12
ERDC TR-05-1
AISA is a very compact system, consisting only of two units, the sensor head
(front end) and a rugged portable PC with graphical user interface. The image
data are stored as a default to a large capacity hard disk.
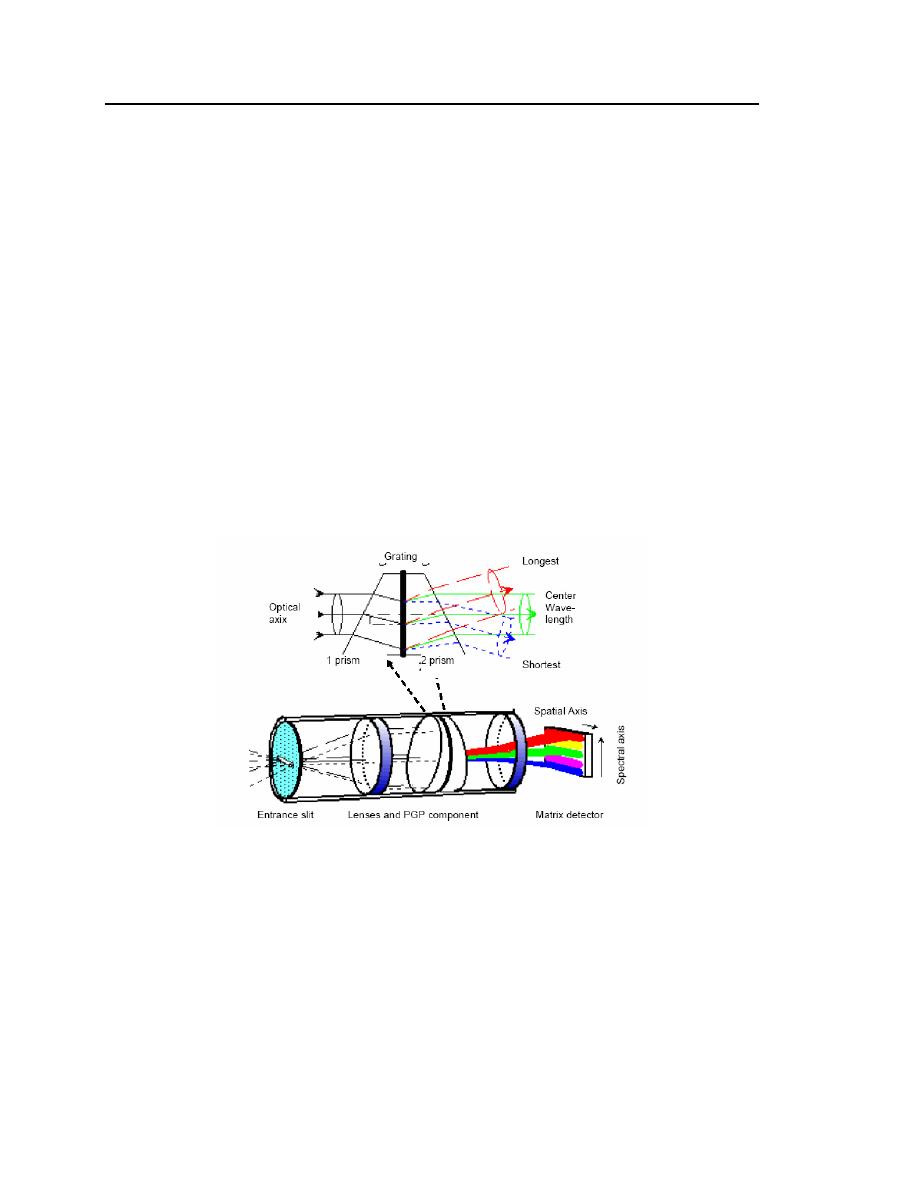
The basic operation of the direct-vision, dispersing prism-grating-prism
(PGP) spectrograph is illustrated in Figure 6. A spectrograph based on the PGP
element is composed of a narrow slit, a collimator lens, a PGP element, and a
focusing lens (Fig. 6). Radiation entering the spectrograph through the slit is
collimated by the first lens and refracted at the prism surface to the right incident
angle of the holographic grating. The grating disperses the light according to the
common grating equation. Spatial information on the entrance slit is transferred
to the image plane at the axis parallel to the slit length direction. The spectrum is
formed perpendicular to the optical axis with a good spectral linearity. The
tubular direct vision (on-axis) construction leads to low geometrical aberrations
in both the spatial and the spectral axes. The optical properties are further guar-
anteed by using very high quality triplet lenses that are specially designed for
imaging.
Figure 6. Direct-vision, dispersing prism-grating-prism (PGP)
spectrograph used in the AISA sensor.
2.3.1
Operating Modes
AISA provides flexibility in its operation mode, depending on user-defined
image requirements.. There are four operation modes, which are programmable




 Previous Page
Previous Page
