EM 1110-2-2907
1 October 2003
roofs. A preliminary analysis suggests that this is possible because of the strong covariance
displayed by roofs shingled with monochromatic materials. Any automated process devel-
oped would need to address the limitations posed by non-monochromatic shingles (which
would appear spectrally mixed and indistinguishable from damaged roofs).
(4) A vegetation analysis was also explored to test the resolution required to accu-
rately describe tree type and condition. At the 1-ft (30.5 cm) resolution, researchers were
able to determine leaf on/off conditions (data were collected in February). However, at this
resolution it was not possible to delineate any details regarding leaf morphology. At the 8-in
(20.3 cm). resolution, palms were distinguishable, although it was not possible to differenti-
ate broad versus narrow leaves.
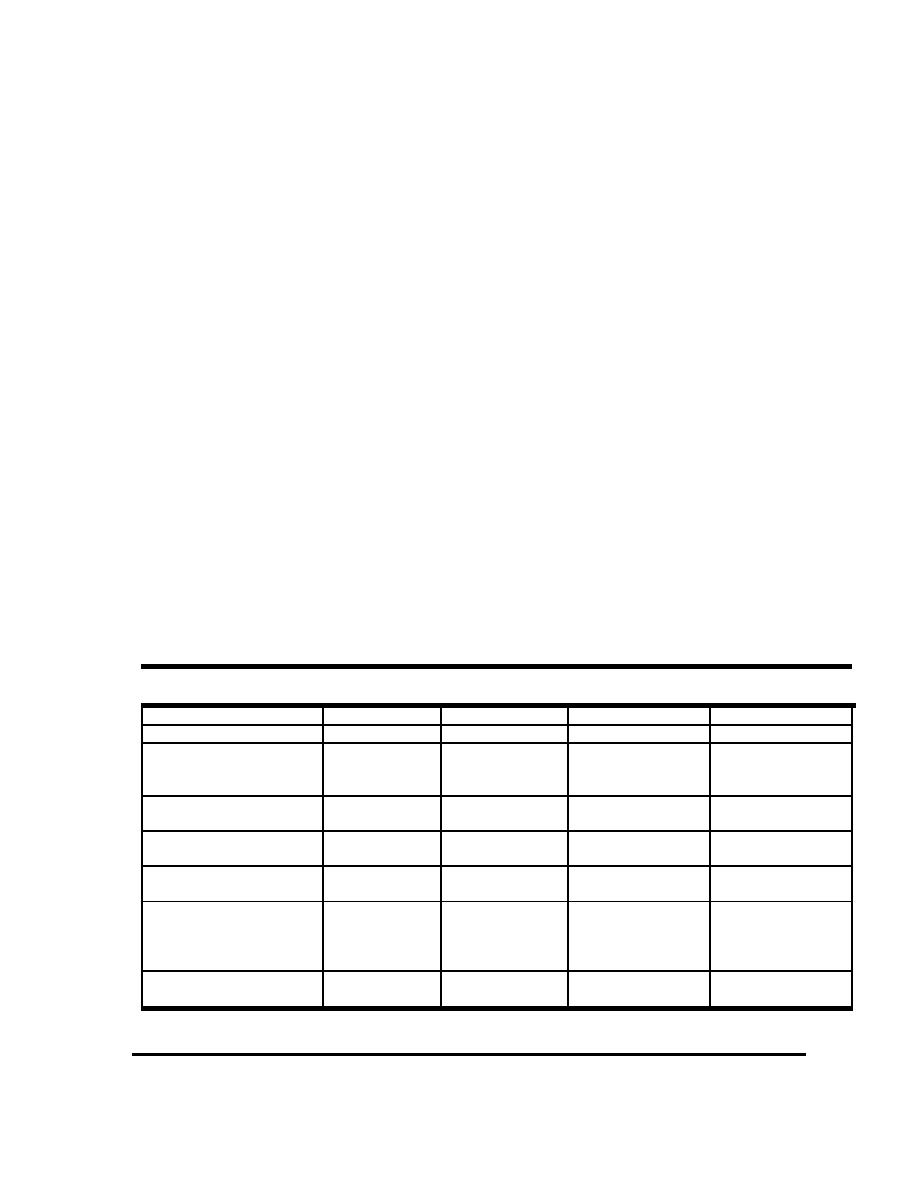
f. Conclusions. Evaluation of the Emerge sensor led to the development of a detection
matrix. This matrix reviews the capabilities of the sensor at various spatial resolutions for all
objects studied (see Table 6-1). This study determined that Emerge could adequately meet
the requirements of emergency management systems. High-resolution data can be acquired
within 4 hours of the plane's landing. This includes the time needed for pre-processing
(orthorectification and the production of geo-TIFF files for CD-ROM and ftp). Shingles and
tarpaper are not resolvable, though rafters and plywood are at the 2-ft (~61 cm) resolution.
For high-resolution images, a medium sun angle increased roof detail. Palm trees and leaf
on/off conditions can be visually identified at the 8-in (20.3 cm). resolution; however,
broad-leafed trees cannot be distinguished from narrow-leafed trees. The only limitations
placed on these data centered on over-saturation and sensor inability to distinguish tree
types. The covariance displayed by band 1 relative to band 2 indicates the potential success
for developing an automated algorithm to locate and count damaged roofs.
Table 6-1
Detection Matrix for Objects at Various GSDS
Objects/GSD
3-ft (91.4)
2-ft (61 cm)
1-ft (30.5 cm)
8-in. (20.3 cm)
Roof rafters
Not visible
Barely visible
Often visible
Visible
Shingles/tarpaper
Can
Can often
Can determine
Can determine
(other) vs. plywood
sometimes
separate
wood vs. other
wood vs. other
separate
cover
cover
Rafters in 3-band
Causes rafter
Causes rafter
Causes rafter
Causes rafter
saturation
detail loss
detail loss
detail loss
detail loss
Broad-leaf vs. narrow-
Cannot
Can determine
Can determine
Palms are always
leaf
separate
leaf on/off
leaf on/off
visible
All in cloud shadow
Degrades
Some info
Some info
Some info
image
recoverable
recoverable
recoverable
Roofs as a function of
Best detail,
Best detail,
Best detail,
Best detail,
sun zenith angle
near zero
medium angle,
medium angle,
medium angle,
angle,
shadow casting
shadow casting
shadow casting
overhead sun
All in 1, 2, 3 RGB, 2∑
Enhances
Enhances
Enhances imagery
Enhances imagery
stretch
imagery
imagery
Point of Contact: Robert Bolus, Phone: (603) 646-4307
6-7




 Previous Page
Previous Page
