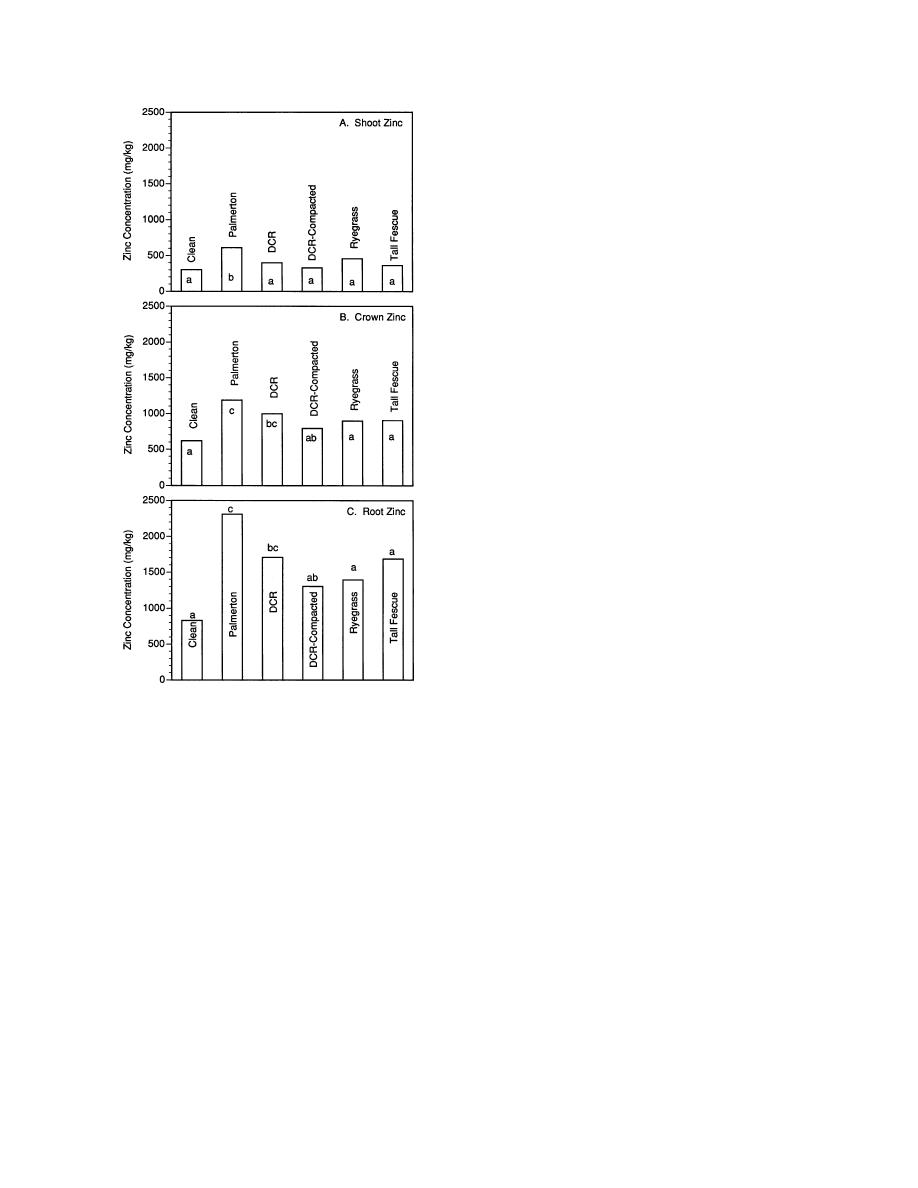
Figure 7. Plant Zn concentrations as affected by soil
treatment and plant species. A different lower-case
letter within the four soil treatments or the two plant
species implies a statistically significant difference
within soil treatments or plant species, respectively.
Palmerton soil (Fig. 7), were low in biomass (Fig.
organic constituents. Lower-molecular-weight
6). Conversely, the clean soil was high in biomass
volatile constituents, such as BTEX, are no doubt
but low in Zn concentrations. The consequence of
lost to volatilization; however, intermediate- and
this inverse relationship between biomass and Zn
higher-molecular-weight petroleum hydrocar-
concentrations are Zn uptakes that are indepen-
bons are probably largely sequestered into the
newly formed Ca(OH)2 matrix. The results were,
dent of soil treatment or plant species.
however, not consistent between wastes, indicat-
ing that the specific nature of the wastes will play
CONCLUSIONS
a major role in the efficacy of the DCR process to
The DCR process was originally developed for
remediate the wastes.
the immobilization of heavily oiled sludges,
We also examined two organic wastes that
water-in-oil emulsions, oil-contaminated wastes,
were solids at the prevailing temperature. One
and industrial wastes such as acid-tars (Boelsing
was the asphalt tar from Shemya, and the other
1988, 1995). All of these wastes contain liquid
was the pesticides from Rocky Mt. Arsenal. In
hydrocarbons. Only the three laboratory-scale
neither case was there a significant overall im-
tests on Shemya wastes were tests of the efficacy
provement in chemical properties due to the DCR
of the DCR process to stabilize liquid hydrocar-
treatment (Tables 4, 5, 8, 9). In some cases, there
bons. The DCR process caused a major decrease
were actual increases in organic concentrations;
in many monitored hydrocarbons (Table 6). Both
in other cases, reductions in organic concentra-
volatilization and Ca(OH)2 encapsulation may
tions could be accounted for primarily as a dilu-
have played a role in the disappearance of these
tion effect. It would appear that unless the hydro-
17




 Previous Page
Previous Page
