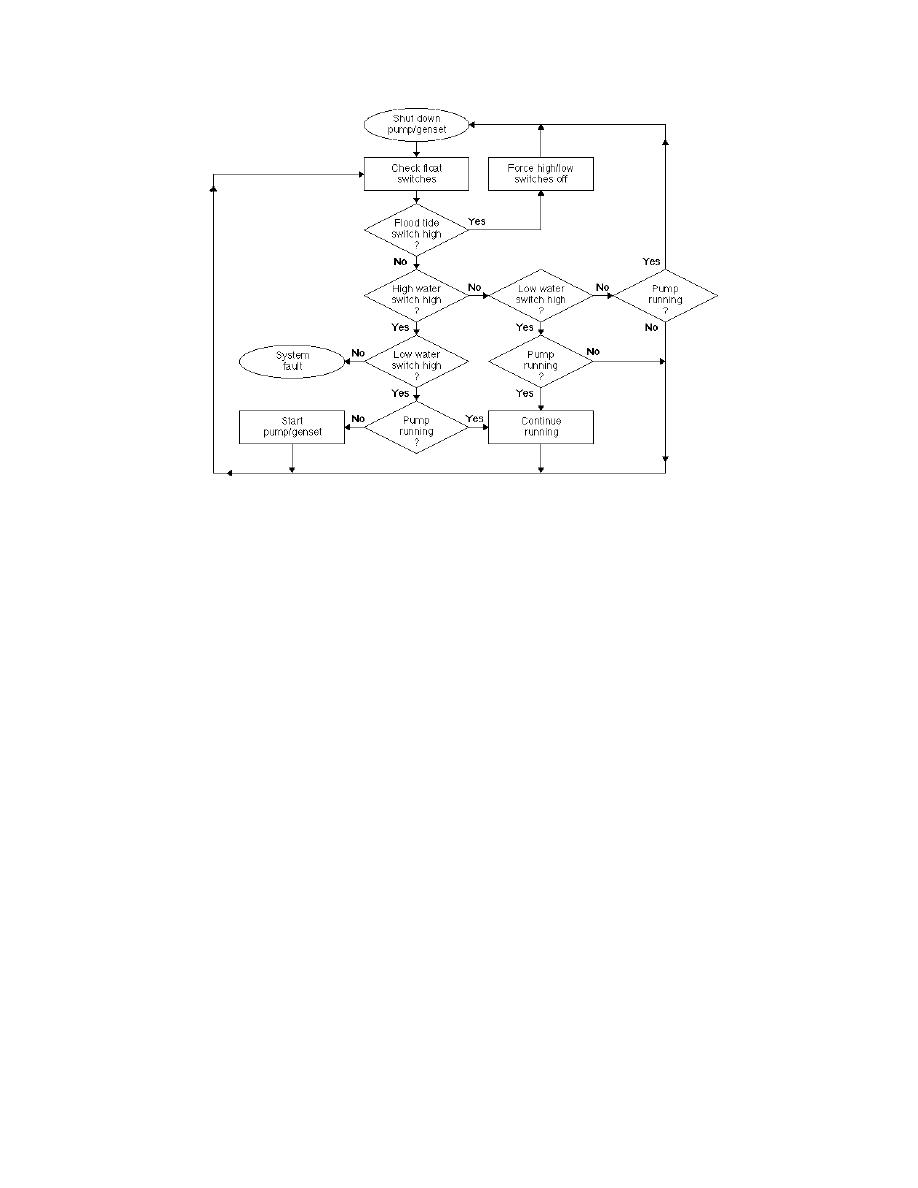
Figure 8. Switch logic diagram for pump operation.
minor flooding event on the 15th. The gate pre-
1H Huey helicopter. Retrograde operations
vented flooding of the pond.
required only a few days. During this time, a sec-
The final design modification to the system
ond 126-L/s pump system arrived for testing and
was a check valve for the discharge line. The line,
run-in. This system was tested in the dredge chan-
335 m in length and 20 cm in diameter, holds
nel in Pond 146 prior to retrograde of the original
approximately 11,000 L of water when full. This is
system. Based on the system performance results
equivalent to one-fifth the volume of the sump, or
in Pond 183, four additional units ranging in cap-
7.5 minutes of pump operation. Preventing the
acity from 63 to 190 L/s were ordered from the
backflow of this water will thus increase the
manufacturer for deployment in future years.
apparent size of the sump by about 20%. The
check valve was installed and successfully tested
Monitoring methods
in September.
The success of remediation of the white phos-
The pump system was originally designed to
phorus contamination at ERF is monitored in
operate with a 200-m discharge line. The use of
several ways because of the complexity of the site
the longer line (335-m) for deployment in Pond
and its unconventional contaminant. One compo-
183 resulted in the increase of line head loss and
nent of the monitoring process is to confirm that
thus a decrease in discharge flow rate. An ultra-
the amount of white phosphorus in surface sedi-
sonic flowmeter was installed on the line in Sep-
ments is decreasing, thereby becoming less of a
tember to check the discharge rate. The change in
threat to waterfowl. Using both composite and
line length resulted in a 12.5% decrease in flow
discrete samples, we measured white phospho-
rate, from 126 L/s to 110 L/s. This has a direct
rus concentrations and examined sediment sam-
impact on the time required to initially drain the
ples for the presence of contaminant particles. We
pond after flooding events, but has little effect on
also monitored groundwater level, surface water
subsequent pumping of the sump due to the
level, sediment temperature, and moisture level
small volume of water involved.
to determine if conditions were conducive to sub-
In mid-September, during a high flooding tide
limation/oxidation. We then confirmed whether
(> 10.3 m), the genset and pump were manually
conditions were favorable or unfavorable by
floated back to the dredge channel adjacent to the
measuring the residue of white phosphorus par-
EOD pad for retrograde to Ft. Richardson. The
ticles that we placed at various points in the
pipe was flown back to the EOD pad using a UH-
drained ponds.
10




 Previous Page
Previous Page
