Portland Cement
Class 3 Special
Open Graded Base
Concrete
(with drain)
(cm)
(in.)
Class 4 Special
Class 5 Special
Class 6 Special
0
0
20
10
15
40
15
15
20
24
15
20
1.00
20
1.00
1.00
1.00
1.25
1.25
1.50
20
27
1.25
40
40
27
24
24
24
60
24
30
80
100
40
p = 20
d = 1.00
w = 27
120
50
R-5
R-6
R-7
R-8
R-9
R-10
R-11
R-12
R-13
5 Year Design Life
10 Year Design Life
a. 5-yr design life.
b. 10-yr design life.
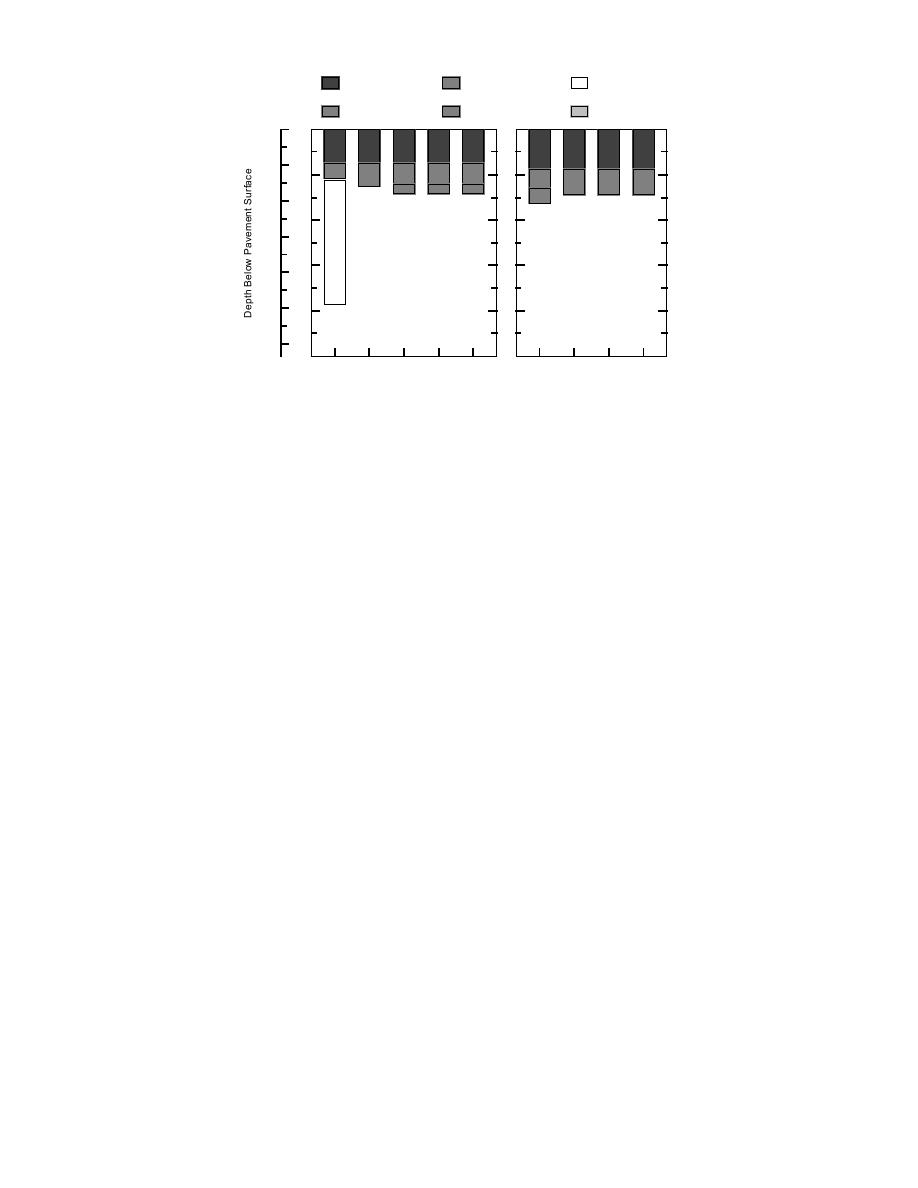
Figure 5. Mainline concrete test sections. In the figure, p refers
to panel length (ft), d--dowel diameter (in.), w--panel width (ft).
Supplemental steel rebar is included in the concrete of 5-year
section R-8.
class 5, class 4 and class 3, are all well-graded sands
through spring 1992. This effort, which included
with increasing amounts of finer size particles and
swamp excavation and backfill, and grading of
associated increasing frost susceptibility. Also in-
the test roadway to the top of the base materials,
required moving about 765,000 m3 (1,000,000 yd3)
cluded in one of the 10-yr sections is a porous
of material. Completion was significantly delayed
asphalt-stabilized open graded base. The subgrade
due to extremely wet weather during the 1990 and
beneath all test sections is a sandy lean clay. Bigl
1991 construction seasons.
and Berg (1996a) and Berg et al. (1996) detail
Stage 2 construction, which included paving
properties of the various materials at the site.
and installation of instrumentation, occurred dur-
In the concrete-surfaced test sections, param-
ing the 1992 and 1993 construction seasons. An
eters varied are the thickness of the concrete, panel
extensive period of sensor calibration, nondestruc-
width and length, dowel diameter, thickness and
tive pavement testing and collection of baseline
quality of underlying base materials, and pres-
data took place during winter 1993 and spring
ence of open-graded bases (Fig. 5). The concrete
1994. The test road was opened to traffic in Au-
paving surface is plain jointed concrete in all sec-
gust of 1994.
tions, with a constant thickness in the 5-yr and 10-
Three other reports have been prepared as part
yr sections. Panel lengths vary from 4.6 to 7.3 m
of this study (Bigl and Berg 1996a,b and Berg et
(15 to 24 ft); panel widths are 7.3, 8.2, or 12.2 m
al. 1996). This report summarizes the results of
(24, 27 or 40 ft). Dowel diameters are 2.5, 3.2 or
the other three. If additional details are desired or
3.8 cm (1, 1.25, or 1.5 in.). Base materials em-
needed, the other reports should be used.
ployed in the concrete sections are similar to those
used in the asphalt sections. The subgrade is also
a lean clay.
A number of different instrumentation types
MODEL DESCRIPTION
were installed at Mn/ROAD to measure the envi-
A mechanistic pavement design procedure is
ronmental conditions at the test sections, the traf-
being developed for use in seasonal frost areas
fic loadings, and the engineering behavior of the
and considers seasonal variations in pavement
materials.
strength such as:
Stage 1 construction took place June 1990
3




 Previous Page
Previous Page
