Asphalt Concrete
Open Graded Base
Class 3 Special
(cm)
(in.)
Class 4 Special
Class 5 Special
Class 6 Special
0
0
20
10
Low
VH
High
Low
40
VH
H
Low
20
H
60
Low
High
H
M
30
80
Low
L
Low
High
High
High
Low
100
H
M
H
VH
40
Low
L
H
Low
M
120
50
F-1
F-2
F-3
F-4
F-14
F-15
F-16
F-17
F-18
F-19
F-20
F-21
F-22
F-23
5 Year Design Life
10 Year Design Life
a. 5-yr design life.
b. 10-yr design life.
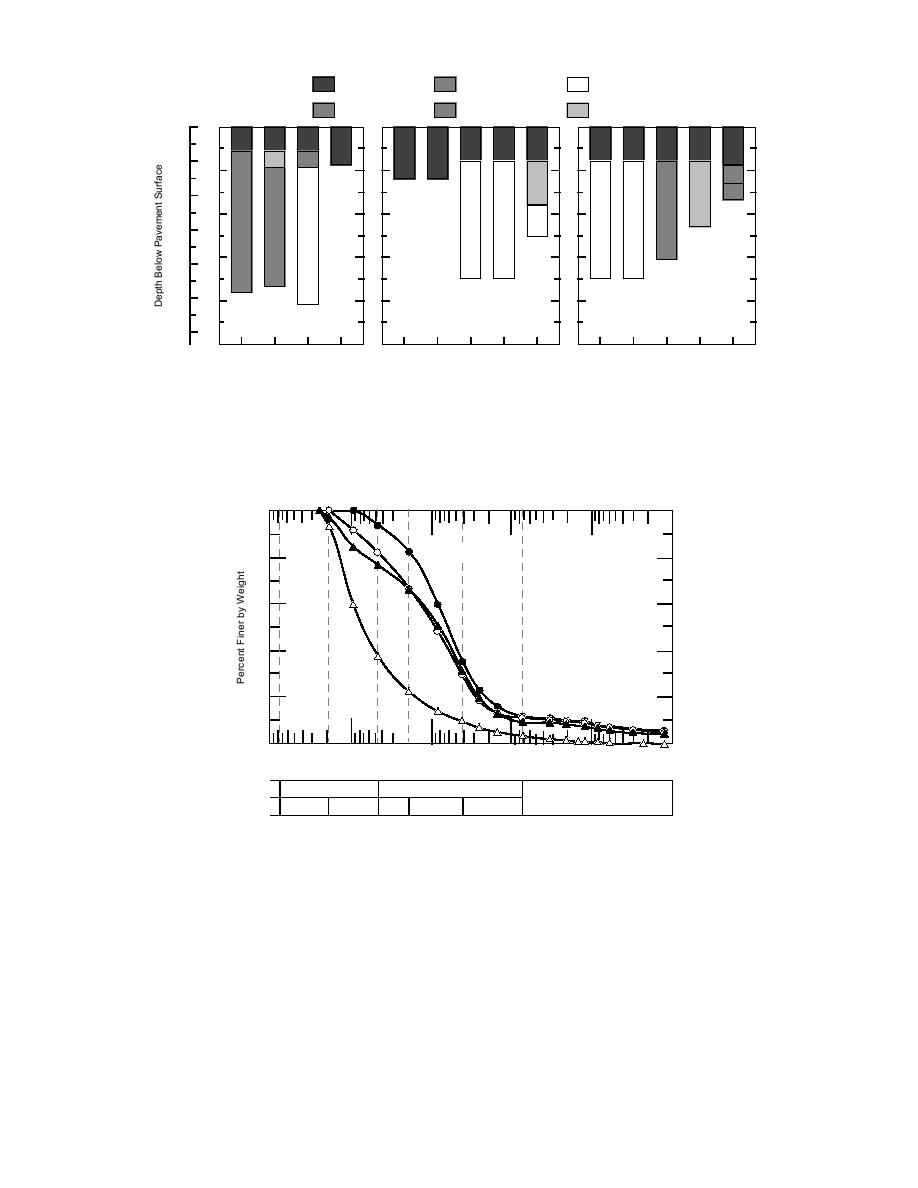
Figure 3. Mainline asphalt test sections. In the figure, beneath the base materials, High/
Low refer to the asphalt penetration viscosity number; design compactive effort is indicated
by VH--very high, H--high, M--medium, and L--low.
U.S. Std. Sieve Size and No.
Hydrometer
3/4
3
4
10
40
200
100
Class 3 Special
80
4
5
6
60
40
20
0
1.0
0.1
0.01
0.001
100
10
Grain Size (mm)
Gravel
Sand
Silt or Clay
C'rse
Fine
C'rse
Medium
Fine
Figure 4. Grain size distribution in tested specimens of Mn/ROAD
base materials.
Parameters included in the designs of the as-
PVN is more brittle. The design compactive effort
phalt test sections are the thickness and character-
applied to the asphalt also varies from low to very
istics of the asphalt surface and the presence, thick-
high, which resulted in varying asphalt cement
ness and quality of base materials (Fig. 3). The
contents in the field.
asphalt cement used was an 85/100 pen grade as-
The four granular base materials included in
phalt. The asphalt design included either of two
the test sections were specified and manufactured
temperature susceptibilities: one with a low pen-
to include a range in frost susceptibility (Fig. 4).
etration viscosity number (PVN) is characteristi-
The class 6 special is a relatively clean, non-frost-
cally more compliant and the other with a high
susceptible gravel with sand; the special bases,
2




 Previous Page
Previous Page
