such as landfarming and composting. In this
claimed material. Rotary kiln incinerators and cir-
method, the contaminated soil is mixed with water
culating bed combustion incinerators are common
and other additives in a reactor to form a slurry. It is
types of thermal treatment (Gerace-Coles 1991).
similar to other soil and sludge biotreatment tech-
Vapor extraction technologies use an air stream to
nologies in terms of microbiological interactions
remove dissolved molecules from liquids. The vola-
and contaminant degradation pathways. However,
tile compounds are trapped out of the air stream
it differs from the other technologies because bio-
using an adsorptive material such as carbon, which
slurry systems substantially increase the rate at
is then treated by incineration. Most commonly,
which contaminants degrade by increasing the avail-
TCE is remediated through pumping and treating
ability of contaminants, electron acceptors, nutri-
it, using either air stripping or granular activated
ents, and other additives, such as surfactants, to the
carbon. These technologies are very expensive, cost-
microbial populations. The result is a biological sys-
ing
||content||
to per 1000 gallons (3785 L) of ground-
tem that is conducive to optimum microbial activity
water.
and increased contaminant degradation rates.
Bioremediation, using either bioreactors or bio-
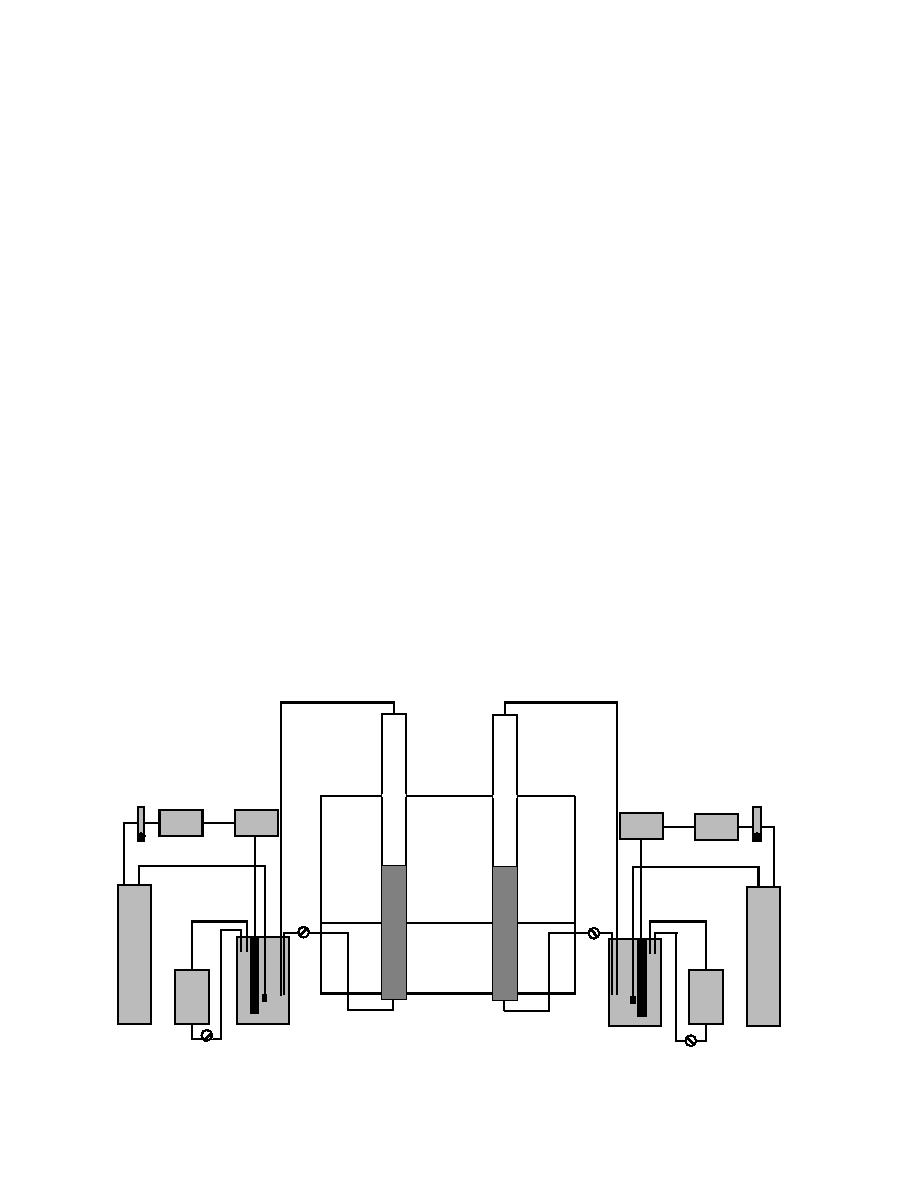
A new bioremediation technology is now being
slurries, has been examined as an alternative to
examined for treatment of groundwater contami-
incineration. Bioremediation utilizes microbes to
nated at low concentrations--the fluidized-bed
convert hazardous substances into nonhazardous
adsorption bioreactor. In this system, groundwater
compounds. The microorganism uses the contami-
is passed through a packed bed of adsorbent mate-
nant as a carbon source and ultimately converts it to
rial, such as carbon, carbonaceous resins or, organo-
CO2 and water.
philic clays (OPC). When the bed has adsorbed as
Bioreactors are large vessels in which either con-
much as it can, it is put into a closed-loop system
taminated soils or groundwater are treated. The
with a bioreactor. The bed is fluidized, meaning that
process allows for rapid bacterial growth, which
fluid is pumped through it at a high flow rate, caus-
results in maximum degradation rates. The system
ing the bed material to become suspended in the
is made optimal for a given contaminant and type
solution. As the fluid passes through the bed, it acts
of microorganism, and can be operated under either
as an extractant, removing the contaminants from
aerobic or anaerobic conditions. Once the contami-
the adsorbent material. The fluid is cycled through
nated soil or water has been remediated, it can be
the bioreactor and then back through the packed
returned to its original site as a recovered resource.
bed. Once the bed is deemed remediated, more
Bioslurry treatment of soils is a relatively new
groundwater is pumped through the sorbent and
remediation technology. It is a reconfiguration of
the process starts over.
other more widely used biotreatment technologies,
Flow
Flow
DO Meter
Meter Biotester
DO Meter
Biotester Meter
Pump
Pump
O2
O2
CO2
CO2
Reactor
Reactor
Pump
Pump
Figure 2. Fluidized-bed adsorption bioreactor.
2




 Previous Page
Previous Page
