Table 10. Effect of residual water in acetonitrile on peak heights of
various analytes.
Conc.
Mean peak height (n = 2)
(g/L)
Analyte
0% water
5% water 10% water 15% water
20% water
DNB
25
783
700
718
756
755
2,6-DNT
25
2279
2142
2199
2279
2226
2,4-DNT
25
1458
1339
1408
1436
1427
TNB
25
1023
889
930
962
1038
TNT
25
2125
2001
2073
2149
2202
RDX
50
2963
2684
2740
2808
2695
4-Am-DNT
25
1688
1450
1502
1668
1613
2-Am-DNT
25
1953
1697
1757
1919
1856
HMX
250
9271
7421
9405
10211
9206
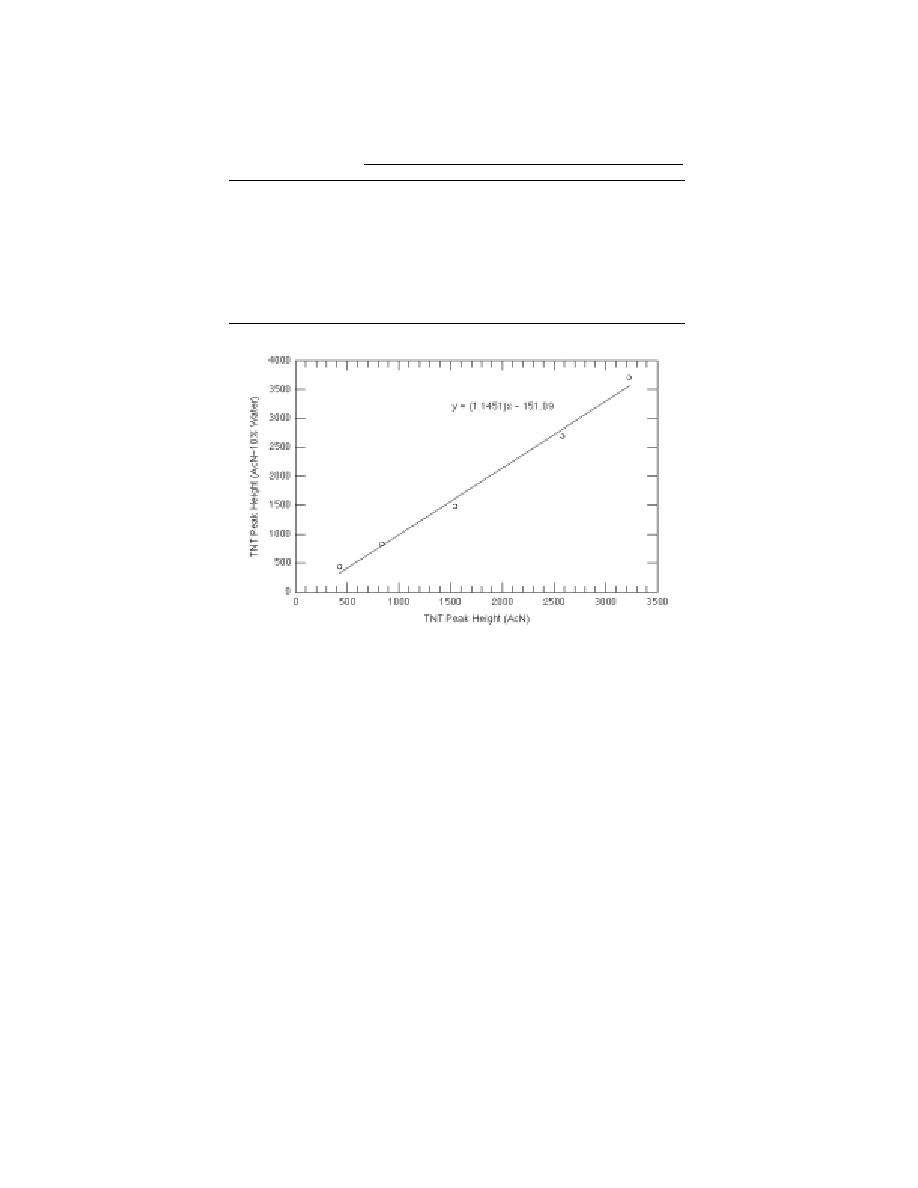
Figure 6. TNT peak heights for acetonitrile solutions containing
10% water vs. solutions without water. Concentrations of TNT were
2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 30 g/L.
prior to analysis.) We found good recovery for all
Problems such as low recovery of the nitramines
the analytes by both methods. In general, repeat-
and interfering peaks in HPLC chromatograms
ability was better using HPLC-UV. Overall, the
have been solved (Jenkins et al. 1995). We per-
formed an initial spike recovery study using the
results indicated that SPE with acetonitrile elu-
two SPE protocols that are expected to be includ-
tion was a feasible sample preparation procedure
ed in SW-846 Update IV for Method 8330A. These
prior to GC-ECD.
protocols specify preconcentration with Empore
SDB-RPS (47-mm-diameter) disks or the Water
Field samples
Sep-Pak Vac Porapak RDX cartridges, and analyte
We analyzed several solid-phase extracts of
elution with acetonitrile. The purpose of this ini-
water samples collected from various explosives-
tial spike recovery was to determine whether a
contaminated sites. These included extracts from
solid-phase extract prepared for analysis by
LAAP in which 500-mL samples were preconcen-
Method 8330 could also be analyzed by GC-ECD.
trated using Porapak RDX cartridges and eluted
Using both disks and cartridges, we precon-
with 5 mL acetonitrile. These extracts were pre-
centrated duplicate 50-mL samples spiked at
pared and analyzed by HPLC at the U.S. Army
5-g/L aqueous concentration for most of the
Engineer Waterways Experiment Station (Vicks-
analytes (Table 11). We divided each 5.0-mL ace-
burg, Mississippi). Water samples from Umatilla
tonitrile extract and analyzed each by GC-ECD
Army Depot and CFB-Valcartier were precon-
and HPLC-UV. (The portion of acetonitrile extract
centrated at CRREL using either cartridges or Em-
used for HPLC was mixed 1/1 v/v with water
pore disks, with the HPLC analysis performed at
12




 Previous Page
Previous Page
