100
3% Fines
80
5% Fines
60
10% Fines
U (%)
40
15% Fines
20
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
Drainage Time (days)
Figure 16. Effect of fines content on drainage.
the airport consisted of 330 mm (13 in.) of AC, 584
mm (23 in.) of base and 914 mm (36 in.) of subbase
over a silty, fine sand subgrade. The base and sub-
base gradations are shown in Figure 18. The sub-
base falls within the FAA P-154 specifications,
while the base falls within the P-208 aggregate
base course specifications. The percentage passing
the no. 200 sieve for either material was approxi-
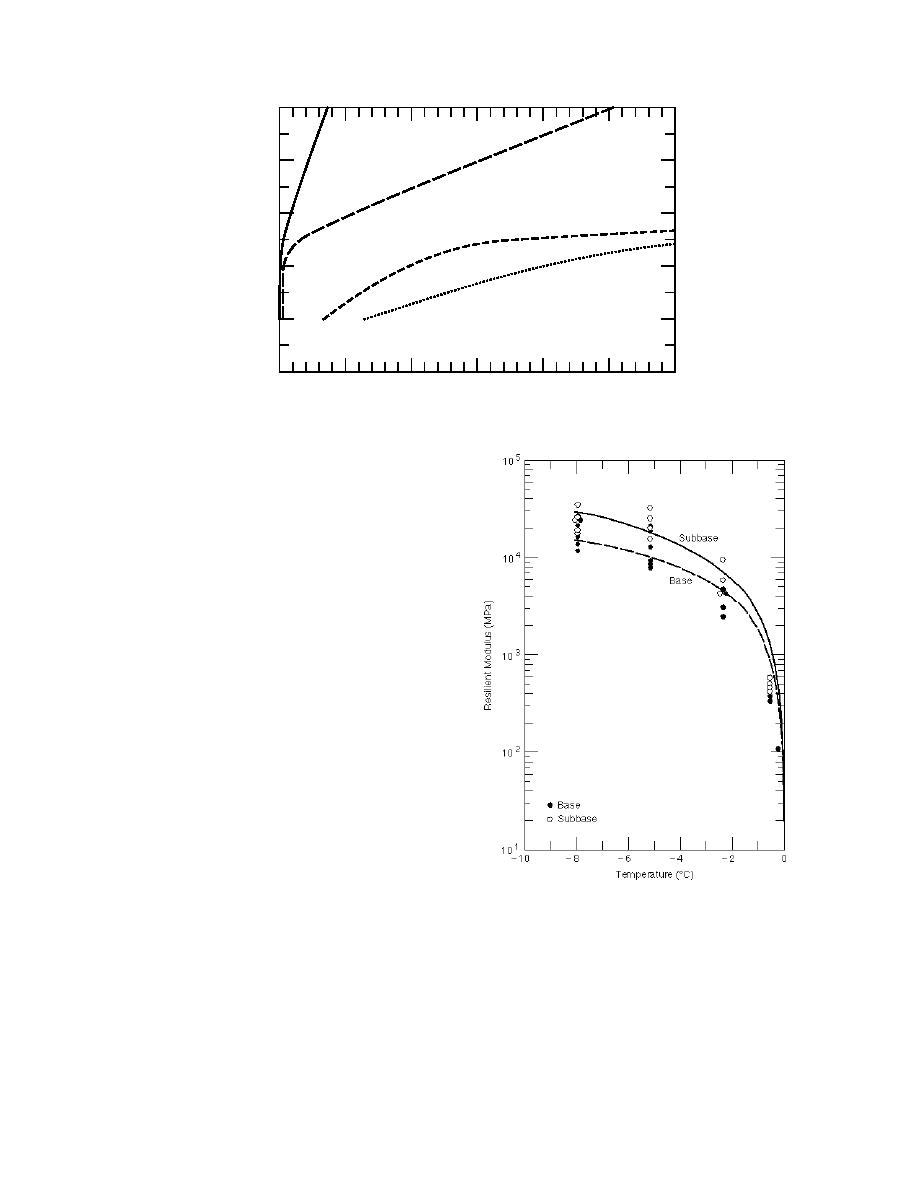
mately 12%. The results in Figure 17 were deter-
mined from laboratory tests and clearly show that,
as the base and subbase material thawed, there is a
significant decrease in the material modulus.
Other indications of the reduction of the bear-
ing capacity of base and subbase were obtained
from field CBR tests by the COE in the mid-1940s.
In-place CBR tests were conducted on the top of
the base or on top of the subgrades at several air-
fields (flexible) during the fall and in the thaw-
weakening period in the spring. Table 15 shows
the change in average CBR during the normal and
thaw-weakening periods on top of the base and
subbase layers. The base and subbase materials in
the table are classified using the United Soil Classi-
fication System. When possible, the amount of fines
in the material is shown in the table. There is a reduc-
Figure 17. Change in resilient modulus of base and
tion of 13 to 62% in CBR during the thaw-weakening
subbase during thaw (1 kip/in.2 = 6.89 MPa).
period. Factors that would affect the amount of re-
duction are the depth of frost penetration, fines
ized materials are inferred from the freezethaw
content, and permeability of the base or subbase
durability tests (D559 and D560, ASTM 1992c,
layers.
1996). The results of these tests simply show
Stabilized materials such as the lime-treated
whether or not the material would retain a speci-
subgrade (P-155), soilcement base (P-301),
fied percentage of weight at the end of 12 cycles of
cement-treated base (P-304) and econocrete sub-
freezethaw cycling. If it does, then it is consid-
base (P-306) are classified as cementatious materi-
ered to be frost resistant. The results from the du-
als. The thaw-weakening resistance of these stabil-
rability test cannot be used as engineering proper-
21




 Previous Page
Previous Page
