the concentration of frazil floes is low during the
Czechoslovakia border. The 3000-ft-long boom
formation period, large sheets of shore ice are
stabilizes shore ice and prevents it from entering
broken or sawed free from locations below the
the forebay area. In conjunction with the effort to
boom and allowed to drift downstream to bridge
stabilize the shore ice, an ice-free main channel is
in the channel, promoting arch formation. Like
maintained, allowing for conveyance of floes
the International Section of the St. Lawrence,
from upstream through the gates on the dam.
booms were installed only after major channel
Two ice booms were installed on the lower
dredging projects failed to promote ice cover
Vistula River in Poland during the winter of 1986
growth at all critical locations. Also like the up-
to hasten the formation of a stable ice cover and
per St. Lawrence, the ice formation period is care-
help prevent hanging dam formation on the up-
per part of the Wloclawek Reservoir (Grzes 1989).
fully coordinated with flow control at hydro sta-
The first boom was located on the reservoir itself,
tions up and down the river, and a special ice
and the second on the free-flowing river up-
management group oversees the entire operation
stream of the reservoir. Similar to ice control on
(Billfalk 1984).
the International Section of the St. Lawrence,
A physical model study by Decsi and Sze-
boom placement was done in conjunction with
pessy (1988) aided in the design of an ice boom
on the Danube River, upstream of the dam on the
dredging to reduce the surface water current
velocity.
DunakilitiHrusov Reservoir, on the Hungary
Approximate Path of
Maximum Surface Velocity
ts
Uni
om
Bo
1989-'90
Boom
Deadman
Cable
Anchor
0
100 ft
1990-'91
Ice Boom
Cable
3 ft
2 ft
Connector
Chain
20 ft
PLAN VIEW
END VIEW
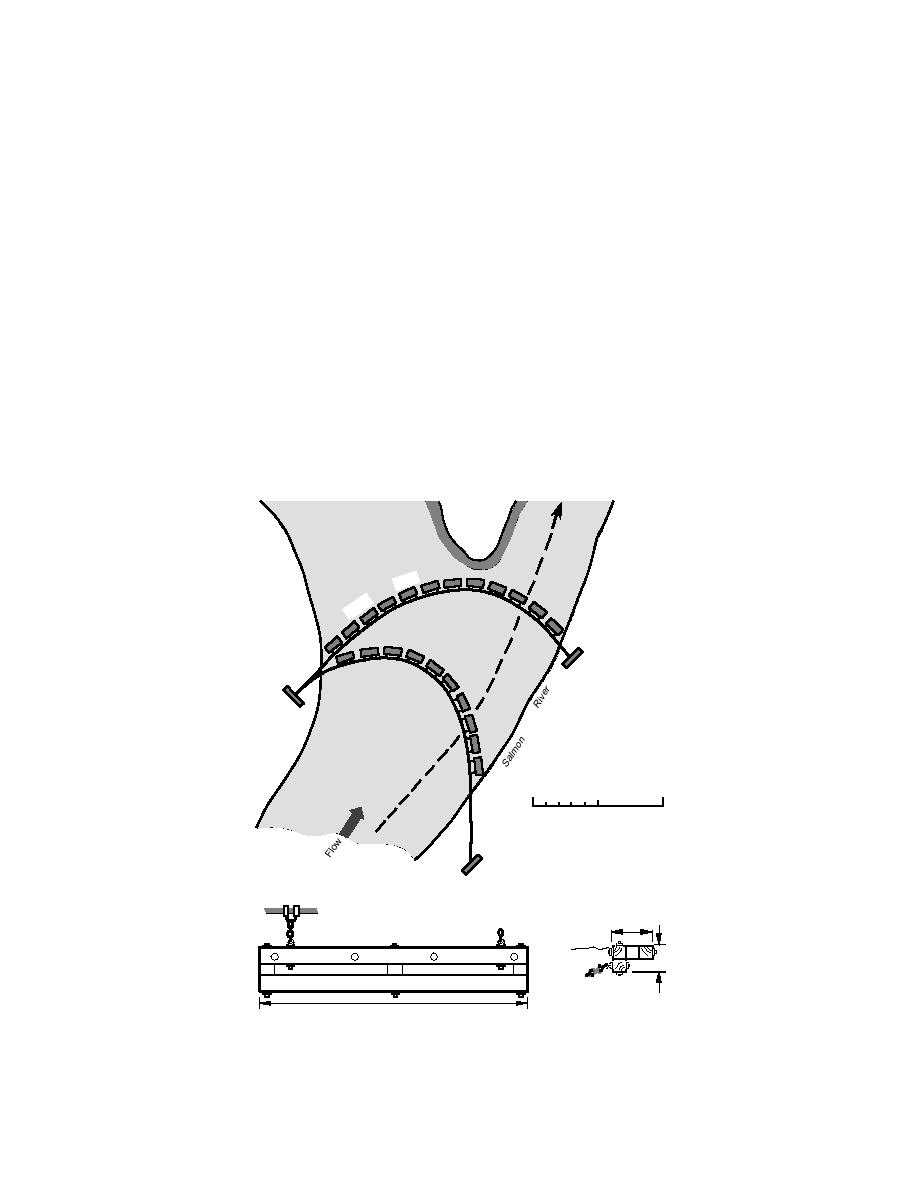
Figure 8. Two boom configurations tested at Salmon, Idaho.
8




 Previous Page
Previous Page
