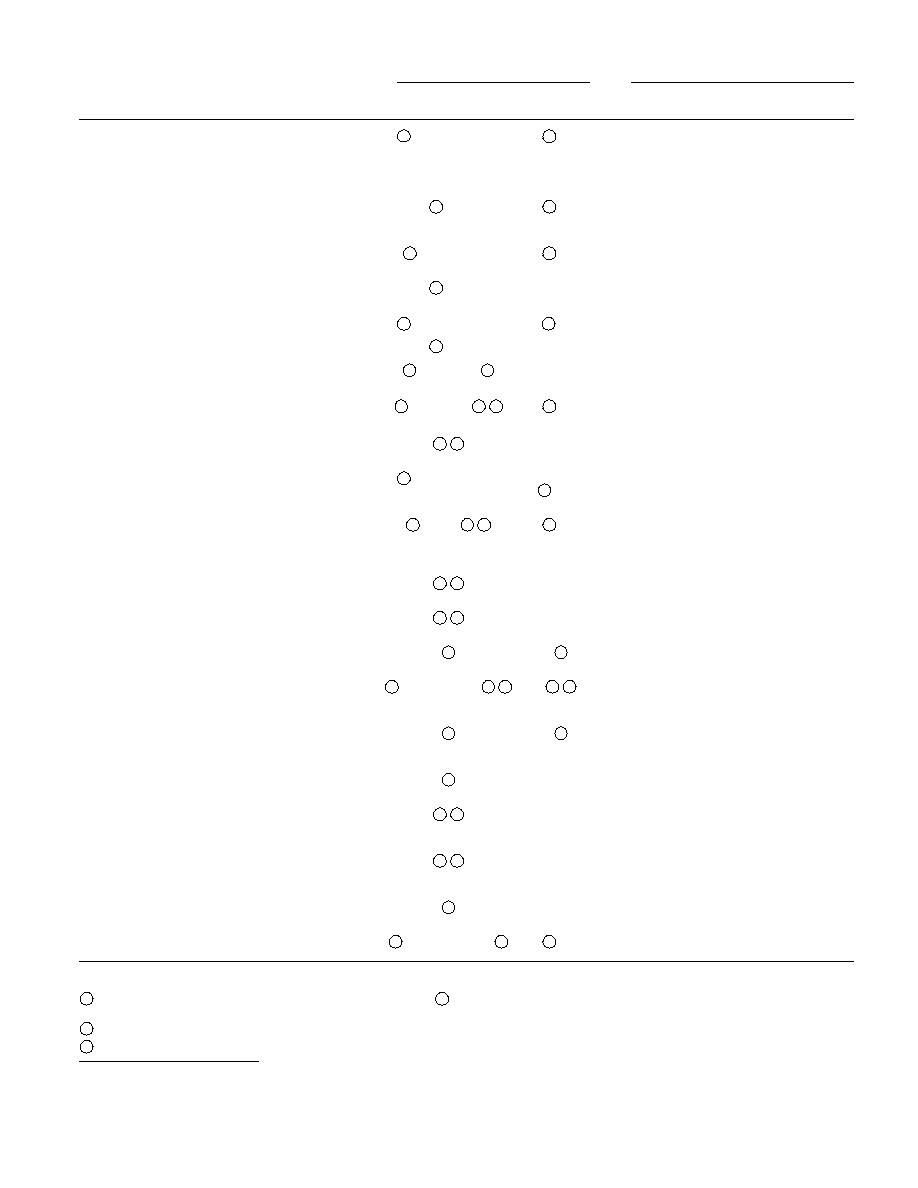
Table 1. Interactions of bank erosion and failure processes and conditions.
* Effects on bank soils
Climatic zones
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
(F)
(G)
Process or
Causes of a
Surface
Subsurface
Seasonal
condition
process/condition
soils
soils
Permafrost
frost
No frost
→ 2, 5, 6, 9, 10, 1418
→ 14
Excessive soil
Heavy and/or prolonged precipitation
X
X
X
1
1
pore water (1)
Snowmelt
Rapid river/lake level drop
Irrigation
Ground ice melt
→ 14
→ 14
Soil water piping (2)
Water flow through coarse-grained,
X
X
X
2
1
permeable soil strata discharging
along bank face
→ 2, 5, 6, 911, 14, 18
→ 14
Soil freeze-thaw (3)
Ground temperatures fluctuating
X
X
1
1
below and above 32F cause soil
pore water to freeze and thaw,
→ 14
2
and soil mass to swell and shrink
→ 2, 5, 6, 911, 14, 18
→ 14
Ground temperatures below 32F
Growth of ground ice (4)
X
X
1
2
and suction of soil water to freezing
→ 14
2
soil zone
→ 911, 1517 2
no effect
X
X
River/lake ice
Ice moving along a bank
1
scour/abrasion (5)
→ 911, 1517 2
→ 14
River/lake ice push (6)
Ice moving into or onto a bank due
X
X
1
3
1
to thermal expansion, wind or currents
River/lake ice
Previously grounded ice with incorpor-
no effect
X
X
2
3
rafting (7)
ated sediment breaks free and flows away
→ 2, 57, 911, 1318
Changes in soil grain
Normal chemical and physical weather-
X
X
X
1
→ 6, 14
mineralogy and
ing actions and reactions
1
physical condition (8)
→ 1417 2
→ 14
Water wave actions (9)
Wind
X
X
X
1
3
1
Boat passage
Landslides
Water current detach-
Gravity
no effect
X
X
X
ment and transport (10)
Thermal
2
3
Wind
Wind detachment
Wind blowing over transportable soil
no effect
X
X
X
2
3
and transport (11)
Toppled trees (12)
Loss of soil support below
X
X
X
2
2
root zone
→ 57, 911, 1418 2
Man and animal
Burrowing, trampling (compacting),
X
X
X
1
3
2
3
actions (13)
excavating and disrupting the surface
of bank soils
Soil failures (14)
Excessive soil water
X
X
X
2
2
Seismic action
Loss of bank toe support
Raindrop detachment (15)
Rain drop impacts on unvegetated
no effect
X
X
X
2
bank soils
Overland sheet flow (16)
Infiltration capacity of soil is exceeded,
no effect
X
X
X
2
3
resulting in flows on the soil surface
Rill/gully flow (17)
Flow on a sloped soil surface becomes
no effect
X
X
X
concentrated in surface depressions
2
3
often where vegetative cover is sparse
Snow sliding (18)
Binding forces between bank face sedi-
no effect
X
X
ments and snow become insufficient
2
to hold snow mass in place
→ 2, 57, 911, 1418 2
→ 14
Ground ice melting/
Exposure to solar radiation, water
X
X
1
1
and air temperatures above 32F
sublimation (19)
*Effects on bank soils:
→ 3, 810
1 Reduction in granular interlocking and/or soil cohesion with associated
Effect could increase the susceptibility of bank soils to other processes or condi-
1
loss of soil strength and stability
tion in column A with their associated effects in columns C and D and so on.
2 Removal of soil particles from in-situ position
3 Removal of soil particles from site
Note: This table may not include all factors.
2




 Previous Page
Previous Page
