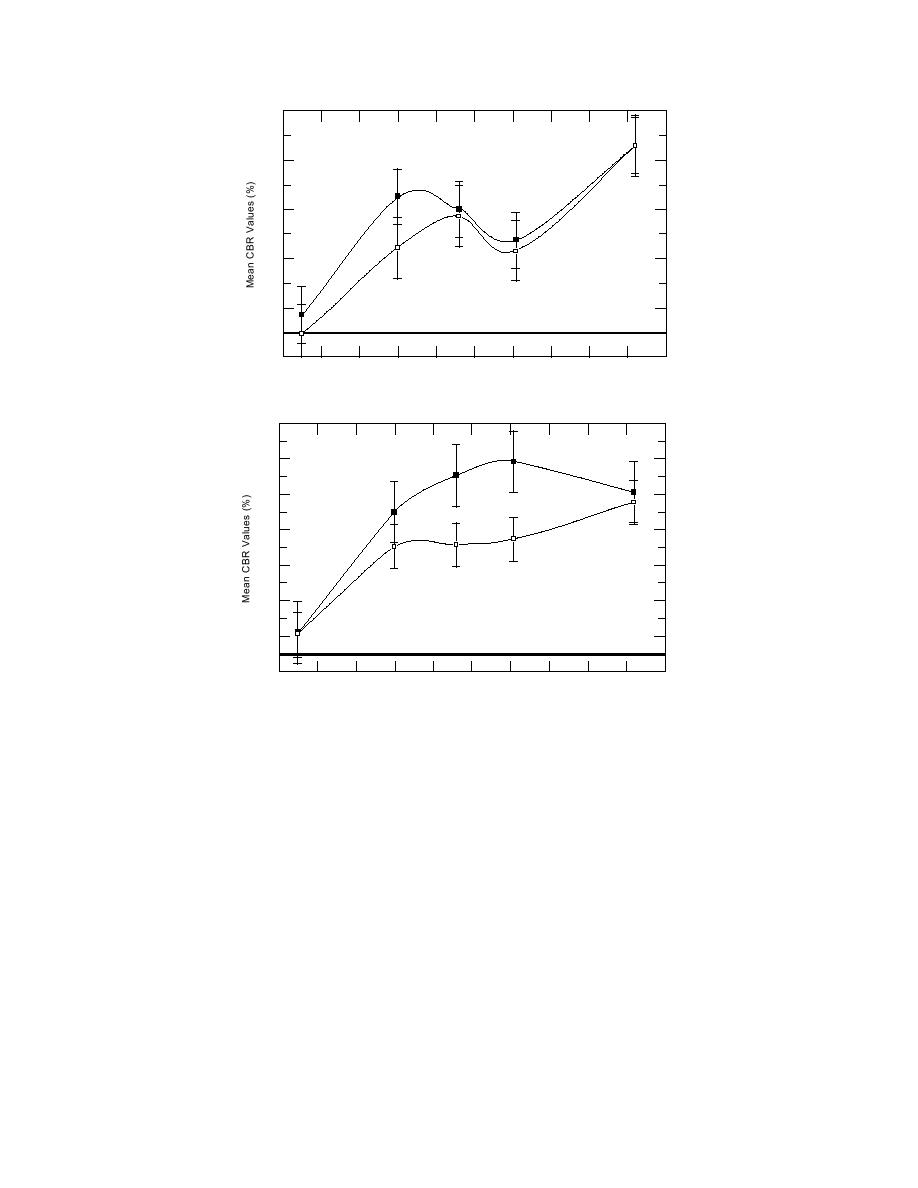
100
80
60
40
20
CBR 10 Limit
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
Depth (mm)
a. Field test site 1.
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
CBR 10 Limit
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
Depth (mm)
b. Field test site 2.
Figure 14. Comparison of mean CBR values with depth for December
and March.
LITERATURE CITED
American Society for Testing and Materials (1992)
pressive strength of cement-stabilized soils.
Standard test methods for laboratory compaction
Transportation Research Record, no. 1295.
characteristics of soil using modified effort [56,000
Webster, S. L., R.H. Grau, T.P. Williams (1992) De-
ft-lbf/ft3 (2,700 kN-m/m3)]. ASTM D1557-91.
scription and application of dual mass dynamic
American Society for Testing and Materials (1985)
cone penetrometer. USAE Waterways Experi-
Compressive strength of molded soilcement cyl-
ment Station, Vicksburg, Mississippi, Instruction
inders. ASTM D1633-84.
Report GL923.
Kessler Soils Engineering Products, Inc. (1996)
Yoder, E.J., D.G. Shurig, and B. Colucci-Rios (1982)
DM Soil Tester User's Manual. Kessler Soils Engi-
Evaluation of existing aggregate roads to deter-
neering Products, Inc., Springfield, Virginia.
mine suitability for resurfacing. Transportation
Research Record, no. 875, p. 17.
Okamoto, P.A., B.T. Bock, and P.J. Nussbaum
(1991) Nondestructive tests for determining com-
11




 Previous Page
Previous Page
