mental transformation products were found at very high
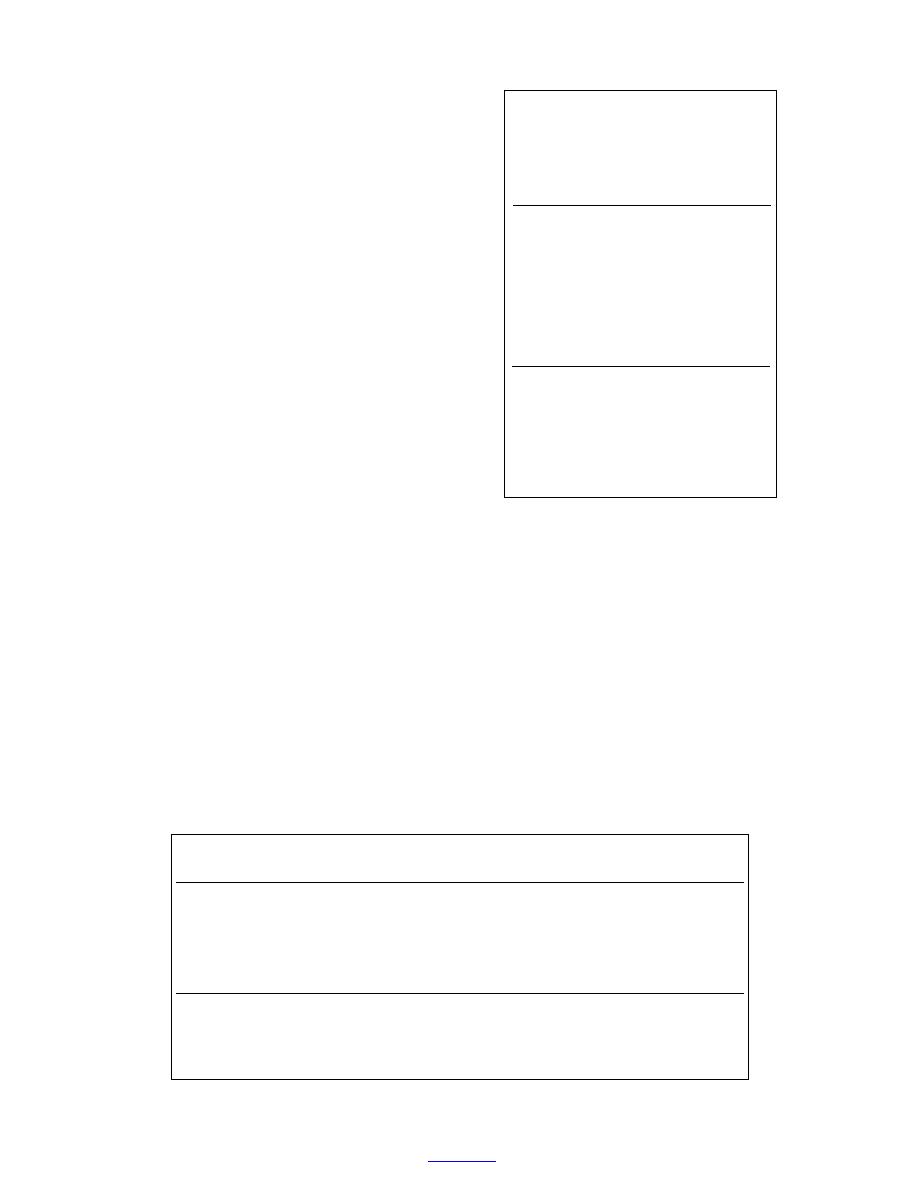
Table 10. RDX concentrations in ground-
water and surface water seepages around
concentrations in soils collected next to this round and
the perimeter of the artillery range at Fort
at depth, under the round. A chromatogram for the
Lewis (g/L).1
extract of a sample collected 15 cm west of the round
is shown in Figure 19.
Sample
Anteon
For example, surface soil collected directly under
CRREL2
EL3
Corporation3
no.
the round had a 2,4,6-TNT concentration of 15,100,000
MW1
0.28
0.38
0.3
g/kg or 1.5%. This was four orders of magnitude higher
MW2
0.19
0.27
0.2
than any samples collected next to craters formed from
na4
MW3
0.18
0.2
high-order detonations. This sample also contained high
MW4
0.51
0.59
0.5
<0.15
concentrations of 4-ADNT and 2-ADNT, 110,000 and
MW7
na
<0.2
102,000 g/kg, respectively, moderately high concen-
A1ASP01
0.31
na
0.4
A1ASP02
0.15
na
0.2
trations of 2,4-DNT and 1,3,5-TNT, and detectable con-
A1ASP03
0.26
na
0.3
centrations of other isomers of DNT and 1,3-DNB.
A1ASP04
0.73
na
0.8
Samples of soil collected at depths of 5 cm and 10
A1ASP05
<0.1
na
<0.2
cm below this round also had very high 2,4,6-TNT con-
1
Samples were collected in August 2000. RDX
centrations, 710,000 and 46,300 g/kg, respectively, and
was the only analyte detected.
the 5-cm sample had even higher concentrations of
2
Analyzed by Method 8095, GC-ECD (U.S. EPA
4-ADNT and 2-ADNT than the surface soil. Concen-
1998).
3
Analyzed by Method 8330, RP-HPLC-UV (U.S.
trations of 2,4,6-TNT and 4-ADNT and 2-ADNT, in
EPA 1994).
particular, are still moderately high in the soils collected
4
Sample not analyzed by this laboratory.
at a distance of 15 cm on three sides of this low-order
5
Less than detection limits.
round. These results indicate what a high concentration
contamination source is caused by a low-order detonation.
there is a low level of RDX contamination in the aqui-
Clearly concentrations are many orders of magnitude
fer below the impact ranges at Fort Lewis. The concen-
trations of RDX in these water samples are below 1 g/L
greater than those from rounds that detonate as engineered.
in all cases, though; 2 g/L is the continuous lifetime
Water analyses
human health advisory level for RDX (EPA 1988).
The results for the analysis of water samples from
monitoring wells and seeps at Fort Lewis are presented
Geochemical parameters
in Table 10. These analyses were conducted using GC-
Groundwater geochemistry is typical of the geo-
ECD method 8095 at CRREL and RP-HPLC-UV
graphic area (Table 11). Groundwater is generally soft
(sum of calcium and magnesium less than 50 mg L1).
method 8330 at ERDC-EL and at the contract labora-
tory. Only RDX was detected above analytical detec-
One sample, MW07, slightly exceeds the drinking water
standard for total iron (0.3 mg L1). None of the sam-
tion limits. The agreement among the three data sets is
excellent, even though two different methods were used
ples exceed the drinking water standard for manganese
(0.05 mg L1). Nitrate/nitrite values are well within the
and the concentrations are near the detection limit of
range for natural waters (0.1 to 10 mg L1). Total organic
the HPLC method.
Overall, RDX was detected in eight of the ten water
carbon, sulfate, and chloride values are relatively low,
samples from Fort Lewis. These results confirm that
not atypical for this environment.
TOC1
Well
Calcium
Iron
Magnesium
Nitrate/Nitrite
Sulfate
Chloride
MW012
<3.03
13J4
8.60
0.069
0.007
2.96
0.37
2.0J
MW02
9.47
<0.02
<0.001
3.63
0.23
<3.0
6.4J
2.1J
MW03
7.87
0.048
0.002
3.05
0.26
<3.0
<20
1.7J
MW04
7.70
<0.02
<0.001
2.67
0.35
<3.0
<20
2.0J
MW07
11.5
0.319
0.014
4.86
1.6
<3.0
<20
1.6J
A1ASP035
7.10
0.029
0.004
2.45
0.055J
<3.0
<20
1.6J
A1ASP05
7.66
<0.02
<0.001
2.31
0.44
<3.0
<20
2.2J
1
Total organic carbon.
2
Monitoring well number.
3
Less than detection limit.
4
J values are below the statistically reliable detection limit.
5
Seepage area number.
24
To contents




 Previous Page
Previous Page
