3
SHEET PILING AND ITS APPLICATIONS
What is sheet piling?
The term sheet piling in general is used for a wall that resists horizontal loads, as opposed to
bearing piles, which are isolated and take loads, which are normally vertical or along the axis of
the piles. However, under certain circumstances, sheet piling can also carry some vertical loading.
Timber, steel, and reinforced concrete used to be the traditional materials for sheet piling until
about 1520 years ago, with the advent of vinyl sheet piling, and then later, composite sheet piles.
Overall costs frequently dictate the material used. Steel sheet piles dominate the market, and a
significant proportion employed in temporary work is extracted and reused one or more times.
Sheet piling applications
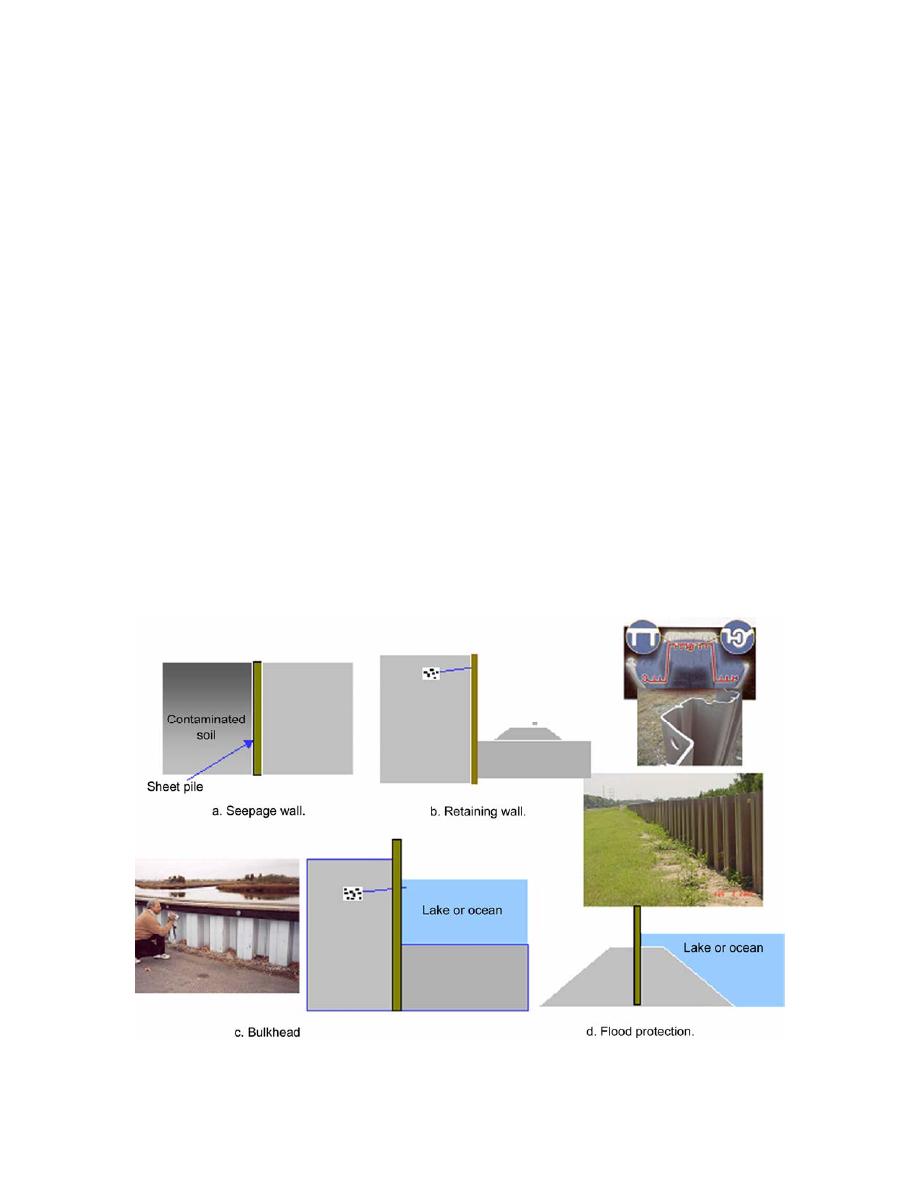
The purposes of sheet piles vary widely. They may be used as a seepage barrier or a cut-off
wall, where the sheet piles would be mostly inside the ground and may be subjected to minimum
side or horizontal loads (Fig. 6a). For a retaining wall (Fig. 6b) or bulkhead (Fig. 6c), the lower
portion of the sheet piles is buried, and the length above the burial point is subjected to horizontal
ground load. In bulkhead applications, sheet piling is used to stabilize the waterfront or shoreline
by preventing erosion and undercutting of soil by tide and wave action. These piles are installed
by driving or jetting them into the soil, and they are typically backfilled either by native soils or
select backfill. While one side of these sheet piles may be subjected to ground pressure, the other
side may have the hydraulic load. In some bulkhead and flood control applications, the sheet pile
Figure 6. Applications of sheet piles.
8




 Previous Page
Previous Page
