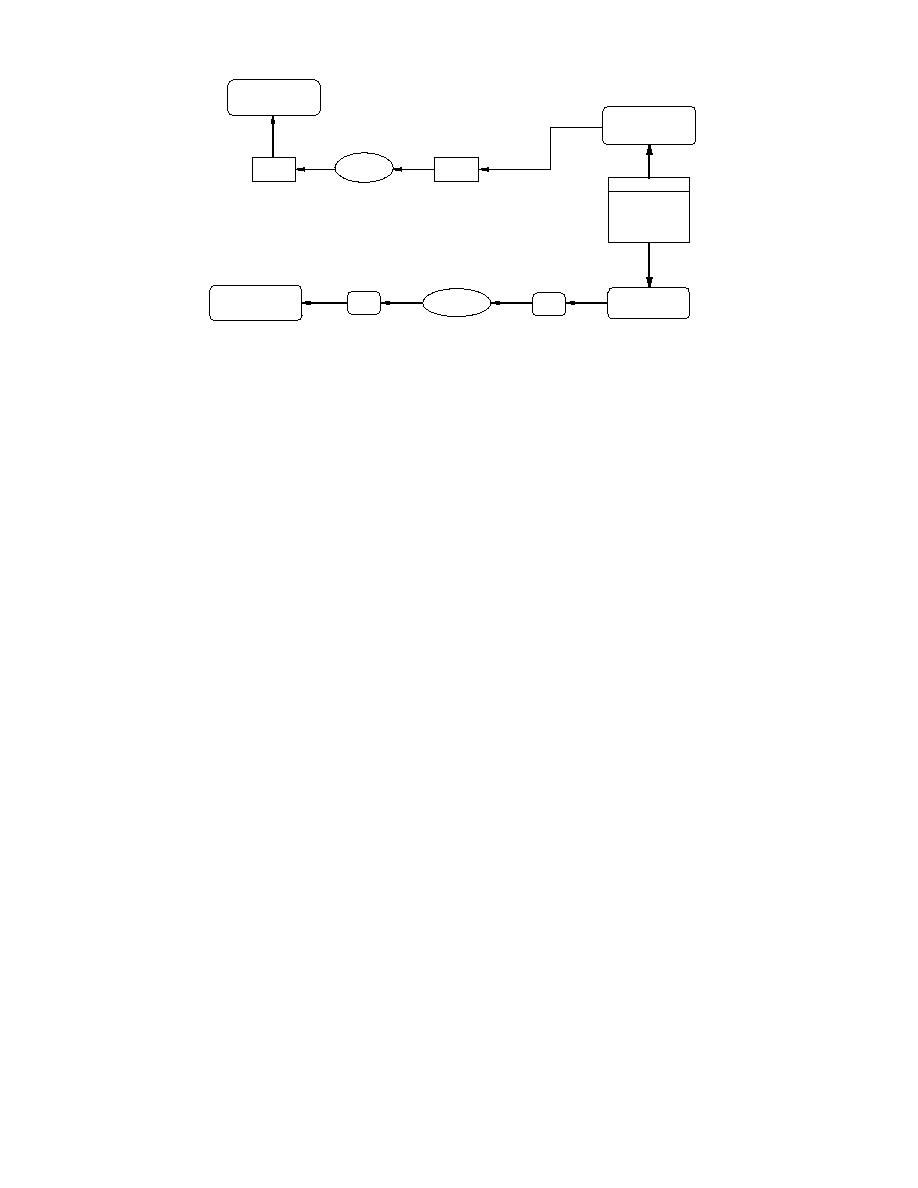
Branch Site
(Microsoft ACCESS
in retrieval mode)
Home Base
PC Anywhere
Host
Phone
Read Only
Modem
Modem
Line
HARD DISK
File transfer over modem.
Download database to remote site.
Ice Database
Read Only
File transfer over internet.
Download database to remote site.
Branch Site
Home Base
(Microsoft ACCESS
INTERNET
FTP/NFS Server
in retrieval mode)
Bridge/Router
Bridge/Router
TCP/IP
TCP/IP
Figure 21. Schematic of complete data download before processing.
communication cost for downloading (no session
extent of damages justifies their cost. Although
costs). The disadvantages are that data may need
the majority of the structural mitigation tech-
to be downloaded repeatedly to stay current, and
niques are, by their very nature, permanent, some
local changes to the database are not reflected
are designed to be removable. These removable
at the home base.
structures are usually installed at the beginning
of winter and removed after spring breakup, when
the threat of ice-jam flooding no longer exists.
Nonstructural measures are those that modi-
ICE JAM MITIGATION
fy vulnerability to flooding or reduce the sever-
MEASURES
ity of ice-jam-related floods. They are generally
A number of ice jam flood mitigation mea-
less expensive than structural solutions. The
sures are possible, depending on the type, length,
majority of the nonstructural techniques are
thickness and accessibility of the jam and the avail-
used for advance and emergency measures
able equipment, personnel and budget. These
when serious ice-jam flooding is imminent or
measures may be broadly labeled as structural or
already occurring. For example, ice weakening
nonstructural; as measures appropriate to control
(ice cutting or dusting) may be implemented be-
breakup or freeze-up jams; and finally, as mea-
fore an ice jam occurs, if sufficient warning is
sures that are permanent, deployed in advance of
provided, while blasting and mechanical removal
an anticipated flood threat, or deployed under
are often employed as emergency mitigation mea-
emergency conditions when a jam has formed and
sures once ice jams have occurred. On the other
flooding has occurred. A brief overview of possi-
hand, the creation of ice-storage zones upstream
ble mitigation measures is followed by a discus-
from a known jam site (to minimize the amount
sion of measures that might be applied in the
of ice reaching the jam site) can be considered a
study area.
permanent measure, since these areas, once es-
Structural measures for ice-jam control, such
tablished and properly maintained, can be used
as levees, dikes and floodwalls, may incorporate
year after year.
features that can be used to alleviate open-water
Freeze-up ice-jam control usually targets the
flooding as well. The costs of such measures in-
production and transport of the frazil ice which
clude construction, operation and land acquisi-
makes up the jam. This may be accomplished by
tion, as well as costs associated with recreation
encouraging the growth of an ice cover, which
and environmental mitigation. Unfortunately,
insulates the water beneath, decreasing the pro-
while they are often very successful, structural
duction of frazil ice. The ice cover can also incor-
solutions tend to be expensive, and current bud-
porate frazil ice which is transported from up-
get climates make their funding less likely. They
stream production areas, decreasing the supply
remain appropriate for rivers where chronic or
available to jam or deposit beneath a downstream
particularly serious threats persist and where the
ice cover.
37




 Previous Page
Previous Page
