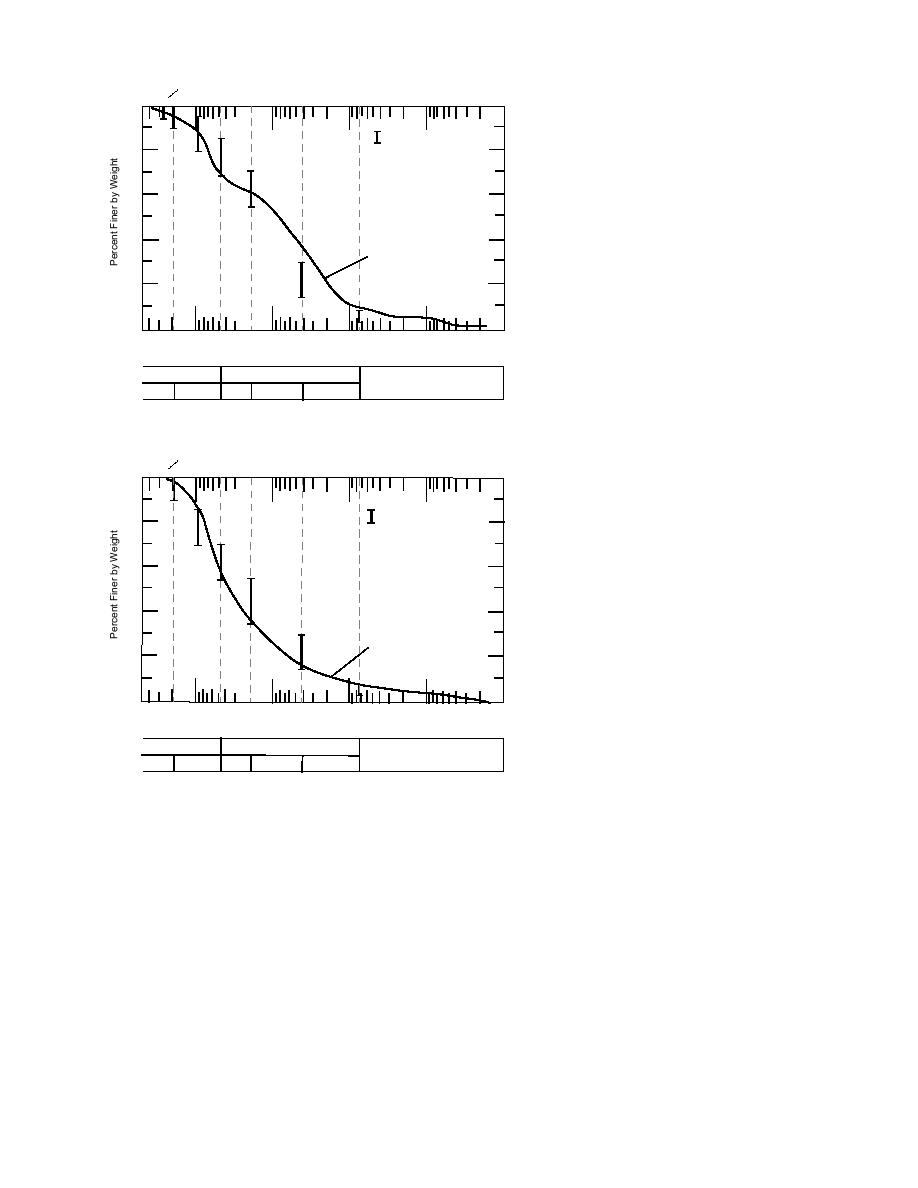
U.S. Std. Sieve Size and No.
Hydrometer
3
4
4
10
40
200
100
Mn DOT Class 4 Spec.
80
60
40
Albany, TW A
Subbase
20
0
10
1.0
0.1
0.01
0.001
Grain Size (mm)
a.Taxiway A subbase, Albany, New York/
Gravel
Sand
Silt or Clay
C'rse
Fine
C'rse
Medium
Fine
class 4 special base.
U.S. Std. Sieve Size and No.
Hydrometer
3
200
10
40
4
4
100
Mn DOT Class 5 Spec.
80
60
40
Dense Graded
Stone
20
0
0.01
1.0
10
0.1
0.001
Grain Size (mm)
b. Dense-graded stone, Winchendon,
Gravel
Sand
Silt or Clay
C'rse
Fine
C'rse
Medium
Fine
Massachusetts/class 5 special base.
Figure 9. Comparison of grain size distribution of substitute materials and specifications for equivalent
Mn/ROAD bases.
Physical characteristics
Hydraulic properties
The general physical properties of the Mn/
The moisture retention and hydraulic conduc-
ROAD materials were tested according to stan-
tivity tests were conducted using the procedures
dard techniques (Table 5). Grain size gradations
outlined in Ingersoll (1981). A typical test be-
of the base materials were shown in Figure 4; gra-
gins with a saturated sample that is dried incre-
dations of the subgrades classified them as sandy
mentally to determine point values of moisture
lean clays (Fig. 10). Maximum density and opti-
content and pore pressure head. The laboratory
mum moisture content determined in compaction
data are fitted with an equation in the form of
testing are listed in Table 6.
Gardner's (1958) function using a least squares
11




 Previous Page
Previous Page
