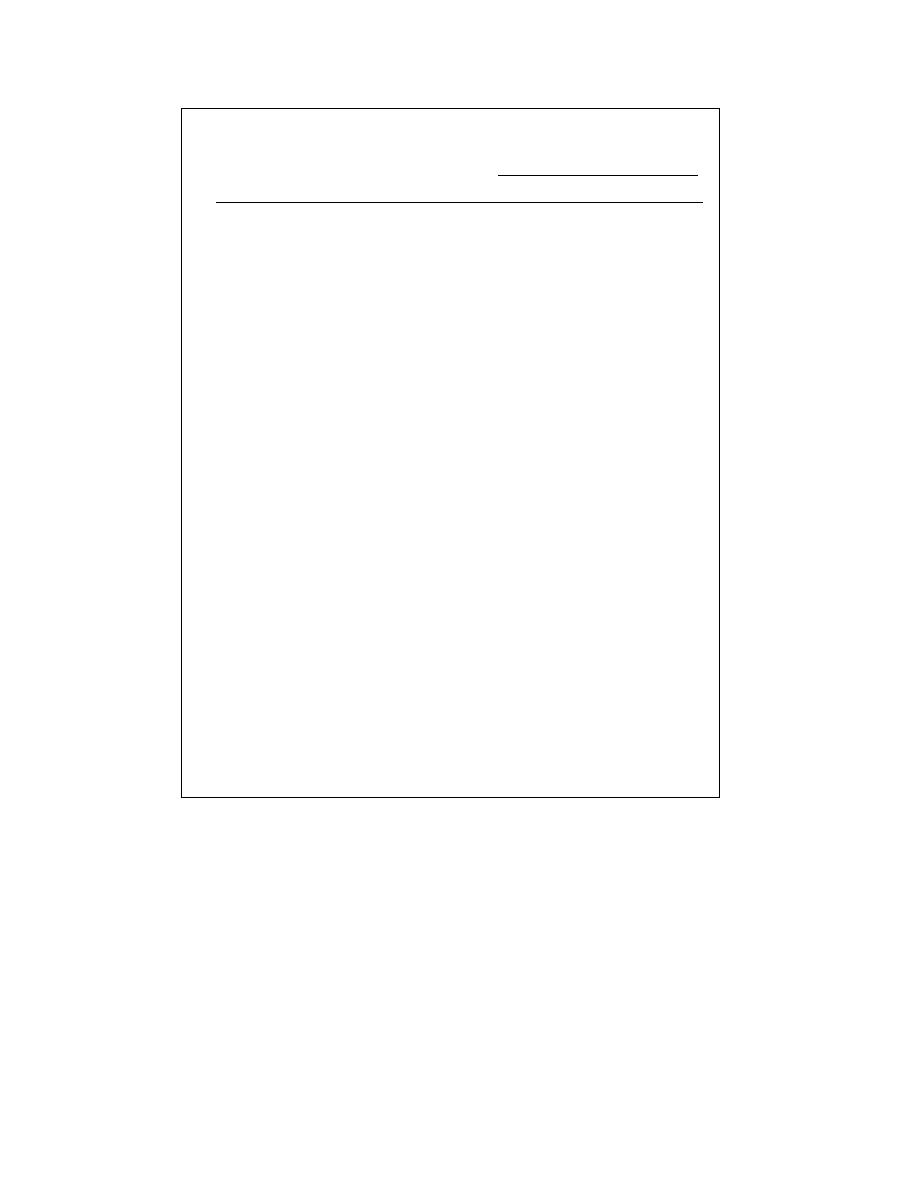
Table 5. Areal extents of ecotypes found within Fort Greely.
Area
Ecotype
ha
%
Alpine Rocky Dry Barrens
3,378
1.3
Alpine Rocky Dry Dwarf Scrub
2,659
1.0
Alpine Rocky Moist Low Scrub
10,570
4.1
Alpine Wet Tussock Meadow
6,698
2.6
Alpine Wet Low Scrub
8,139
3.1
Upland Rocky Dry Meadow
38
<0.1
Upland Rocky Dry Low Scrub
782
0.3
Upland Rocky Dry Broadleaf Forest
815
0.3
Upland Moist Low and Tall Scrub
13,233
5.1
Upland Moist Low and Tall Scrub - disturbed
10,455
4.0
Upland Moist Broadleaf Forest
5,462
2.1
Upland Moist Mixed Forest
4,938
1.9
Upland Moist Needleleaf Forest
12,401
4.8
Upland Wet Needleleaf Forest
509
0.2
Lowland Gravelly Dry Broadleaf Forest
947
0.4
Lowland Gravelly Moist Low Scrub
6,339
2.4
Lowland Gravelly Needleleaf Forest
5,896
2.3
Lowland Moist Tall Scrub
865
0.3
Lowland Low Scrub - disturbed
9,467
3.6
Lowland Wet Low Scrub
36,136
13.9
Lowland Tussock Scrub Bog
55,133
21.2
Lowland Wet Broadleaf Forest
985
0.4
Lowland Wet Mixed Forest
2,021
0.8
Lowland Wet Needleleaf Forest
29,967
11.5
Lacustrine Moist Meadow
6
<0.1
Ponds and Lakes
3,044
1.2
Riverine Gravelly Barrens
4,876
1.9
Riverine Gravelly Dry Dwarf Scrub
1,899
0.7
Riverine Gravelly Dry Broadleaf Forest
4,044
1.6
Riverine Gravelly Needleleaf Forest
4,119
1.6
Riverine Moist Low and Tall Scrub
1,263
0.5
Riverine Moist Broadleaf Forest
135
0.1
Riverine Moist Mixed Forest
688
0.3
Riverine Moist Needleleaf Forest
2,548
1.0
Upper Perennial River
8,106
3.1
Human Disturbed Barrens
1,115
0.4
Human Disturbed Scrub
556
0.2
Total
260,234
100
Ecotype characteristics
Eriophorum vaginatum, V. uliginosum, Ledum
Vegetation.The following discussion highlights
decumbens, Carex bigelowii, Empetrum nigrum, and
some of the similarities and differences in species com-
Sphagnum spp. In areas with water near the surface,
position among ecotypes. Ecotypes were grouped suc-
Eriophorum angustifolium, Carex aquatilis, Carex
cessively by physiography, soil texture and moisture,
canescens, Salix planifolia, Potentilla palustris, and
and vegetation structure to help us compare species
Sphagnum spp. were important.
composition (Table 6).
In upland areas, there also were large differences in
Alpine ecotypes were either rocky or mixed texture
the floristics between dry rocky soils and moist loamy
classes. Ecotypes with exposed, dry rocky soils were
soils, but floristics were similar among forest types, with
dominated by Dryas octopetala, Arctostaphylos alpina,
differences mostly occurring only in dominance of tree
Vaccinium uliginosum, Cassiope tetragona, Oxytropis
species (Table 6b). Steep, rocky bluffs were dominated
nigrescens, Hierochloe alpina, Stereocaulon spp., and
by Artemisia frigida, Calamagrostis purpurascens,
other lichens (Table 6a). Wetter ecotypes on loamy or
Juniperus communis, and crustose lichens, whereas less
organic soils were dominated by Betula nana,
exposed dry sites were dominated by Populus
30




 Previous Page
Previous Page
