of the storm and had very little damage to their sys-
tem. New Hampshire Electric Cooperative (NHEC),
with a service area spread all over the state but con-
centrated in central New Hampshire, was hardest hit
in the Ossipee and Alton areas (Sharon Yeaton and
Henry Lynch, NHEC, personal communication).
Falling trees broke many poles and caused the worst
damage to its system on record. Public Service of
New Hampshire's (PSNH) distribution system was
hit hard in the Monadnock region, Hillsborough,
greater New London, and the Lakes region into Con-
way and Rochester, with a total of about 55,000 out-
ages (CATV 1998). Granite State Electric had some
problems in its service area east of the Connecticut
River, but the relatively light damage to its system
allowed it to help neighboring utilities recover from
the storm (Richard Holmes, Granite State Electric,
personal communication). Exeter and Hampton Elec-
tric, with a service area covering thirteen towns near
the seacoast, saw minimal ice loads and had no prob-
lems in its system (Ray Letourneau, Exeter and
Hampton Electric, personal communication). Con-
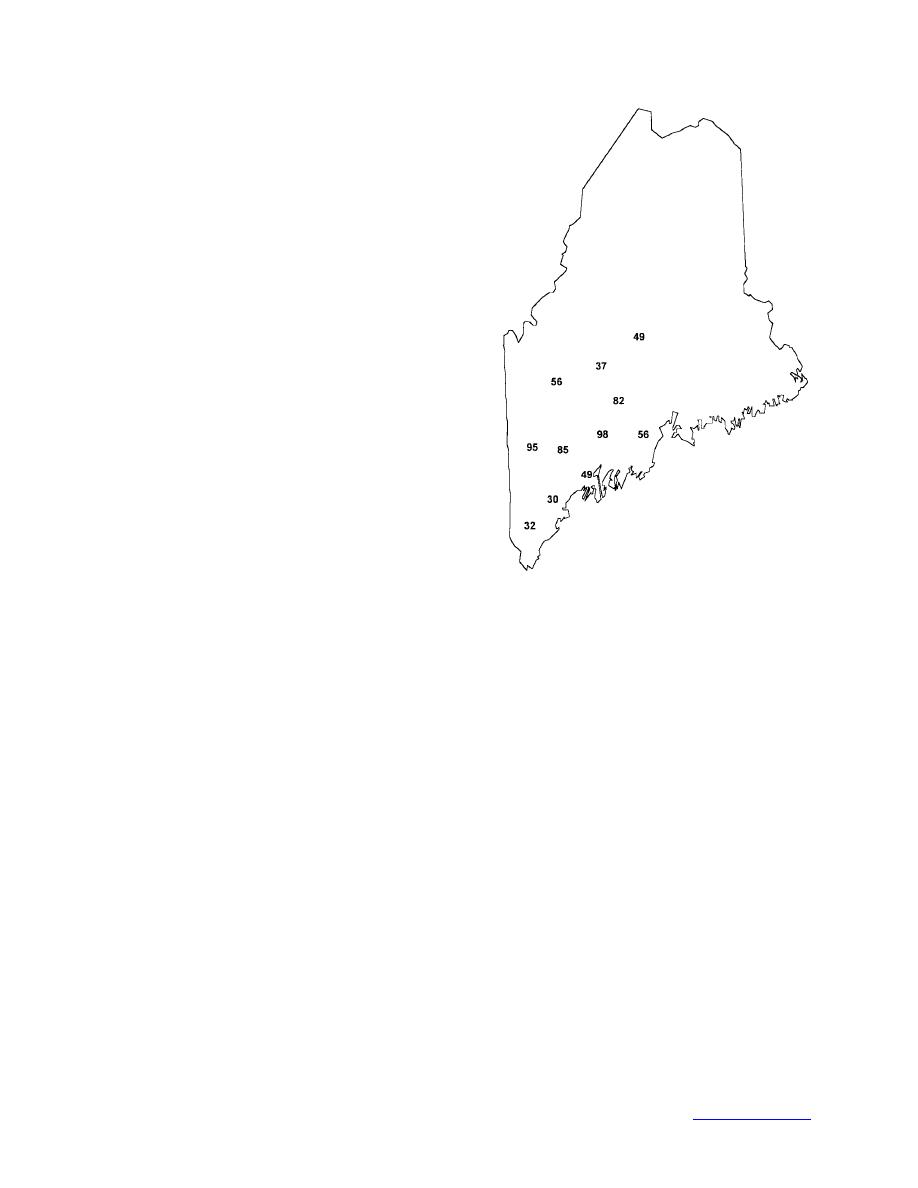
Figure 16. Central Maine Power outages at
cord Electric's problems were confined to Webster
the peak of the January 1998 ice storm.
and Boscawen, where broken trees and branches
caused outages to fewer than 10% of its customers
(Eric Werner, Concord Electric, personal communication).
The worst damage in Vermont was in the northwest corner of the state (Tom Dunn, Public
Service Department, personal communication). Outages in Central Vermont Public Service's
(CVPS) distribution system began on January 7 and all customers were back on line by January
13. Twenty-thousand customers were affected in its service area, which covers most of southern
and central Vermont, the regions around St. Johnsbury and Burlington, as well as towns in Ver-
mont and New Hampshire in the Connecticut River valley (Jack Crowther, CVPS, personal com-
munication). Repairs were most time-consuming in heavily wooded areas in difficult terrain. The
tree damage to CVPS's distribution lines was the worst in thirty years. Damage to Green Moun-
tain Power's (GMP) distribution system totaled ,000,000 (Dottie Schnure, GMP, personal
communication). The ice load on Citizens Utilities' wires was three times any load experienced
in the past (Steve Guyette, Citizens Utilities, personal communication), with much heavier ice
loads, and more damage to its distribution system, in the region around the north end of Lake
Champlain, than in the Grande Isle region farther south.
6.1.3 Transmission system
While trees leaning or falling on wire cause problems in electric power distribution systems,
tree problems are less common in the electric power transmission system because the wires are
on taller poles in right-of-way clear-cuts. Thus transmission system outages are likely to be good
indicators of severe ice and wind-on-ice loads on the wires and conductors.
25
Back to contents page




 Previous Page
Previous Page
