1994 Arctic Ocean Section
60
60
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
10
10
0
0
70
80
90
80
70
80
90
80
Latitude (N)
Latitude (N)
Pacific
Atlantic
Pacific
Atlantic
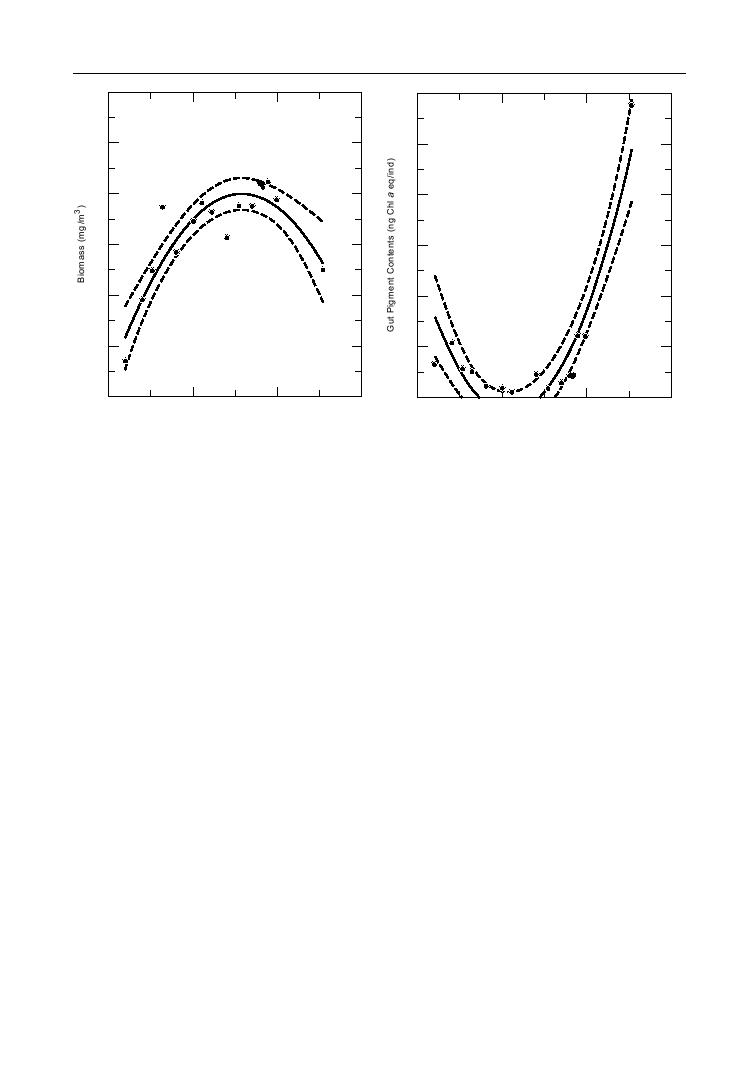
Gut pigment contents of Calanus hyperboreus female in
Mesozooplankton biomass in the upper 100 m along the
the upper 100 m along the transect. The solid line is a
transect. The solid line is a second-order regression, and
second-order regression, and the dashed lines show the
0.8158.
mesozooplankton population was high (6.58.5) compared to lower lati-
tudes (4.5), but it stayed in the range typical at high latitudes (6.312.5)
(Bamstedt 1986). The high lipid content (used as reserve) observed in the
zooplankton may explain these high values.
The Arctic mesozooplankton taxonomic composition did not change
along the transect and within the three depths. This population was mainly
represented by copepods (7090% of the total number) and specifically by
three large species (Calanus hyperboreus, C. glacialis and Metridia longa) and
three small genera (Oithona, Oncea and Paracalanus). However, the first group
of species accounts for more than 80% of the total biomass and includes
mainly late stages (C4, C5 and adult). The two species of Calanus are typi-
cal Arctic species. A third species of Calanus is present but less abundant
(C. finmarchicus, Atlantic species). The highest concentration of this species
was found at the last stations in the Nansen Basin, closest to the inflow of
Atlantic water. In total, 21 species of copepod were identified. This low
number is consistent with the diminution in the number of zooplankton
species with latitude (there are approximately 100 species in the Mediter-
ranean Sea). The other taxa were mainly amphipods, ostracods, pteropods,
isopods, chaetognaths, siphonophores, appendicularia, medusa and
euphausiacea.
The ingestion of phytoplankton by the main species of copepod was
estimated by analyzing the gut pigment content. The values are expressed
38




 Previous Page
Previous Page
