Hut Point
Peninsula
Scott Base
Williams Field
Pegasus
Ross Ice
Site
Shelf
White
Island
Black
Island
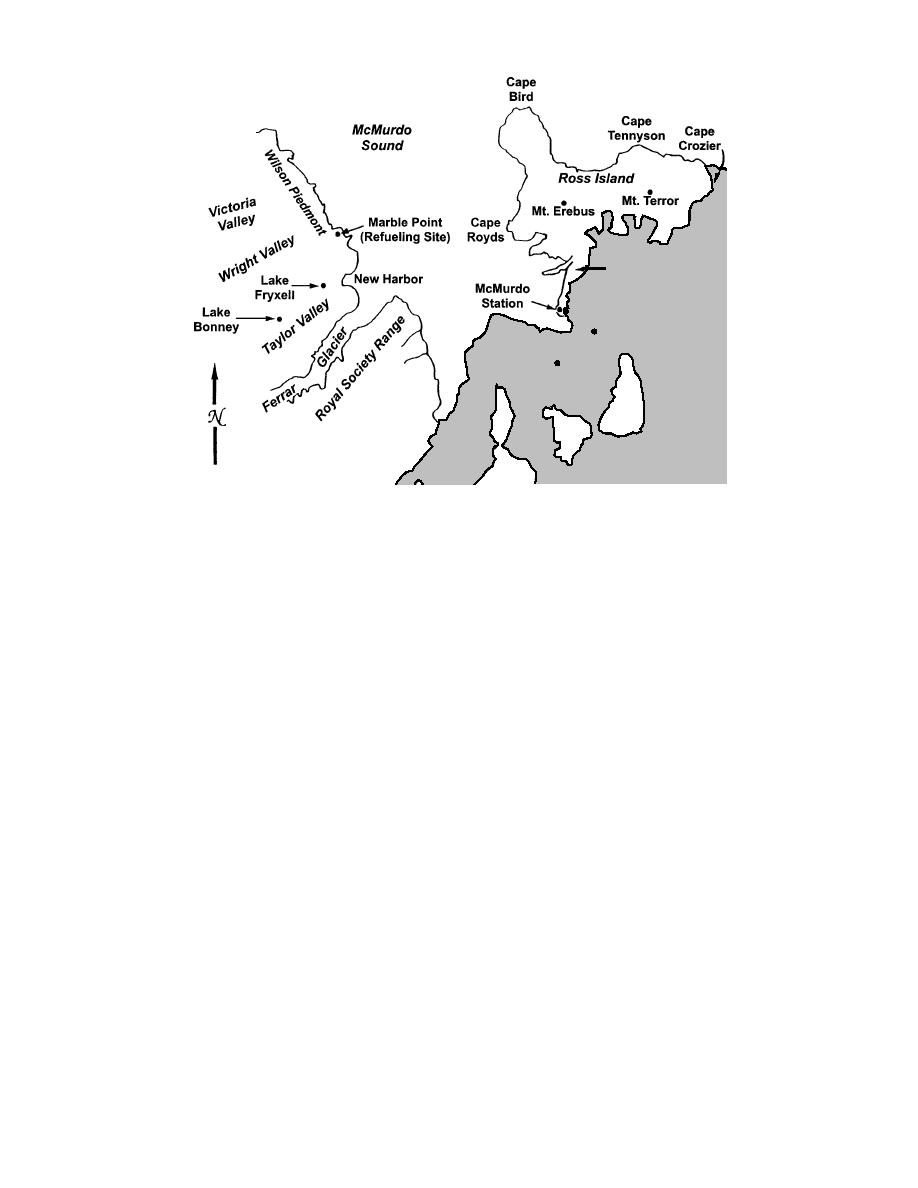
Figure B2. McMurdo Sound and vicinity. (From NSF 1991.)
Development of a compacted-snow
The concept for the Pegasus I runway is to
runway at the Pegasus site (Pegasus I)
prepare a compacted-snow runway by placing
The USAP, with the assistance of the Cold Re-
and subsequently compacting a thin (25-cm) layer
gions Research and Engineering Laboratory
of snow over the blue-ice base (Blaisdell et al.
(CRREL), has been investigating the feasibility of
1992). Initial work on the Pegasus I runway in-
constructing either a compacted-snow (Pegasus
volved stripping off the snow cover into wind-
I) or a blue-ice runway (Pegasus II) at the Pegasus
rows and redistributing the snow with graders
site since 1987 (Fig. B3). The Pegasus site is the
and snow planes. The snow was compacted using
only blue ice (snow ablation zone) in reasonable
a variety of machinery that was available at
proximity to McMurdo Station. A Pegasus run-
McMurdo and Williams Field. The density of the
way would be 10,500 ft long and would be lo-
compacted snow that was obtained was not suffi-
cated on the ice shelf between Black and White
ciently great to support test landings during the
Islands, known as "Herbie Alley," oriented ap-
first season. When conditions were favorable in
proximately northsouth towards McMurdo (Fig.
the following December (1991), the runway was
B3). As noted earlier, the main use is anticipated
compacted with a heavy pneumatic-tire roller.
to be redeployment of personnel at the end of the
Problems were encountered with snow melt at
austral summer season in February. Once proven,
the southern end of the runway and much of the
the possibility of using the runway for winter fly-
snow cover was lost in January at that end of the
in ("WINFLY") and of accessing McMurdo Sta-
runway.
tion during the winter may be considered.
Two test landings were made on the Pegasus
Work at the Pegasus site was initiated during
runway during the 199192 season. An empty
the 198990 season and has continued through
LC-130 on a return flight from the South Pole
the 199293 season. Environmental impacts of the
made a ski landing then taxied on wheels the full
experimental work performed were addressed in
length of the runway and took off. The second
an Environmental Action Memorandum (NSF
test landing involved a fully loaded LC-130 that
1990) prepared in October 1990.
took off from Williams Field and then landed on
101




 Previous Page
Previous Page
