a. High velocity: shear plug out.
b. Low velocity: no shear plug-out.
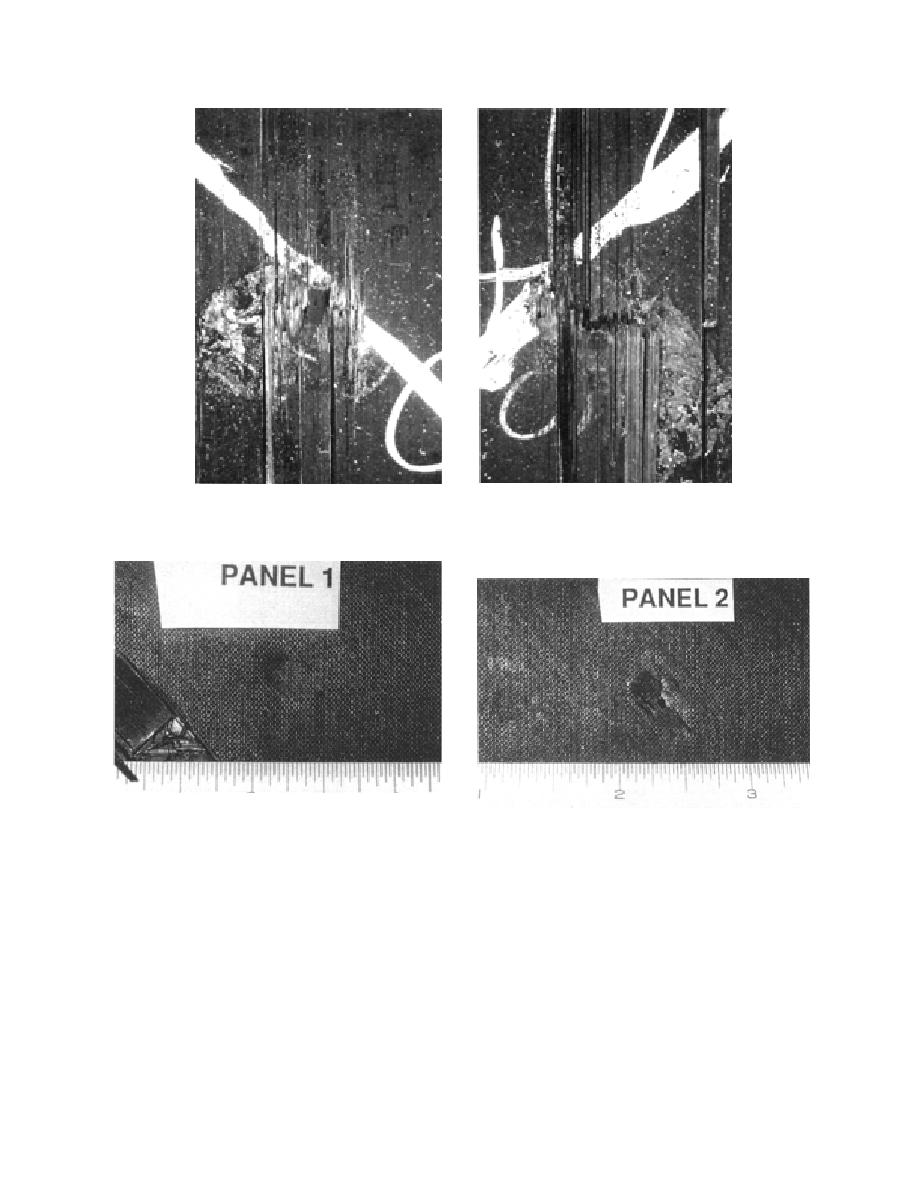
Figure 5.Effect of velocity on the damage of unidirectional Gr/Ep plates.
a. Low velocity impact damage (unperforated).
b. High velocity impact damage (unperforated).
Figure 6. Impact damages to quasi-isotropic composite plates.
seemed to contain interlaminar joint surfaces.
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROGRAPH
Fibers oriented in 45 and 90 angles are clearly
ANALYSIS OF BALLISTIC FRAGMENTS
visible in these fragments. Many of the samples
As mentioned before, the composite fragments
in this category of tests showed hackle marks (Fig.
from the 30-ply Gr/Ep target panels were collect-
7a, b).
ed on the adhesive-coated paper, lining both the
front and rear sides of the target test chamber. As
expected more fragments were collected on the
DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
rear side. Most particles appeared to be of longi-
tudinal shapes, indicating that fragmentation hap-
The results of nonperforated low-velocity im-
pened by crack propagation more in the direction
pact, perforated low-velocity impact, and the per-
of the fibers than across it. A few larger pieces
forated high-velocity impact manifest progressive
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
