76
ERDC TR-04-1
ground surface. Therefore, an exclusionary approach, while less precise than
other methods, is less likely to lead to false identifications of the OHWM.
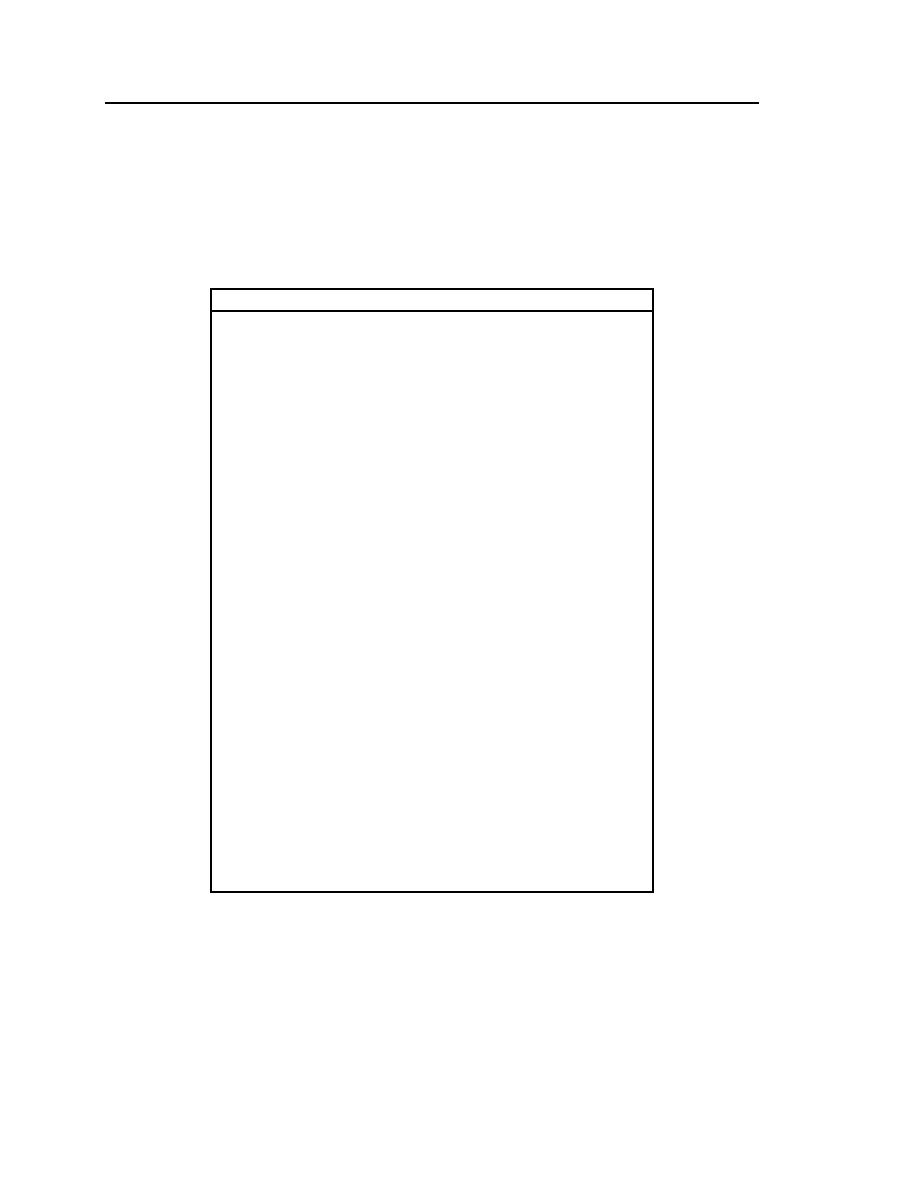
Table 11. Sedimentary structures common to ephemeral
streams. See Picard and High (1973) for additional structures.
Sedimentary structure
Reference
Malisce (1993)
Dunes and megadunes - sand bed rivers
Williams (1970)
Karcz (1972)
Mud drapes
Reid and Frostick (1997)
Sand tongues
Packard (1974)
Field (1994)
Cobble bars/trains behind obstructions
Blair (1987)
Field (1994)
Scour holes downstream of obstructions
Picard and High (1973)
Transverse sinuous crested ripples
Tooth (1999)
Flaser bedding - ripples covered by mud
Martin (2000)
Malisce (1993)
Narrow berms and levees
Wells (1977)
Muddy point bars of low relief
Malisce (1993)
Longitudinal gravel bars
Malisce (1993)
Gravel sheets grading to rippled sands
Malisce (1993)
Malisce (1993)
Streaming lineations
Picard and High (1973)
Abdullatif (1989)
Dessication/mud cracks
Glennie (1970)
Stepped-bed morphology in gravel
Bowman (1977)
Meander bars
Karcz (1972)
Harrow marks - flow aligned sand ridges
Karcz (1972)
Obstacle marks
Karcz (1972)
Armored mud balls
Picard and High (1973)
Recognition of the Transitory Tendency of Arid-Region Rivers
Rivers in any climatic region are always adjusting to changes in watershed
conditions in a direction that will bring the river into equilibrium with the new
conditions. Given the wide discrepancy in record and average annual peak flows




 Previous Page
Previous Page
