Table 11. Average resilient modulus of subgrade soils as a function of temperature.
C
NH5
NH4
NH2
NH3
NH1
20.0
59 (8505)
289 (41,904)
45 (6570)
5.0
47 (6795)
35 (5080)
55 (7985)
43 (6284)
0.5
52 (7516)
38 (5458)
52 (7535)
315 (45,756)
54 (7820)
0.5
40 (5846)
3569 (517,576)
299 (43,310)
349 (50,583)
497 (72,099)
2.0
225 (32,653)
13,276 (1,925,517)
3585 (519,960)
1974 (286,245)
2736 (396,763)
5.0
1143 (165,769)
17,556 (2,546,266)
6174 (895,404)
2424 (351,524)
9737 (1,412,232)
10.0
2861 (414,959)
21,198 (3,074,546)
10,562 (1,531,915)
2527 (366,486)
15,833 (2,296394)
20.0
5335 (773,768)
10.0
3106 (450,546)
14,818 (2,149,167)
5.0
1586 (230,002)
18,064 (2,620,028)
6931 (1,005,290)
2452 (355,607)
7107 (1,030,833)
2.0
106 (15,445)
12,434 (1,803,385)
3851 (558,608)
2017 (292,569)
3327 (482,500)
0.5
24 (3477)
6386 (926,212)
577 (83,617)
995 (144,353)
1315 (190,736)
0.5
14 (2060)
15 (2108)
49 (7166)
223 (32,279)
176 (25,578)
5.0
14 (1991)
10 (1482)
20.0
48 (6981)
220 (31,863)
38 (5451)
MPa
psi
5
10
7
10
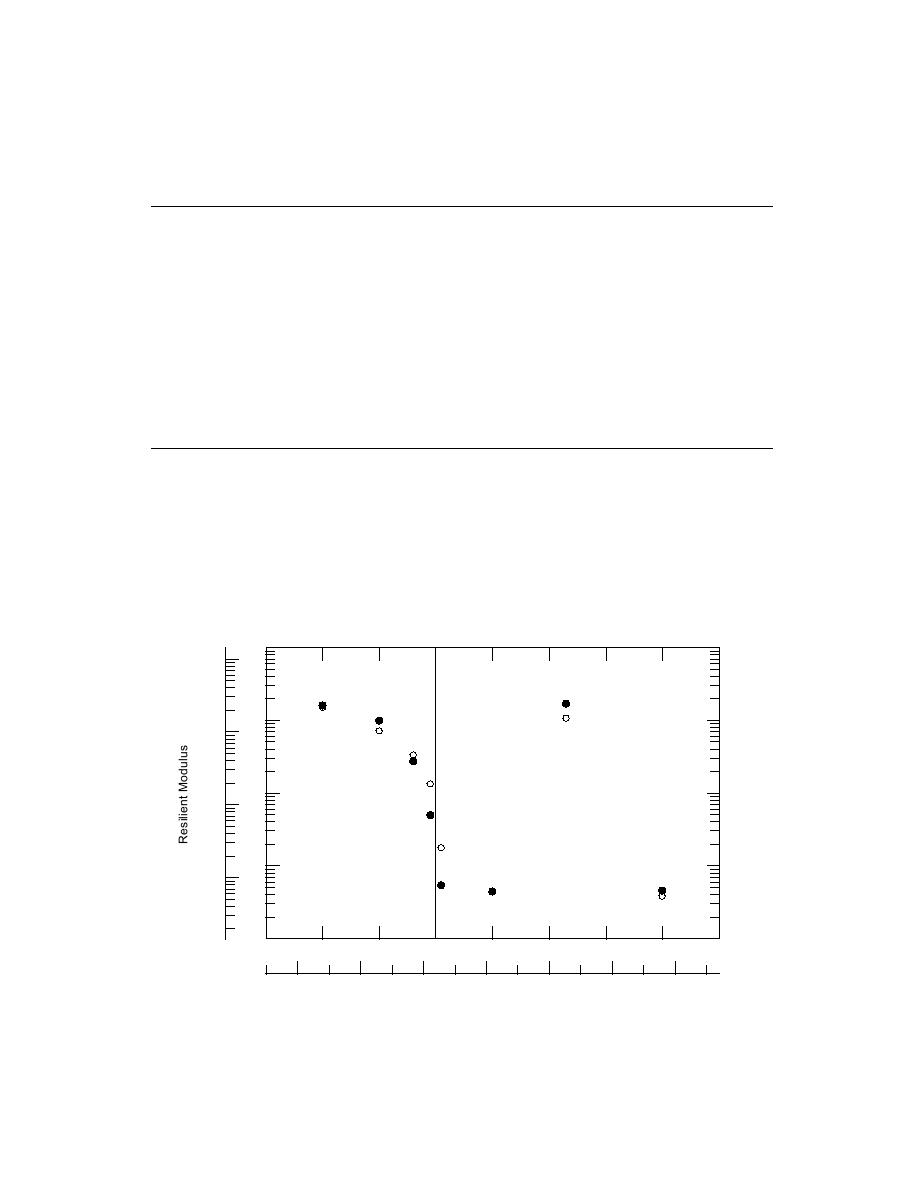
Silty Glacial Till
Unfrozen to Frozen
4
Frozen to Thaw
10
6
10
3
10
10 5
2
10
4
10
1
10
25 C
15
10
5
0
5
10
15
20
F
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Temperature
Figure 5. Effect of freezing and thawing on the resilient modulus of silty glacial till.
14




 Previous Page
Previous Page
