lutions. By freezing columns of sand saturated with a
EXPERIMENTS
NaCl solution at constant rates, Baker and Osterkamp
Experiments were conducted in which closed soil
(1989) found that BPS theory approximately holds true.
columns, initially with the uniform dry density and the
Konrad and McCammon (1990) conducted step freezing
uniform contents of water and Br , were subjected to a
tests on a saturated clayey silt with various salinities.
constant and linear temperature gradient. The apparatus
They found that the rate of cooling is the main factor
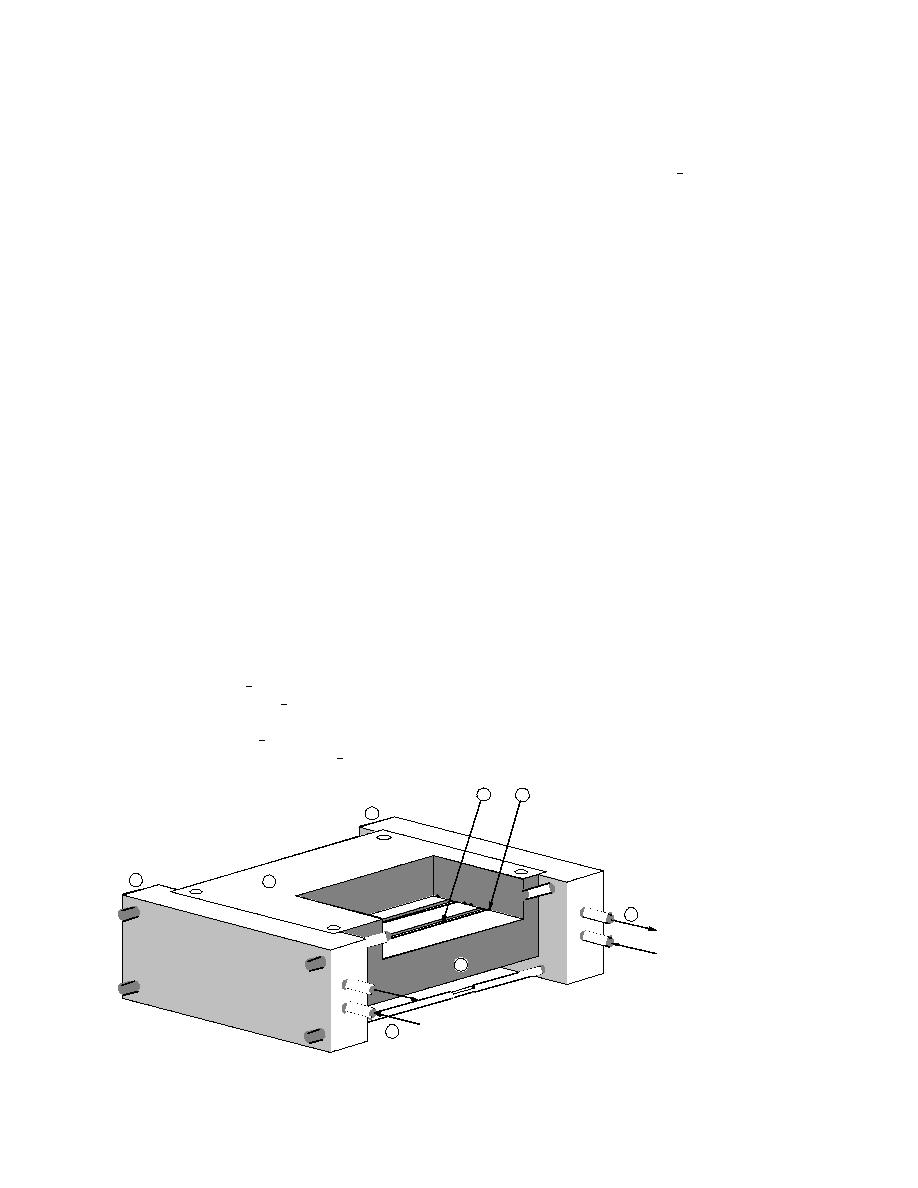
used in the experiments is shown in Figure 1.
controlling solute redistributions and that there is a
The apparatus consists of four parts made of alumi-
threshold rate of cooling of 3C/day above which no re-
num: an upper plate, a lower plate and two end plates.
distribution takes place (k = 1).
The upper and lower plates are approximately 23 cm
The flow of aqueous solutions through unfrozen po-
long 20 cm wide 5 cm thick. Four grooves with a
rous media has been investigated extensively (Nielsen et
rectangular cross section, 20.32 cm long 1.27 cm wide
al. 1972). In saturated systems, the flow of a solute is
0.625 cm deep, were machined on the upper surface of
described as the sum of a convective term and a diffusive
the lower plate. The center lines of these grooves, which
term. The diffusive term is equivalent to Fick's law of
are parallel to the longer side of the plate, are spaced 3.8
diffusion where the diffusivity coefficient includes the
cm apart. Grooves for O-ring seals were also machined
effect of both molecular diffusion and hydrodynamic
around each rectangular groove in the upper plate so that
dispersion. Such a description is not accurate for fine-
when the upper and lower plates are bolted together,
grained soils with small water contents because the inter-
four closed empty spaces of rectangular column shape
action between solutes and surfaces of soil particles be-
are formed to be used as containers of soil.
comes significant. It has been shown experimentally that
Each of the two end plates has a 2.54-cm hole drilled
a soluble salt and water in which it is dissolved move at
into it, through which an antifreeze mixture from a tem-
different rates through fine-grained soil (Biggar and
perature-controlled bath is circulated. The two end
Nielsen 1962, Krupp et al. 1972). For example, when a
plates are positioned by four bolts. Two sides of the up-
CaCl2 solution containing 36Cl and 3H is passed through
per and lower plates bolted together have a small taper
soils, the 36Cl appears earlier in the effluent than the 3H.
that matches the taper of the end plates so that the bolted
This behavior can be explained by anion repulsion or
upper and lower plates smoothly slide into the spaces
negative adsorption of salt by the negatively charged soil
created by the two end plates, with assured close con-
particle surfaces.
tact. The four aluminum parts, when assembled, are
While it has been anticipated that the phenomenon of
thermally insulated by foam plastic. A row of 10 copper-
anion repulsion is important in the transport process of
constantan thermocouples is placed with equal spacing
solutes in frozen soils, no supporting data are available.
through the upper plate along the centerline of each
The objective of this study is to examine experimentally
groove to measure and record temperatures in a soil
the transport of the Br ion in unsaturated and partially
sample.
frozen soil. The content of Br was intentionally kept low
The soil selected for the experiment, called Morin
so that the transport of unfrozen water would not be al-
clay, is a marine-deposited clay obtained from the
tered significantly by Br . This study also aims to find
Morin brickyard, Auburn, Maine. Morin clay is a non-
the effect of interactions between Br and surfaces of
swelling clay with a specific surface area of 60
soil particles.
5
6
3
3
1
4
2
1Upper plate
4Inlet and outlet of an antifreeze mixture
2Lower plate
5Groove
4
3End plates
6O-ring
Figure 1. Apparatus.
2




 Previous Page
Previous Page
