Table 14. Explanation of the surface routing variables.
Initial
Variable
Description
condition
Units
DSa
adjusted depression storage depth
0
mm
I
inflow to linear reservoir
0
mm/h
INFLOW_2
inflow to lag and route structure
0
mm/h
INFLOW _5
inflow to linear reservoir
0
mm/h
K
linear reservoir lag
15
h
KOa
adjusted overland linear reservoir lag
15
h
KL
first linear reservoir lag
12.5
h
LG_RT_STOR
lag and route storage
0
mm
LIN_RES_STOR
linear reservoir storage
0
mm
O
outflow from linear reservoir
0
mm/h
OUTFLOW_2
outflow from LG RT STOR
0
mm/h
OUTFLOW _5
outflow from LIN RES STOR
0
mm/h
OUTFL_2_LAG
OUTFLOW 2 lagged by TLO
0
mm/h
m3 h/s
RSUM
total surface runoff
0
m3/s
S
storage in linear reservoir
0
SRF_RUNOFF
surface runoff
0
mm
SURF1w
weighted surface runoff from GROFF1
0
mm/h
SURF2w
weighted surface runoff from GROFF2
0
mm/h
SURF3w
weighted surface runoff from GROFF3
0
mm/h
SURF4w
weighted surface runoff from GROFF4
0
mm/h
SURF5w
weighted surface runoff from GROFF5
0
mm/h
TLO
overland linear channel lag
5
h
LIN RES STOR
KOa
KL
TLO
OUTFLOW 5
INFLOW 5
SURF1w
LG RT STOR
SURF2w
OUTFLOW 2
OUOULOL 22 LAG
TF TFW LAG
SURF3w
INFLOW 2
RSUM
SURF4w
SRF RUNOFF
DA
SURF5w
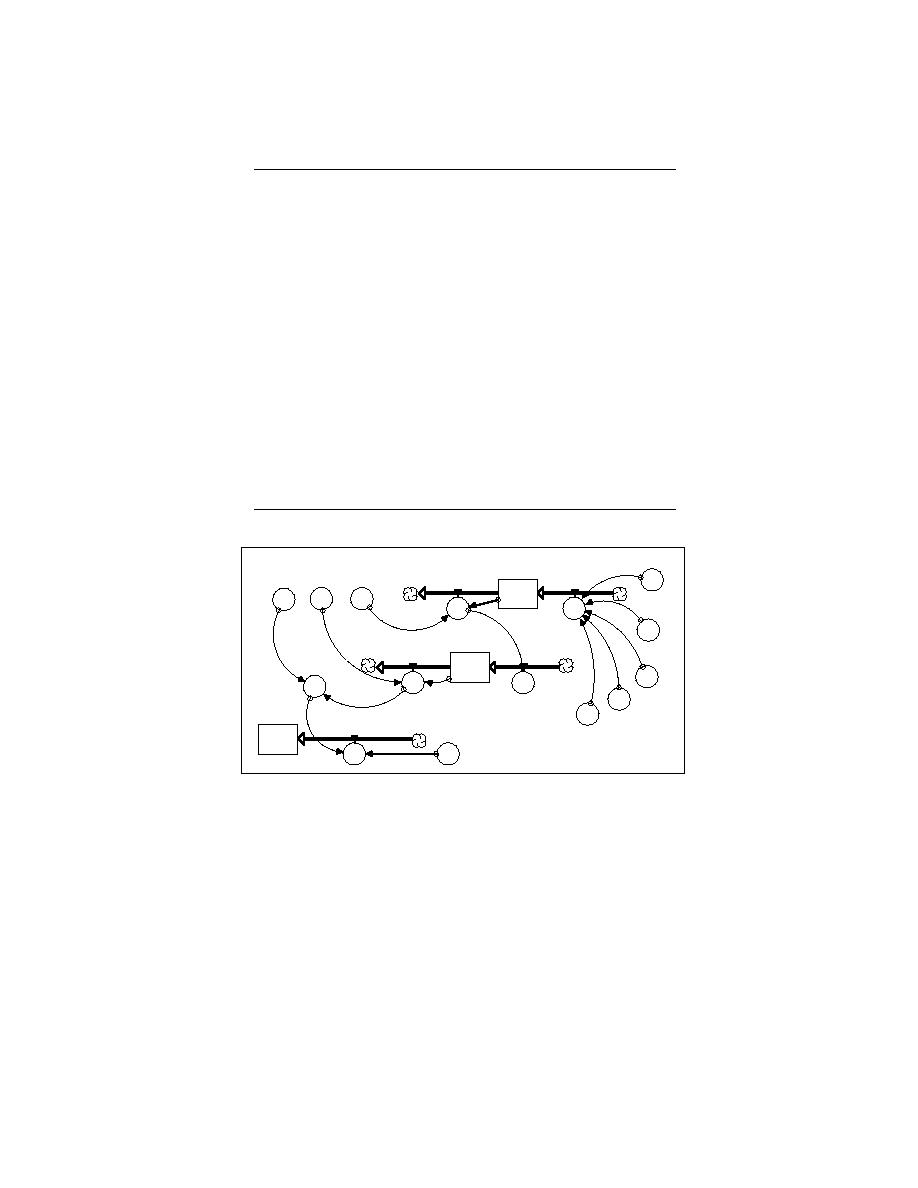
Figure 21. Runoff routing. Runoff is routed through a linear reservoir followed
by a lag and route structure to simulate the average time for a molecule of water
to travel as runoff to the outlet of a watershed. INFLOW_5, LIN_RES_STOR,
OUTFLOW_5, and KL collectively represent the linear reservoir. INFLOW_5
represents the input to the linear reservoir and contains the sum of SURF1w,
SURF2w, SURF3w, SURF4w, and SURF5w. The outflow from the linear reser-
voir in OUTFLOW_5 is lagged by the quotient of LIN_RES_STOR divided by
KL. The lagged outflow from the linear reservoir becomes the inflow to the lag
and route structure via INFLOW_2. INFLOW_2, LG_RT_STOR, OUT-
FLOW_2, OUTFLOW_2_LAG, and TLO represent the lag and route structure.
The lag and route structure is composed of a linear reservoir (represented by
INFLOW_2, LG_RT_STOR, and OUTFLOW_2) and a lag (represented by
OUTFLOW_2_LAG and TLO). In sum, the outflow from the lag and route
structure is lagged twice. First, the outflow is lagged in OUTFLOW_2 because
OUTFLOW_2 is the quotient of LG_RT_STOR divided by KOa and not the full
amount of water contained within LG_RT_STOR (eq 51). Second, the outflow
in OUTFLOW_2 is lagged in OUTFL_2_LAG by an amount specified in TLO
(eq 52).
33




 Previous Page
Previous Page
