH/kg
samples (Table 1) and soil and water matrices,
Lot. No. 40017
(8382210)
fortified with locally obtained petroleum prod-
ucts, were analyzed during the laboratory trials.
III. No. 2 Diesel in water
All of the certified PE materials were pack-
1000 mL†
Water
Cat. No. 764
0.903 mg TPH/L
aged in sealed glass ampoules, the soils as 20-g
Lot. No. 50022
(0.2971.120)
quantities and the waters as a 1-mL concentrate
Water
Cat. No. 764
2500 mL
0.360 mg TPH/L
in methanol (MeOH). After an ampoule contain-
Lot. No. 50022
(0.1190.448)
ing a PE soil sample was opened, a 5.0 0.2-g
* Performance acceptance limits.
portion was poured directly into a VOA vial
† Volume of water to which certified stock standard was added.
containing an extraction solvent. While the soil
3




 Previous Page
Previous Page
