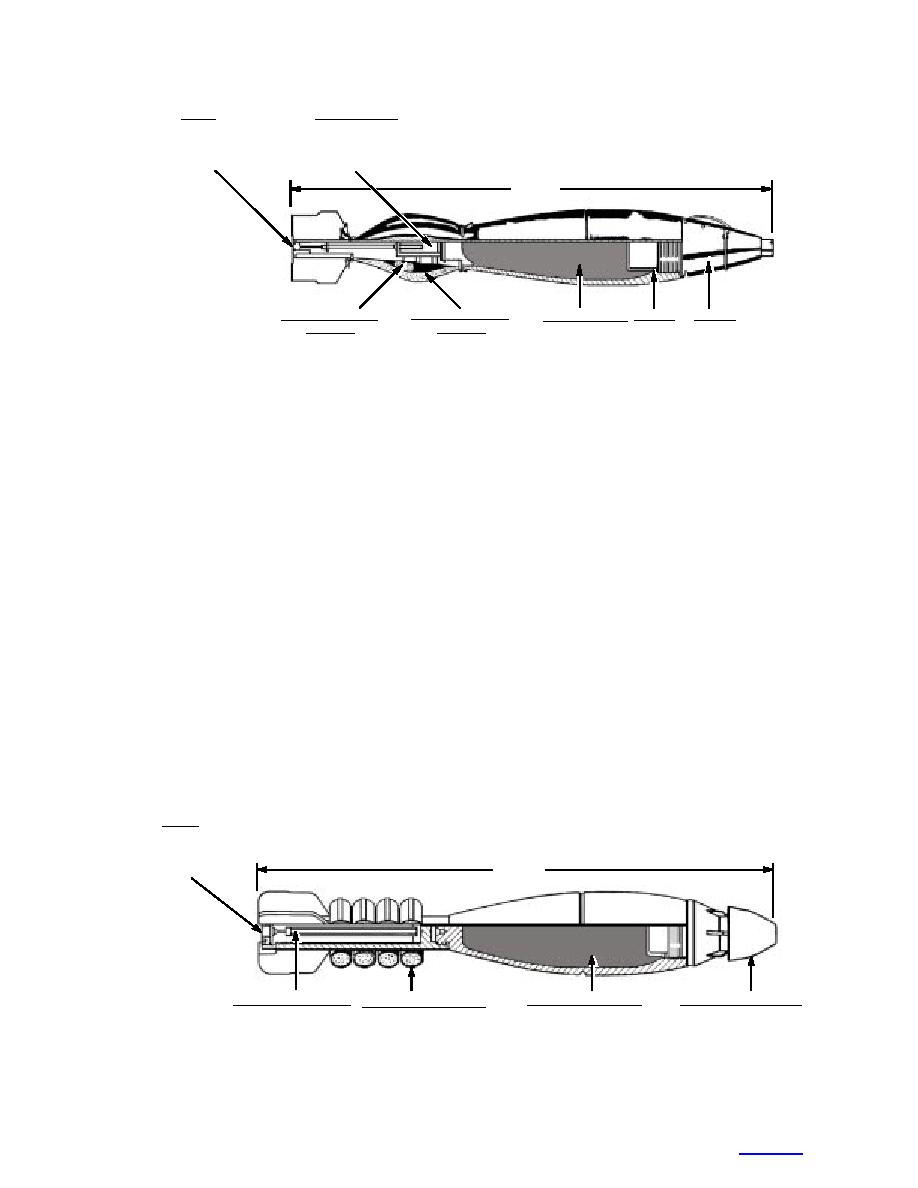
Primer:
Ignition Cartridge:
Lead Thiocyanate (25.00%)
Ethyl Centralite (0.75%)
Potassium Chlorate (53.00%)
Potassium Nitrate (1.50%)
Antimony Sulfide (17.00%)
NC (57.75%)
TNT (5.00%)
NG (40.00%)
52.93 cm
(20.84 in.)
Propellant Increment
PD Fuse
Propellant Increment
HE Filler Comp B: Booster:
Lead Azide
RDX
Charge A:
Charge B:
RDX (60.00%)
RDX
Ethyl Centralite (0.75%)
TNT (39.00%)
Ethyl Centralite (0.75%)
Various Primers
Potassium Nitrate (1.50%)
Potassium Nitrate (1.50%) Wax (1.00%)
NC (57.75%)
NC (57.75%)
NG (40.00%)
NG (40.00%)
Figure 1. Diagram of 81-mm mortar rounds detonated with C4 at Camp Ethan Allen Firing Range.
lb [0.57 kg]) and an M7 blasting cap that was attached
impact. In the second, the residues that result from the
to the outside of the casing. The second experiment was
practice of attaching C4 to an item of unexploded ord-
conducted at Fort Drum, New York, on 13 March 2000.
nance and detonating it in place were examined.
Three 60-mm mortar rounds were fired by U.S. Army
Because concentrations would likely be low, we used
personnel and the rounds were allowed to detonate on
much larger samples than did Collins and Calkins
impact in a snow-covered range.
(1995), and a new gas chromatographic electron cap-
The main charge in a 81-mm mortar round is 2.1 lb
ture (GC-ECD) method developed recently by Walsh
(0.95 kg) of Composition B, which is 60% RDX and
and Ranney (1998, USEPA 1999), which provides much
39% TNT (Fig. 1). The propellant increment charges A
lower MDLs than the earlier RP-HPLC method.
and B were removed from the round before detonation.
The propellant is composed of 40% nitroglycerine,
METHODS
57.8% nitrocellulose, 1.5% potassium nitrate, and 0.7%
ethyl centralite. A smaller portion of these propellant
Overview of mortar round detonations,
chemicals was present in the ignition cartridge, how-
Camp Ethan Allen and Fort Drum
ever, and that was not removed before detonation (Fig.
Two mortar detonation experiments were complet-
1). The C4 used to detonate the 81-mm mortar rounds
ed. The first was conducted at Camp Ethan Allen Fir-
is composed of 91% RDX and 9% plasticizers (poly-
ing Range, Vermont, on 6 March 2000. Three 81-mm
isobutylene, motor oil, di(2-ethylhexyl)-sebacate). The
mortar rounds were placed on a pristine snow surface
rounds used for these tests were loaded in 1975.
and individually detonated by EOD personnel from the
The main charge in the 60-mm mortar rounds used
Vermont Air National Guard using a C4 charge (1.25
at Fort Drum is 0.79 lb (0.43 kg) of Composition B
(Fig. 2). The propellant used with this munition is M204,
Primer:
Lead Thiocyanate (25.00%)
Potassium Chlorate (53.00%)
Antimony Sulfide (17.00%)
37.69 cm
TNT (5.00%)
(14.84 in.)
Ignition Cartridge M702: Propellant Charge M204:
Comp B Filler (0.79 lb):
Multi-Option Fuse M734:
NC (57.75%)
RDX (59.50%)
RDX
DNT (9.90%)
NG (40.00%)
TNT (39.50%)
HMX
Diethylphthalate(4.90%)
Potassium Nitrate (1.50%) Diphenylamine (1.00%)
Wax (1.00%)
Lead Azide
Diphenylamine (0.75%)
Various Primers
NC (84.20%)
Figure 2. Diagram of 60-mm mortar rounds that were fired at Fort Drum, New York.
2
to contents




 Previous Page
Previous Page
