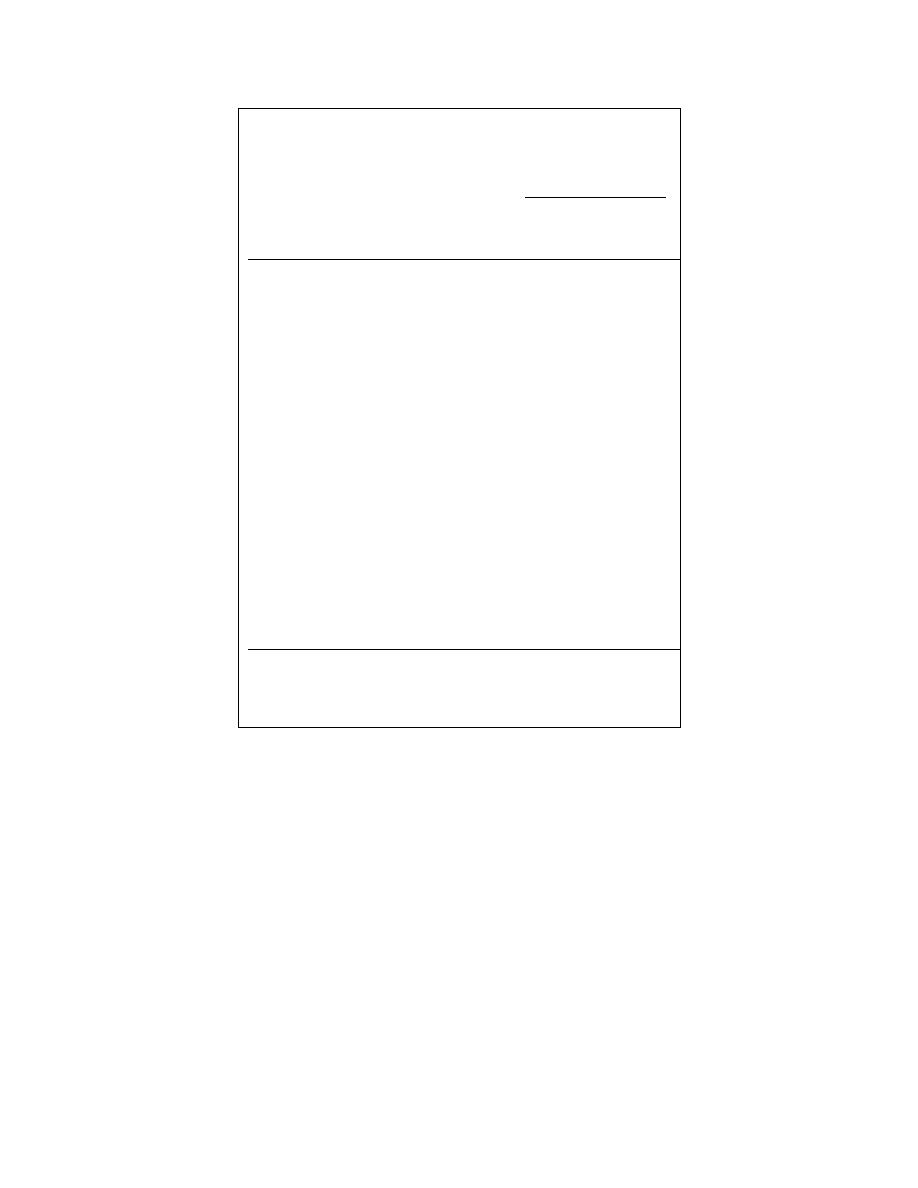
Table 9. Percent recoveries and relative percent differences esti-
mated by the off-site laboratories and on-site by the technology
developer for the matrix spike duplicates.
Hanby
CRREL
Ref. Lab
HM 2000
Sample
% Recov.
% Recov.
Visual
%Recov.
no./ID
(% RPD)
(% RPD)
% Recov.
(% RPD)
GRO
SG-6, 7
88
160
170
160
(100 mg TPH/kg)
(4.5)
(50)
(0)
SG-20, 20
91
92
97
123
(500 mg TPH/kg)
(2.2)
(8.7)
(34)
IF*
WG-6, 7
53
46
310
(0.48 mg TPH/kg)
(28)
(27)
IF
SL**
WG-15, 16
81
46
SL
(24 mg TPH/kg)
(15)
(0)
SL
SL
DRO
NA†
SDM-6, 7
78
180
310
(250 mg TPH/kg)
NA
(5.1)
(10)
SDM-21, 22
NA
65
250
160
(1000 mg TPH/kg)
NA
(77)
(38)
91.6*
WDM-1, 2
NA
70
<5
(0.98 mg TPH/kg)
NA
--
OR††
WDM-16, 17
NA
NR†
170
(24 mg/kg TPH/kg)
NA
NR
OR
RRO
43*
M1, M9
NA
95
60
(1000 mg TPH/kg)
NA
--
(12)
* Instrument failure.
** Sample lost.
† NA= not analyzed; NR = not reported.
†† Greater than value reported.
Protection Agency as a reliable field screening method
different hydrocarbon ranges and matrices still had to
for TPH in environmental matrices (EPA 1993). The
be developed. Sample analysis was completed after the
highest data-quality level that has been assigned to this
HM 2000 was serviced by the company that had devel-
technique states that it is capable of producing TPH
oped the software program, in which all of the soft-
values that are within an order of magnitude of the true
ware and applications were reloaded back onto the
or accepted concentration (EPA 1997). The performance
laptop computer that had been furnished with the HM
of the visual method of analysis for the QA samples
2000 analyzer. A final data report was available 12 days
distributed during this field exercise supports this clas-
after the end of the field exercise. Soon after sending in
sification, as there were no TPH values outside of this
this final data report, the technology developer recom-
range. Indeed, there were only a couple of values yielded
mended that the TPH values yielded by HM 2010 be
(Table 5b, WG-2, WG-4, and WG-7) by the visual
omitted from this evaluation.
method of analysis that were a factor of 5 or slightly
greater than the expected concentration. One of the fea-
DISCUSSION
tures of the HM 2000 is its ability to provide a digital-
readout of a discrete TPH value following sample analy-
sis. This feature removes the subjectivity associated with
The Hanby Test Kits and the visual method of analy-
a visual comparison of colors between samples and a
sis are currently recognized by the U.S. Environmental
14




 Previous Page
Previous Page
