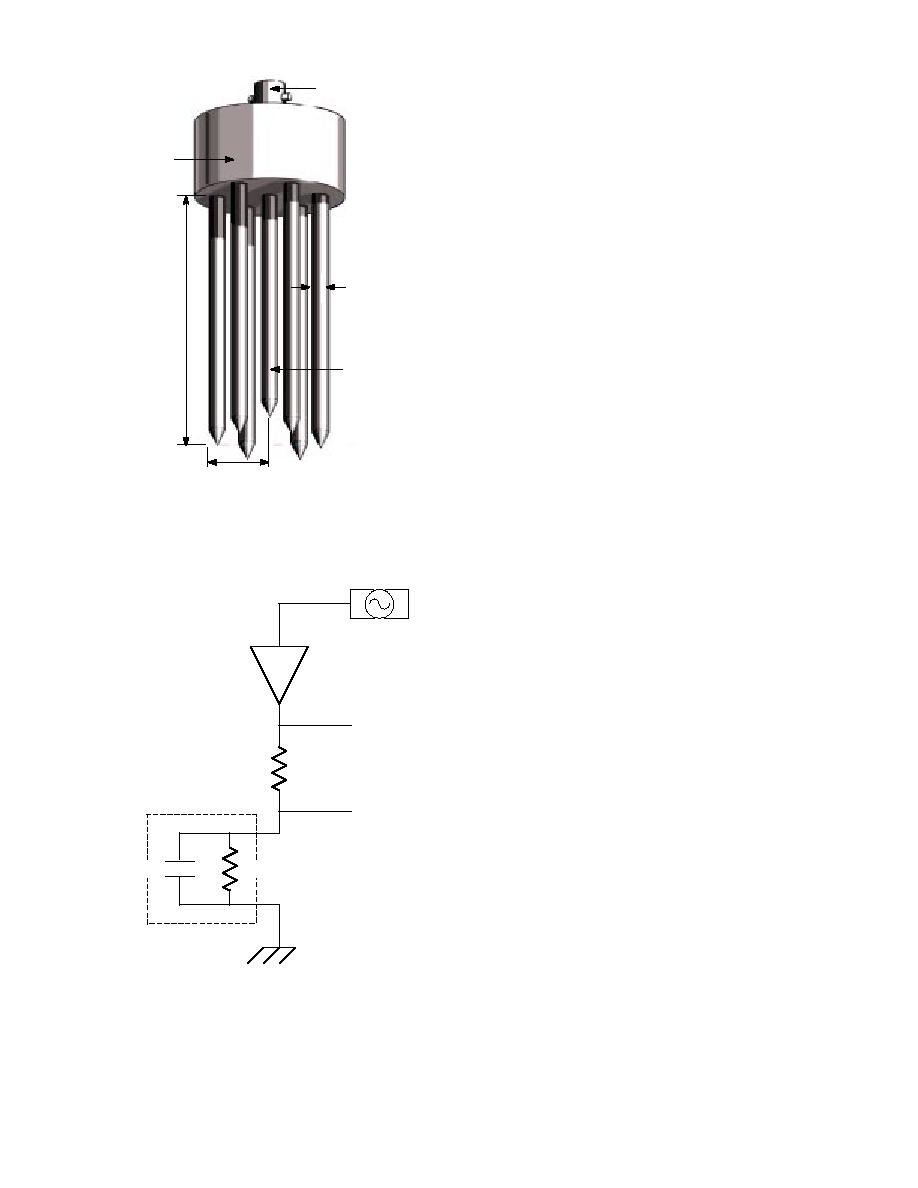
A simplified circuit diagram of the measure-
BNC Connector
ment electronics is shown in Figure 2. As can be
seen, three measurement voltages are required:
The applied voltage, Vref
Base
The voltage drop across the probe circuit,
Vdiv
The phase voltage between Vref and Vdiv,
Vph.
In this simplified example, the capacitance of the
probe is calculated using
Tine
Diameter
C = V ref sin Vph/(Vdiv ω R)
(1)
Probe
Length
where R = 500 ohms for this circuit
ω = 62.8 106 Hz.
Short
Inner Tine
The total probe circuit actually consists of the
probe capacitance in parallel with the capacitance
of the coaxial cable that connects the probe to the
readout box. To provide optimum sensitivity to
the measurement of the capacitance of the soil, a
Probe Radius
variable inductance was placed in parallel with
Figure 1. Coaxial probe configuration.
the probe cable input connector so that the ca-
pacitance of the cable itself could be nulled out of
the measurement process. By using this variable
inductor, the individual cable's capacitance may
be eliminated from the measurement so that only
U1
the probe's capacitance is "seen" by the measure-
ment electronics, thus simplifying the calculations
required to determine the probe capacitance us-
ing Vref, Vdiv, and Vph. In addition, as long as a
standard cable length is used for each field mea-
U2
surement, the process of nulling out the cable
capacitance is required only once for each of the
measurement circuits. Since the capacitance per
Vref
unit length of coaxial cable is very uniform, the
error caused by using different cables should be
500 ohms
very small as long as the cables are all of the same
length and have the same capacitance per unit
Soil Probe
length.
Vdiv
While the correction for various cable lengths
may be reduced to a small error or actually mea-
sured and accounted for in the calculations, there
Csoil
Rsoil
are two problems with this method that need
careful consideration and that can cause consid-
erable errors if not accounted for.
First, the dielectric constant K of a material is
defined as the ratio of the permittivity of the me-
dium ε to the permittivity of free space (a vacuum
or air as a very close approximation); ε0 = 8.85
Figure 2. Simplified vector voltmeter and probe
circuit.
pF/m in the MKS system, for instance:
2




 Previous Page
Previous Page
