Development of an Analytical Method for White Phosphorus (P4)
in Water and Sediment Using Solid-Phase Microextraction
MARIANNE E. WALSH, SUSAN TAYLOR AND PHILIP G. THORNE
Peppard 1994, Zhang et al. 1994). The technique
INTRODUCTION
has several advantages (fast, simple, precise, sen-
Analytical methods have been developed for
sitive), and requires no solvent (Arthur et al.
white phosphorus (P4) residues in sediment and
1992e). For this technique, a thin fused silica fiber
water (Walsh and Taylor 1993, Walsh 1995, USEPA
coated with a stationary phase is exposed to a sam-
1995). Both methods rely on solvent extraction
ple, either by immersion in a water or air sample
prior to gas chromatographic analysis. The extract-
or to headspace above an aqueous or solid sam-
ing solvents are isooctane and diethyl ether for
ple (Fig. 1). Analytes sorb to the stationary phase,
soils/sediments and water, respectively. The
then the fiber is transferred directly to a heated
method for soils/sediments has been performed
injection port of a gas chromatograph for thermal
successfully in field laboratories (Racine et al.
desorption and analysis. The method can be auto-
1993), but the safety hazards associated with di-
mated and an SPME autosampler is available com-
ethyl ether restrict the analysis of water samples
mercially (Arthur et al. 1992c, Berg 1993).
to laboratories with fume hoods. In this study, we
describe methods that minimize or eliminate the
use of organic solvents.
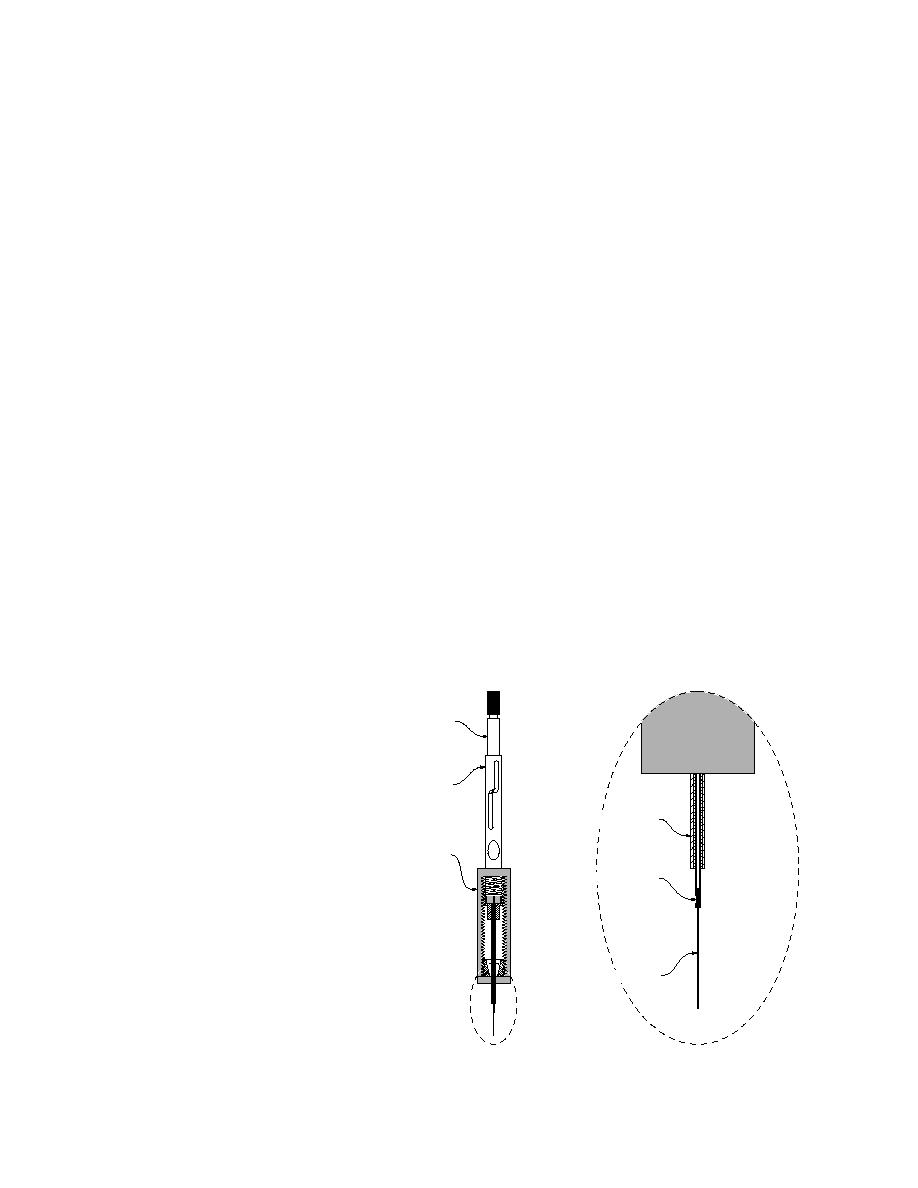
Plugger
Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) is
a new alternative to traditional tech-
niques for extracting volatile or semi-
volatile organics (Belardi and Pawl-
Barrel
iszyn 1989, Boyd-Boland et al. 1994,
Zhang et al. 1994). First developed to
Septum-piercing Needle
analyze for volatile chlorinated
organics, PCBs (polychlorinated G djustable Needle
A
uide/Depth Gauge
biphenyls) and BTEX (benzene, tolu-
Fiber Attachment Tubing
ene, ethylbenzene, xylene) in water
(Arthur and Pawliszyn 1990; Arthur
et al. 1992a, b, d; Potter and Pawlis-
zyn 1992, 1994; Buchholz and Pawl-
iszyn 1993), the method has been
Coated Fused Silica Fiber
successfully used for a wide variety
of analytes in environmental, food
and pharmaceutical matrices (Haw-
thorne et al. 1992, Otu and Pawliszyn
1993, Buchholz and Pawliszyn 1994,
Horng and Huang 1994, Yang and
Figure 1. SPME device.




 Previous Page
Previous Page
